Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Previously, several studies have meta-analyzed clinical, functional or structural efficacy of biologics in treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. However, the comparative efficacy of biologics in inhibiting radiographic progression from a long-term perspective is still not fully understood. We compared 1-year radiographic efficacy of biologics using a Bayesian network meta-analysis (NMA), and reviewed radiographic data for up to 10 years follow-up.
Methods: A systematic literature search of published peer-reviewed articles and scientific meeting abstracts identified randomized controlled trials investigating approved biologic therapies in combination with methotrexate (MTX) or tocilizumab alone in predominantly biologic-na•ve (< 20% biologic experienced) RA patients. Structural damage was analyzed as change from baseline using the modified van der Heijde Total Sharp Score (vdHS). One-year data were included in the NMA. Model parameters were estimated in a Bayesian framework using noninformative prior distributions. Longer term data (>1 year) was reviewed qualitatively in absence of sufficient data points for analysis. To assess the effect of biologic therapies in specific subpopulations, subgroup analyses were performed on: DMARD na•ve, DMARD inadequate responders, early RA, and established RA.
Results: Eleven clinical trials were identified and included in the NMA model. All biologics in combination with MTX showed decreased radiographic progression at 1 year compared to MTX alone, as defined by negative mean difference in vdHS change (Figure). Most interventions showed statistically significant effect, except for golimumab 50 mg every 4 weeks and tocilizumab 8mg/kg every 4 weeks.The largest statistically significant mean difference at 1 year was in adalimumab, where the increase in vdHS was 3.8 fewer units in patients administered adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks + MTX compared with those receiving MTX alone. Patients treated with infliximab 3 mg/kg every 8 weeks had the next highest relative effect at -3.7 versus MTX alone. Longer term radiographic data were found in 8 unique trials spanning 2 to 10 years of follow-up that demonstrate sustained slowing of radiographic progression for the following biologics (abatacept, certolizumab, etanercept, golimumab, infliximab and tocilizumab) in combination with MTX and adalimumab (+/-MTX). While the long term data did not contradict the efficacy of the 1-year outcomes, only 3 biologics (adalimumab, golimumab, tocilizumab) had 5 years of follow-up and only adalimumab had 10 years of follow-up. Subgroup results yielded consistent findings.
Conclusion: Biologics generally inhibit the progression of structural damage from a long-term perspective. Although some biologics like adalimumab have demonstrated radiographic benefits for up to 10 years, more research is needed to replicate this finding. 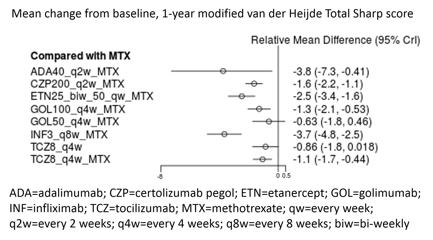
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Murray E, Butylkova Y, Ellis A, Skup M, Kalabic J, Garg V. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Efficacy of Biologics in Treating Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Assessment of Long-Term Radiographic Progression from Published Clinical Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-of-comparative-efficacy-of-biologics-in-treating-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-assessment-of-long-term-radiographic-progression-from-published-clinical-tria/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-of-comparative-efficacy-of-biologics-in-treating-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-assessment-of-long-term-radiographic-progression-from-published-clinical-tria/
