Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Serum Calprotectin level has been shown to correlate with disease activity, ultrasound (US) parameters, treatment response and clinical remission in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The purpose of this study is to systematically review the existing literature on the relationship of calprotectin and ultrasound parameters in RA.
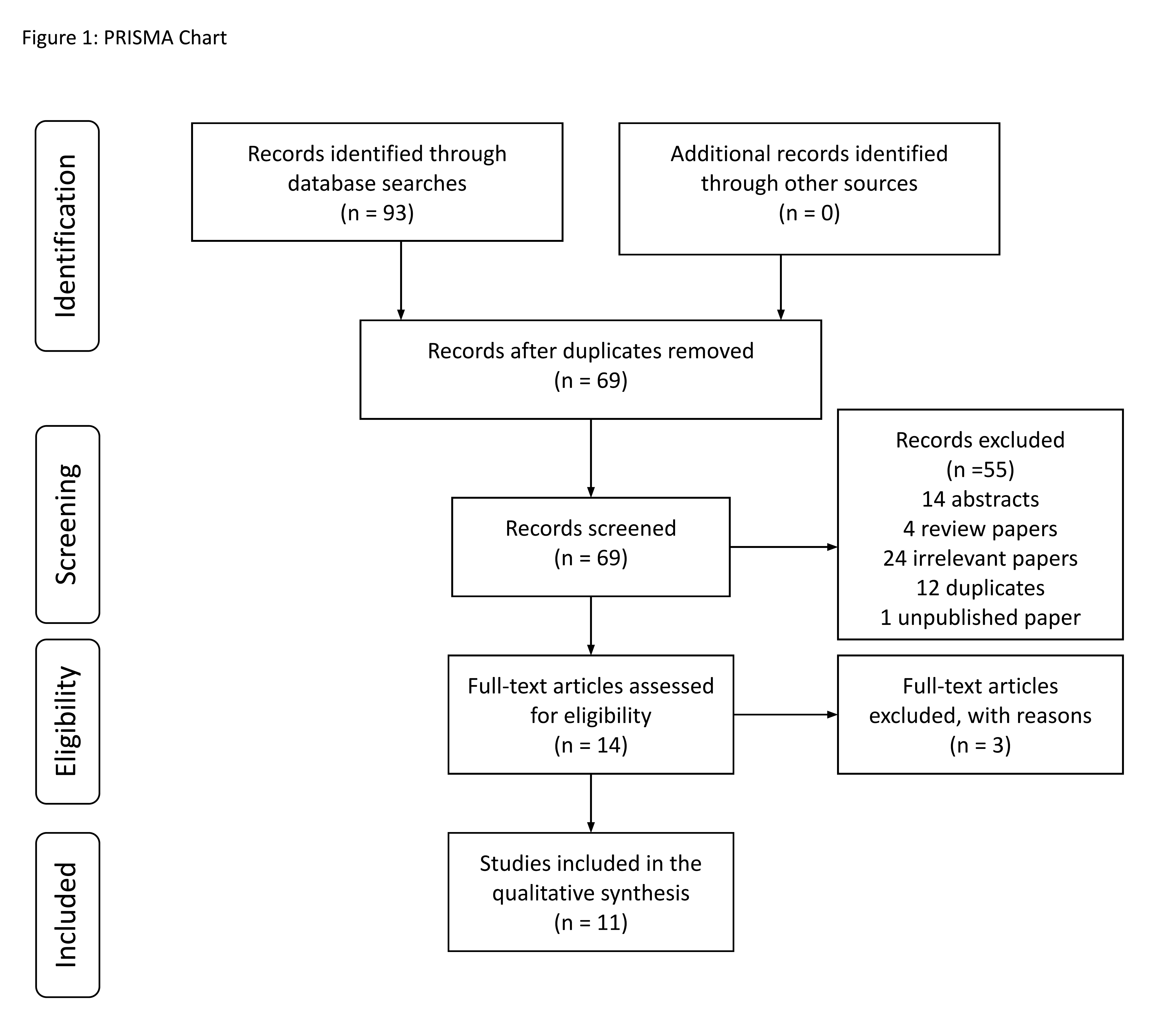
Methods: RA studies reporting serum calprotectin levels and US parameters published between 1 January 1988 to 26 December 2020 were included. A literature search was performed on Medline, Embase, CINAHL and Cochrane which yielded a total of 93 articles. After removing duplicates, screening remaining articles and selecting for full-texts, 11 articles were identified by 2 independent reviewers (Figure 1).
