Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc)-related digital ulcers are a major burden for patients. The purpose of this study was to assess the effectiveness of amnion membrane treatments on healing rate as determined by manual and ultrasound weekly measurements.
Methods: SSc patients that met 2013 ACR/EULAR classification criteria and presented to clinic with a digital ulcer between 02/2019-05/2019 were consented to participate. Consented participants were asked to complete a Raynaud’s Condition Score (RCS), Hand Mobility in Scleroderma (HAMIS), Scleroderma Health Assessment Disability Questionnaire (HAQ-DI), and return every 5-7 days for a wound nurse’s visit until complete healing. All patients received education on wound care management including assessment, cleaning, and dressing. The volume of the wound was calculated and change in volume was tracked over time at the time of wound care.
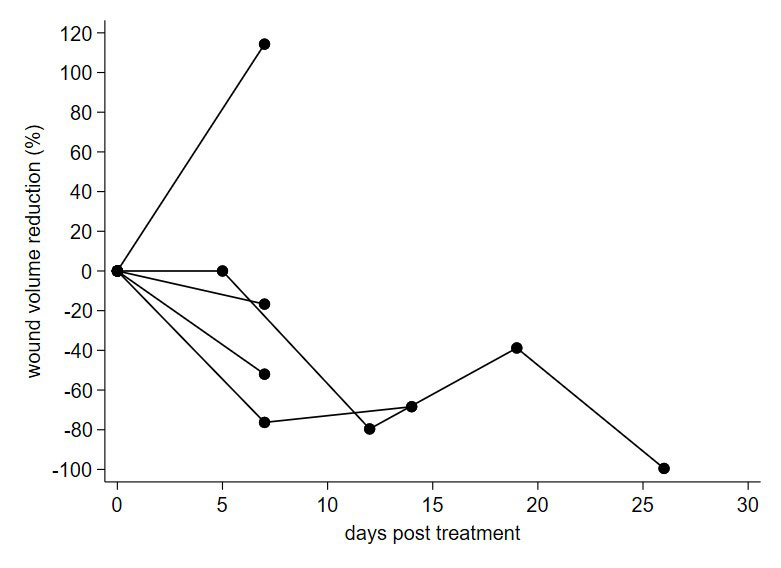
Results: During the two-month study period, 15 SSc patients with a DU were approached for consent at the time of their routine SSc care visit. Two patients refused consent due to perceived burden of participation. Of the 13 consented patients, nine patients subsequently withdrew due to burden of participation; length questionnaires and driving to wound care were the most common reported reasons. Five patients had at least two formal measurements of their DU during wound care. Three patients did not return to wound care after the first follow-up visit due to complete healing reported. The demographics of the 5 SSc patients that returned for care included three female; four white patients; three limited cutaneous SSc, with a mean age of 62 (SD 11). The duration from first non-RP symptom of SSc was 5.8 years (SD 4). Wound volume (length x width x depth) ranged from 3 to 182 mm3. Two wounds (3 mm3 and 9 mm3) healed completely after one application and these patients did not return to wound care. One wound (39.2 mm3) was over a joint contracture and traumatic in origin increased in volume at follow-up measurement. The change in wound volume of these 5 wounds over time after amnion dressing was applied is shown in Figure 1. None of these SSc wound patients completed all questionnaires.
Conclusion: Assessments of SSc-related DU healing must minimize patient burden; the appropriate number of questionnaires used for assessment must be carefully assessed in the study design of this outcome, and remote wound monitoring should be considered. DU healing can be measured effectively by weekly ultrasound that estimates wound volume. Amnion membrane dressings are effective for wound healing in this patient population, especially for wounds that are vascular in origin.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Frech T, Pierce J, Stoddard G, McNeill C, Radic M, Reems J. Amniotic Membrane Dressings Provide an Effective Treatment for Systemic Sclerosis Digital Ulcers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/amniotic-membrane-dressings-provide-an-effective-treatment-for-systemic-sclerosis-digital-ulcers/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/amniotic-membrane-dressings-provide-an-effective-treatment-for-systemic-sclerosis-digital-ulcers/