Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality (1893–1896)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-11:15AM
Background/Purpose: The American College of Rheumatology’s (ACR) 2012 guidelines for the management of gout recommend using a treat-to-target (T2T) approach to lower serum uric acid (SUA). However, few studies report the frequency of achieving a target of SUA < 6 mg/dL for treated gout patients at a population level. Using the ACR’s RISE registry, we examined the proportion of patients with gout receiving long-term urate-lowering therapy (ULT) who achieved an SUA level < 6.0 mg/dL.
Methods: Included patients were required to have at least 1 ICD9/10 diagnosis for gout (ICD9: 274.*; ICD10: M10.*, M1A.*), at least 2 visits with a rheumatology provider prior to December 31, 2019, and continuous use of a ULT (Allopurinol, Febuxostat, Lesinurad, Probenecid, Pegloticase) for a minimum of 12 months. Continuous use was defined as having a prescription or reported use of any ULT medication with an allowable gap of < 90 days for oral medications or < 60 days IV infusions. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who achieved SUA < 6.0 mg/dL (0.36 mmol/l) while still receiving ULT, during the measurement year (2019), consistent with the ACR’s quality measure assessing T2T for patients with gout. Patient characteristics including sociodemographic, comorbidities, and treatment information were extracted from the RISE database. Bivariate analyses were performed across patient characteristics using independent t-tests or chi-square tests, as appropriate. We examined practice-level performance on this measure among practices with > 20 patients in the denominator.
Results: Overall, 8,981 patients were included. The mean (SD) age was 67.2 (12.7) years, 74.6% were males, and 67.3% were White (Table 1). Most patients were using allopurinol (79.7%) or febuxostat (16.6%). Among patients tested (N=4,627), the median (IQR) SUA level in 2019 was 5.2 (4.3, 6.1) mg/dL. 36.8% of patients reached an SUA < 6.0 mg/dL, while 14.6% had an SUA ≥ 6.0 mg/dL, and 48.4% did not have an SUA recorded during the measurement year. In bivariate analyses, patients who did not achieve the target SUA were more likely to be Black and have more comorbidities (see Table 1).
Among practices with at least 20 patients in the denominator, median practice-level performance on this quality measure was 43.5 (27.0, 53.5) (see Figure 1). In the 19 practices with the lowest performance (< 20.0% proportion of patients at target), more than 90% of patients did not have SUA assessed during the measurement year.
Conclusion: Among gout patients followed longitudinally by rheumatologists who were receiving long-term ULT, only one third had a documented SUA at the target level, suggesting that there is significant room for improvement in the management of gout. Quality improvement initiatives should focus on improving the documentation of SUA and optimizing ULT among patient groups less likely to be at target. Routine measurement of serum uric acid to monitor the achievement of a T2T strategy is a first step toward improving quality of care for patients with gout.
Disclaimer: This data was supported by the ACR’s RISE Registry. However, the views expressed represent those of the authors, not necessarily those of the ACR.