Results: A summary of the studies is shown in tables 1 and 2. Ten studies have shown associations between US findings and calprotectin levels in RA patients, seven of which used Spearman’s correlation coefficient to show significant correlation between US power doppler (PD) and grey scale (GS) scores with calprotectin. When examining calprotectin in the context of treatment, calprotectin was shown to have a weak but significant correlation with US scores before and after treatment in Jonsson 2017 6. In patients monitored over their course of treatment with bDMARDs, (Nordal 2017 4) the strongest correlation was found between calprotectin and US sum scores at baseline. Calprotectin had the strongest correlation with US sum scores among patients started on etanercept and rituximab. When calprotectin was evaluated in its utility for defining ultrasound remission, it was found to be superior in its ability to distinguish ultrasound-defined active synovitis (UdAS) and non-UdAS compared to C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) Inciarte-Mundo 20168. Hurnakova 20169 also showed its ability to distinguish between patients in US remission and those with subclinical US disease activity. There was a significantly lower median calprotectin levels in patients with US remission at 1, 3 and 12-month interval. Additionally, Jalborg 20201 reported calprotectin could better predict positive SONAR score in patients with disease progression of less than 5 years [AUC 0.72 (95% CI 0.73-0.83) in all patients compared to AUC 0.65 (95% CI 0.57-0.73) in disease duration less than 5 years]
