Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Despite the well-documented link between cardiovascular (CV) disease and spondyloarthritis (SpA), no animal studies have empirically validated this connection or integrated SpA, vascular inflammation, and Wnt signaling into a single study. This study examines these associations using the HLA-B27 transgenic (TG) rat model, which closely mirrors human SpA.
Methods: Six-week-old HLA-B27 TG rats were injected with M. tuberculosis in incomplete Freund’s adjuvant, while control Lewis rats received phosphate-buffered saline. At seven weeks, HLA-B27 TG rats were classified into two groups: F1 G0 (no arthritis) and F1 G6 (severe arthritis). Both groups, along with control rats (Ctrl G0 and Ctrl G6), were analyzed for aortic protein levels. Histological examination of tail spine samples graded inflammation, bone destruction, and osteoproliferation.
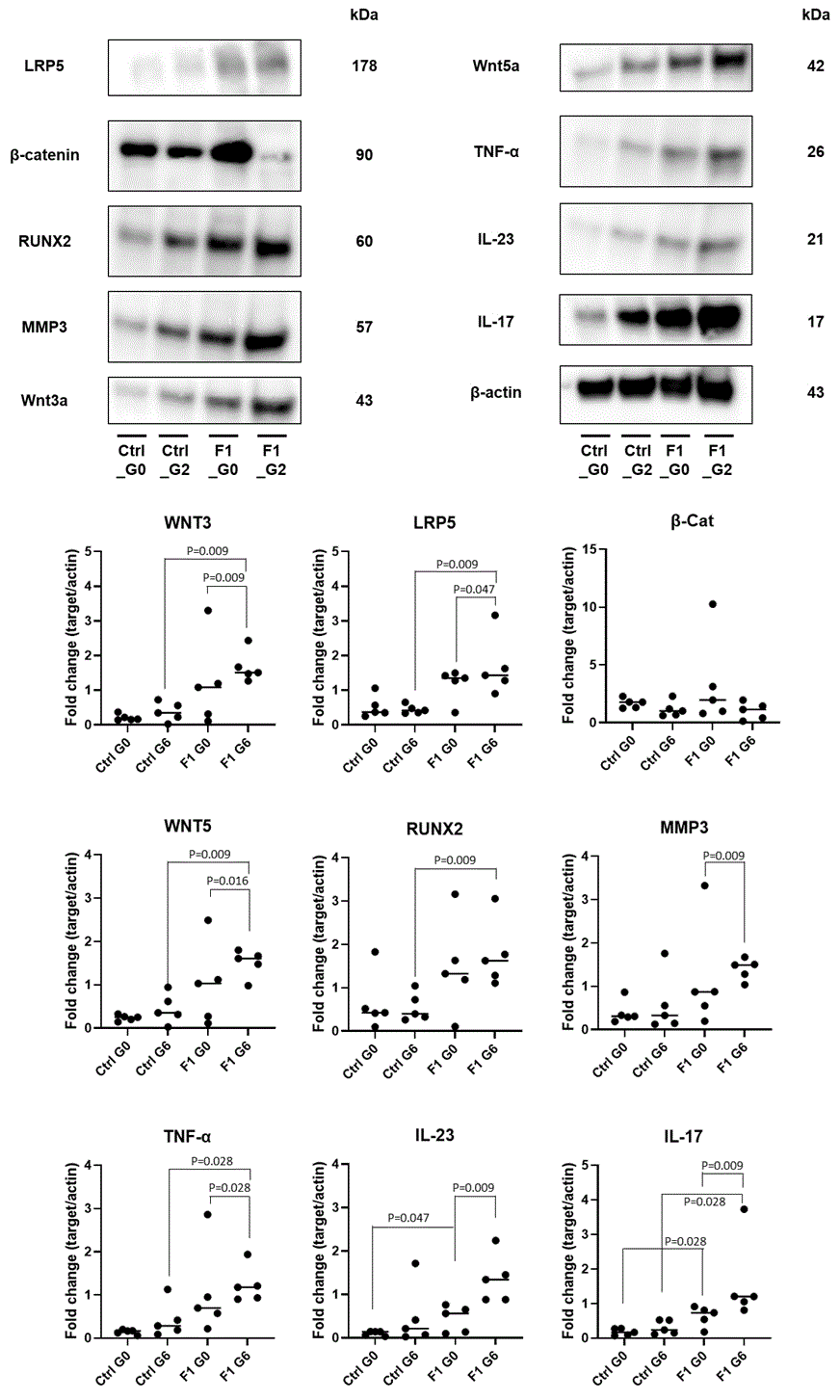
Results: All F1 G6 rats developed clinical arthritis, with 60% also exhibiting spondylitis. Histological analysis revealed a correlation between inflammation and osteoproliferation in F1 G6 rats (r2 = 0.7992, p = 0.041). Aortic protein levels were significantly higher in F1 G6 rats compared to Ctrl G6 rats, with increased expressions of WNT3, LRP5, WNT5, Runt-related transcription factor 2, TNFα, and IL-17 (all p = 0.009, except TNFα at p = 0.028). Elevated levels of WNT3, LRP5, WNT5, matrix metalloproteinase 3, TNFα, IL-17, and IL-23 were also observed in F1 G6 compared to F1 G0 rats (all p < 0.05). (Fig. 1)
Conclusion: These findings suggest that arthritis and spondylitis in SpA may contribute to the development of CV disease by activating Wnt signaling, MMP3, and inflammatory pathways in the CV system.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoon S, Kim C, Song H, Lim M, Kwon S. Activation of Cardiovascular Inflammation and Wnt Signaling in Spondyloarthritis: Insights from the HLA-B27 Transgenic Rat Model [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/activation-of-cardiovascular-inflammation-and-wnt-signaling-in-spondyloarthritis-insights-from-the-hla-b27-transgenic-rat-model/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/activation-of-cardiovascular-inflammation-and-wnt-signaling-in-spondyloarthritis-insights-from-the-hla-b27-transgenic-rat-model/