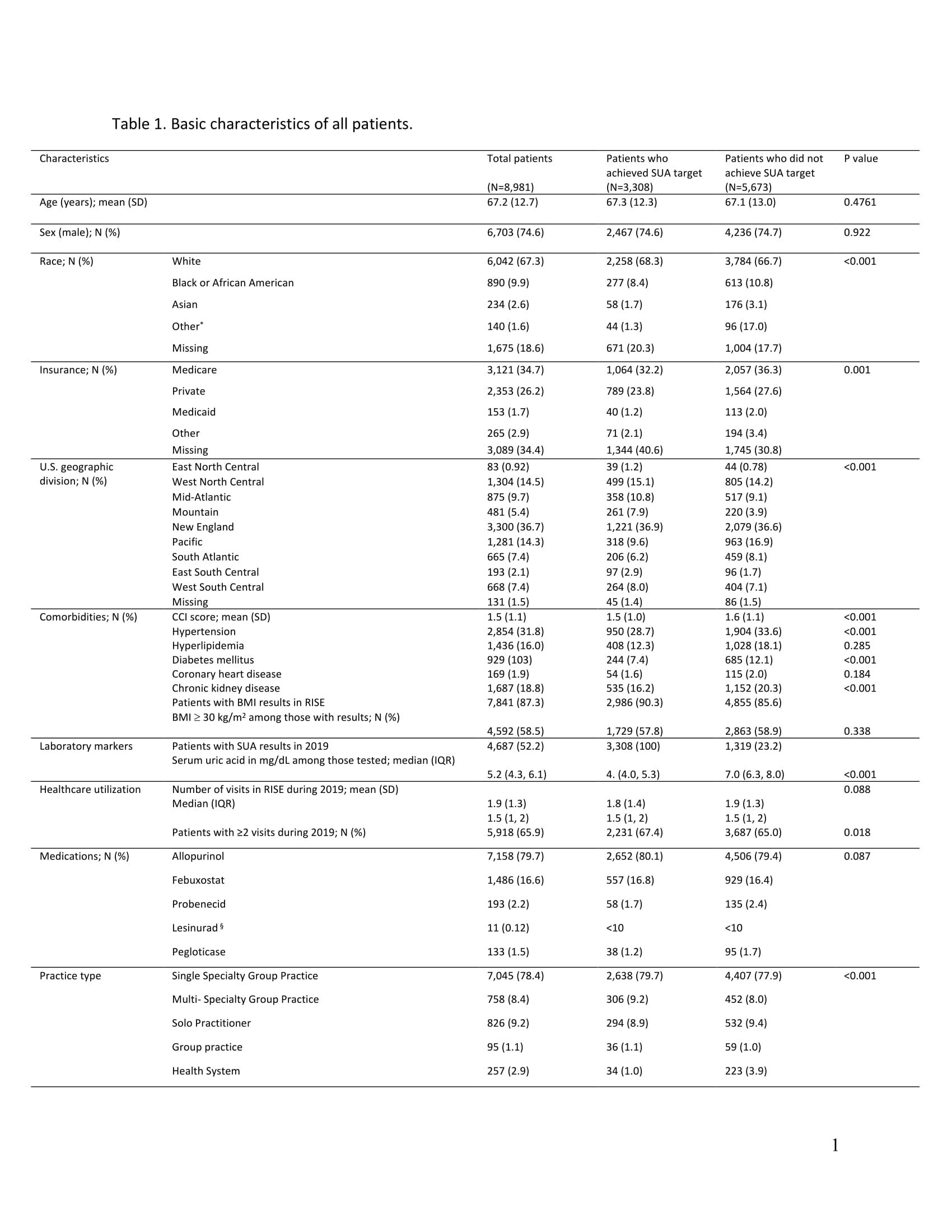 SUA: serum uric acid, CCI: Charlson comorbidity index, and IQR: interquartile range. Other race= AMERICAN INDIAN OR ALASKA, NATIVE HAWAIIAN, Hispanic or Latino, and Multi-racial. †SUA results were for 1,319 patients. §For privacy protections, we reported no cell sizes < 10.
SUA: serum uric acid, CCI: Charlson comorbidity index, and IQR: interquartile range. Other race= AMERICAN INDIAN OR ALASKA, NATIVE HAWAIIAN, Hispanic or Latino, and Multi-racial. †SUA results were for 1,319 patients. §For privacy protections, we reported no cell sizes < 10.
