Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The aim of the present study was to investigate whether the imbalance of CD4+ T subsets can be corrected by supplementing low dose interleukin -2 (IL-2).
Methods: The PB samples from 21 patients with SSc as well as 30 healthy control subjects were analyzed for lymphocyte subsets using flow cytometry. Patients given a small dose of IL-2 (50WIU) for a 5-day course based on standard treatment (including glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, biologics, or combination). Using directly the percentages from flow cytometry combined with internal standard beads calculated absolute number of peripheral lymphocyte subsets and their ratio to Treg cells from the subjects in each group before and after IL-2 treatment.
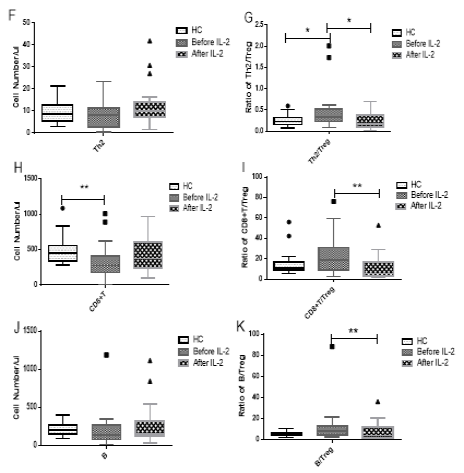
Results: Notably, Treg cells rapidly increase after treatment with low doses IL-2. However, before treatment, the ratios of Th17/Treg(p<0.001) and Th2/Treg£¨p=0.01£©were significantly higher. After treatment, although Th17 and Th2 cells increased, Treg cells increased more, so the ratios returned to normal. Similarly, after treatment, the numbers of Th1, CD8+ T, NK and B cells all increased to some extent, but the ratios of these T cells to Treg cells still were low i.e. they were balanced for the increase in Treg cells after treatment was more pronounced.
Conclusion:Short-term low-dose IL-2 treatment can promote the proliferation of Treg cells mainly and restore the balances of various cell subsets with Treg cells.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shang L, Luo J, Gao C, Yuan J, Li Q, Liu X, Gao H, Li XF. Absolute Reduction of Peripheral CD4+ Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis and Its Restoration By Short-Term and Low Dose IL-2 Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/absolute-reduction-of-peripheral-cd4-regulatory-t-cells-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-and-its-restoration-by-short-term-and-low-dose-il-2-treatment/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/absolute-reduction-of-peripheral-cd4-regulatory-t-cells-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-and-its-restoration-by-short-term-and-low-dose-il-2-treatment/