Sakellariou 2019 was the only study which showed no significant correlation between calprotectin levels and US PD and GS scores. In this study, calprotectin level was also unable to predict ultrasound synovitis2. Finally, Nordal 20173 analyzed plasma and serum calprotectin levels and showed a stronger correlation between plasma calprotectin and US parameters when compared to serum calprotectin.
Conclusion: The majority of studies found that calprotectin correlates with ultrasound synovitis in RA patients; some of which found that calprotectin was a better biomarker compared to traditionally used biomarkers such as ESR and CRP. Calprotectin was also found to be an independent predictor of ultrasound synovitis and was able to distinguish those in ultrasound remission from subclinical synovitis. This suggest that there is a role for serum calprotectin to help define a deeper remission state in RA.
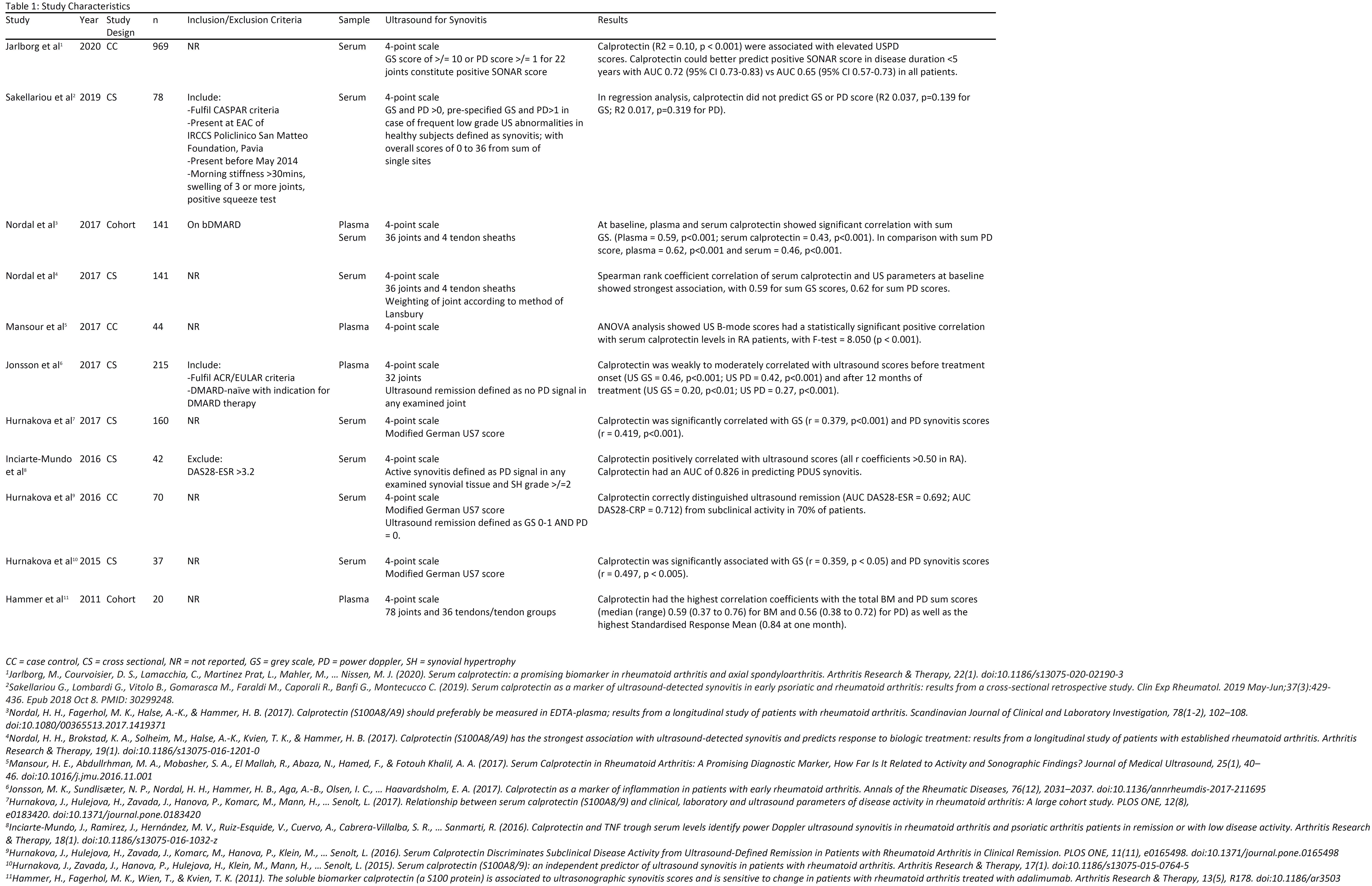 Table 1: Study Characteristics
Table 1: Study Characteristics
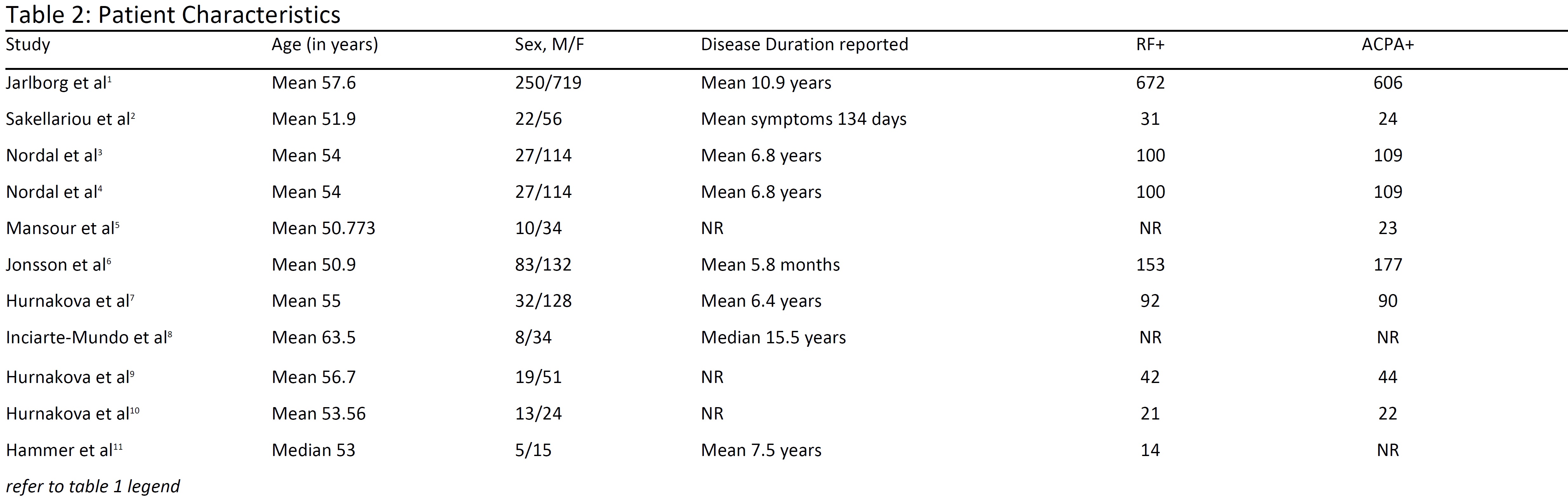 Table 2: Patient characteristics
Table 2: Patient characteristics
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Low A, Lim F, Ma M. A Systematic Review Looking at the Relationship Between Serum Calprotectin and Ultrasound Parameters in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-systematic-review-looking-at-the-relationship-between-serum-calprotectin-and-ultrasound-parameters-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-systematic-review-looking-at-the-relationship-between-serum-calprotectin-and-ultrasound-parameters-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/