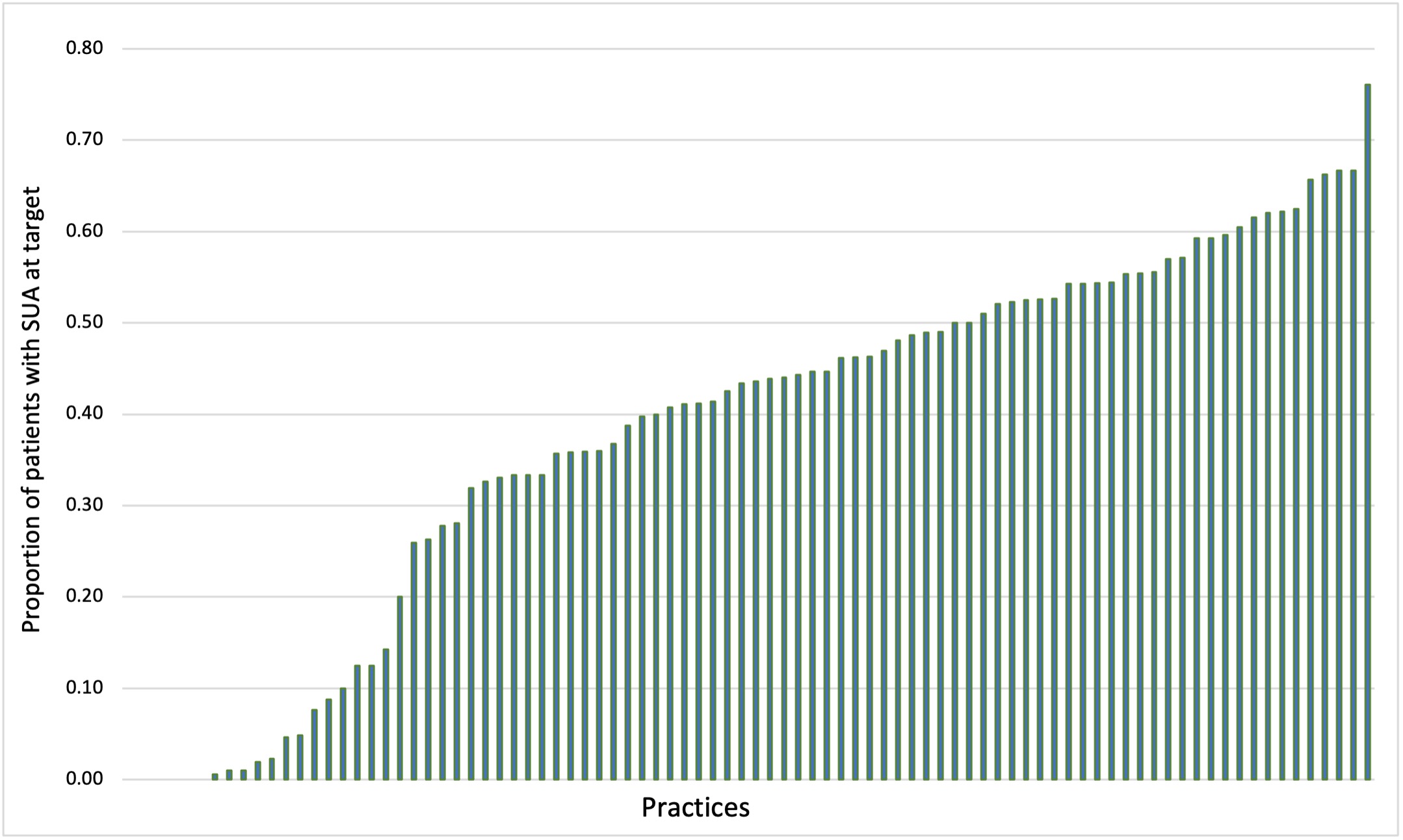 Figure 1: Practice-level performance on quality measure assessing serum uric acid for patients with gout among practices with at least 20 patients eligible (N practices = 88).
Figure 1: Practice-level performance on quality measure assessing serum uric acid for patients with gout among practices with at least 20 patients eligible (N practices = 88).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hammam N, Li J, L Kay J, Yazdany J, Schmajuk G. Achievement of Target Serum Uric Acid Among Gout Patients Treated with Long-term Urate Lowering Therapy in the ACR’s Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE) Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-target-serum-uric-acid-among-gout-patients-treated-with-long-term-urate-lowering-therapy-in-the-acrs-rheumatology-informatics-system-for-effectiveness-rise-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-target-serum-uric-acid-among-gout-patients-treated-with-long-term-urate-lowering-therapy-in-the-acrs-rheumatology-informatics-system-for-effectiveness-rise-registry/
