Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is associated with increased absence from work and reduced work productivity, which can impact employment status.1 TNF inhibitors such as certolizumab pegol (CZP) have been shown to improve work productivity in patients (pts) with axSpA.2,3 However, the association between the extent of clinical improvement and work/household productivity over long‑term CZP treatment has not been evaluated. The objective of this study was to evaluate the association between the extent of improvement in clinical outcomes and burden on paid work and household productivity in pts with axSpA over 4 years’ CZP treatment.
Methods: These analyses use observed data from pts originally randomized to CZP in the phase 3 RAPID-axSpA study (NCT01087762).4 Paid work absenteeism and presenteeism, and household work productivity, assessed using the validated arthritis‑specific Work Productivity Survey (WPS),5 are reported for pts who had: ASAS< 20, ASAS20–< 40, ASAS40 and ASAS partial remission (PR); ASDAS clinically important improvement (CII), major improvement (MI) or non-response; and ASDAS inactive disease (ID). Mean number of days missed or days with reduced productivity each month was calculated by concurrent disease activity/response level and summarized across months to estimate cumulative burden over 204 weeks (wks) using a weighted generalized estimating equations model. An inverse probability-weighted (IPW) model was used to account for predictors of dropout which assigned greater weight to pts who remained in the study vs similar pts who dropped out.
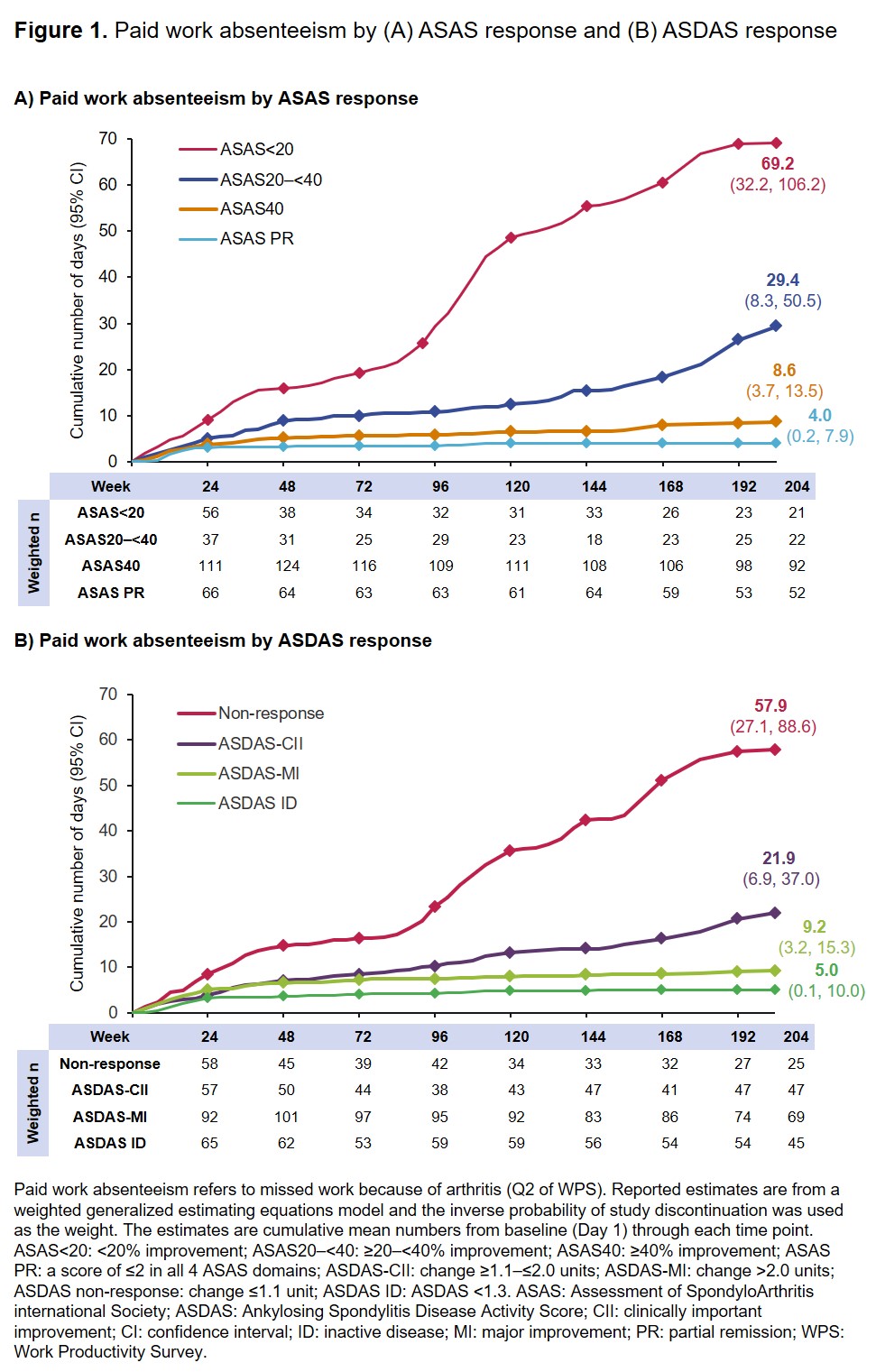
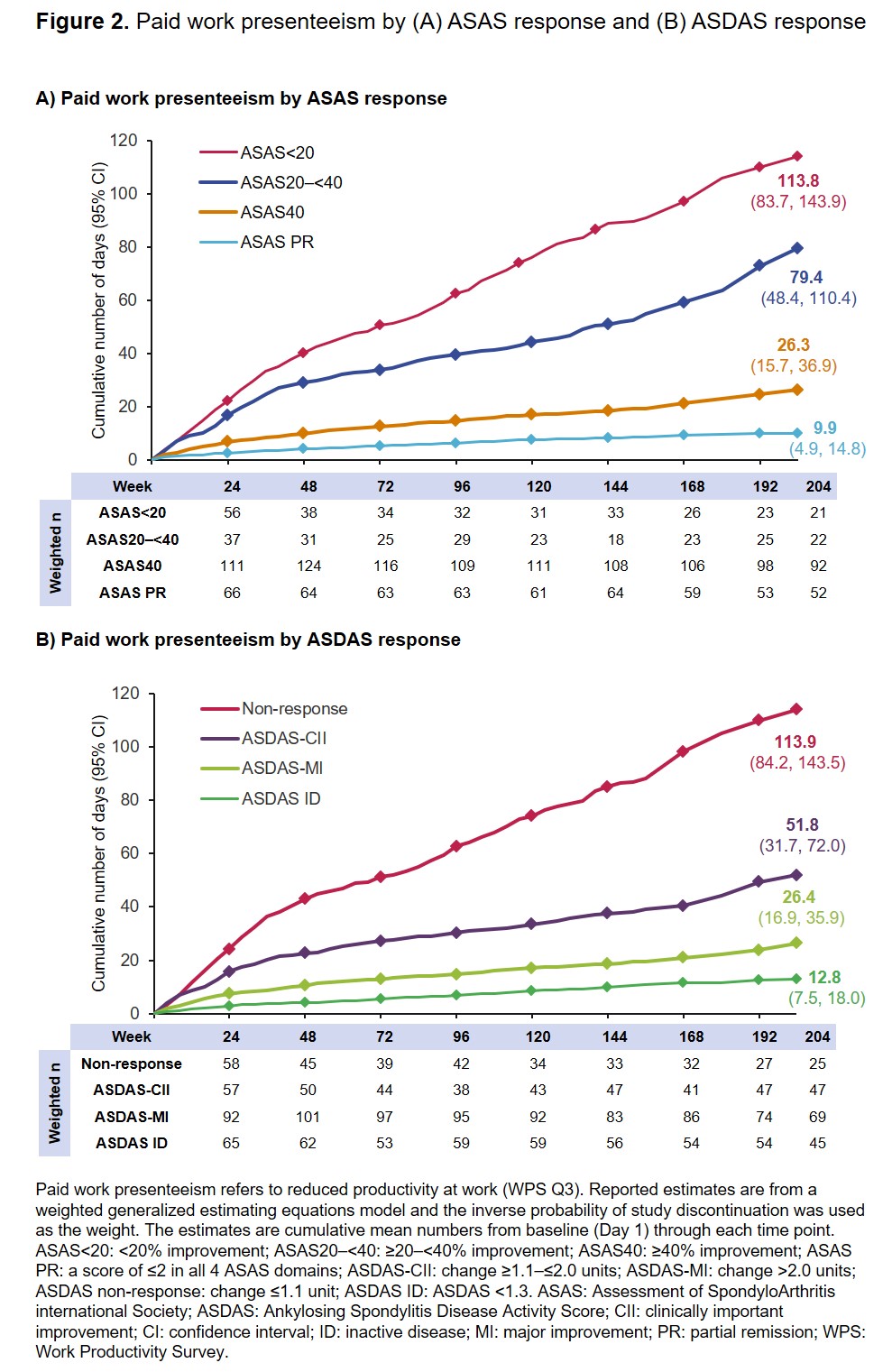
Results: Of 218 CZP-randomized pts, 203, 191 and 142 completed Wks 24, 48 and 204, respectively; at baseline, 157 (72%) were employed outside the home. At Wk 204, 15.8% of pts had ASAS< 20, 16.4% ASAS20–< 40, 67.8% ASAS40 and 37.9% ASAS PR. Up to Wk 204, achievement of the more stringent ASAS PR and ASAS40 was associated with fewer days (4.0 and 8.6, respectively) of paid work absenteeism compared to pts who achieved ASAS< 20 or ASAS20–< 40 (69.2 and 29.4, respectively) (Figure 1A). At Wk 204, 49.0% and 33.1% of pts achieved ASDAS-MI and ASDAS-CII, and 31.8% reached ASDAS ID. ASDAS ID was associated with fewer days of paid work absenteeism over 204 wks (5.0) compared to ASDAS-MI (9.2), ASDAS-CII (21.9) or non-response (57.9) (Figure 1B). Similar findings were observed for paid work presenteeism and household work productivity (Figures 2 and 3), with achievement of more stringent responses associated with fewer days of work presenteeism or days unable to perform housework.
Conclusion: Achievement of optimal thresholds of clinical response in pts with axSpA after 4 years’ treatment was associated with reduced burden on paid work and household productivity, indicating the importance of targeting stringent thresholds of disease control to limit the impact of axSpA on pts’ daily lives.
References: 1. Nikiphorou E. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2020;22:55; 2. van der Heijde D. Rheumatology 2016;55:80–8; 3. van der Heijde D. RMD Open 2018;4:e000659; 4. Landewé R. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:39–47; 5. Osterhaus JT. Arthritis Res Ther 2014;16:R164.
Acknowledgments: The authors acknowledge Tommi Nurminen, David Deering, Otis Rimmer and Domenico Magazzu for their contributions.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rudwaleit M, Machado P, Gensler L, Taieb V, de Peyrecave N, Hoepken B, van der Heijde D. Achievement of Stringent Thresholds of Disease Control Is Associated with Reduced Burden on Work and Household Productivity in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-stringent-thresholds-of-disease-control-is-associated-with-reduced-burden-on-work-and-household-productivity-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-stringent-thresholds-of-disease-control-is-associated-with-reduced-burden-on-work-and-household-productivity-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/