Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1913–1944) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with interstitial lung diseases (ILD) and clinical features of autoimmunity who do not satisfy the classification criteria for a specific autoimmune rheumatic disease are diagnosed with interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF). The treatment approach to ILD in this setting remains undefined. We conducted an observational retrospective study to examine the use of rituximab (RTX) in IPAF.
Methods: Patients from the Mount Sinai/National Jewish Respiratory Institute Patient Registry and Biorepository were included if they met the 2015 classification criteria for IPAF and were treated with RTX. Patients who met the criteria for another autoimmune disorder were excluded. Clinical improvement was defined as improvement in four domains after the use of RTX, including: pulmonary function tests (PFTs), CT chest findings, need for respiratory related hospitalization and survival.
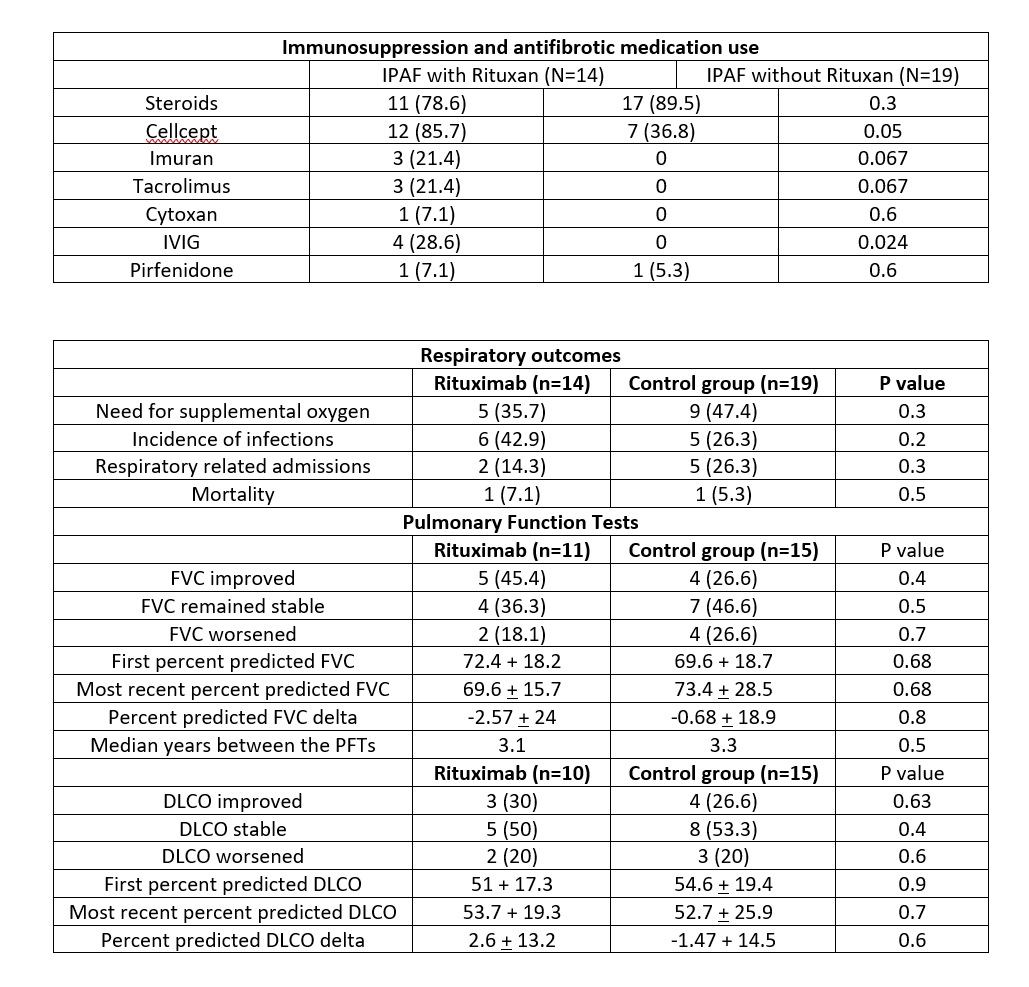
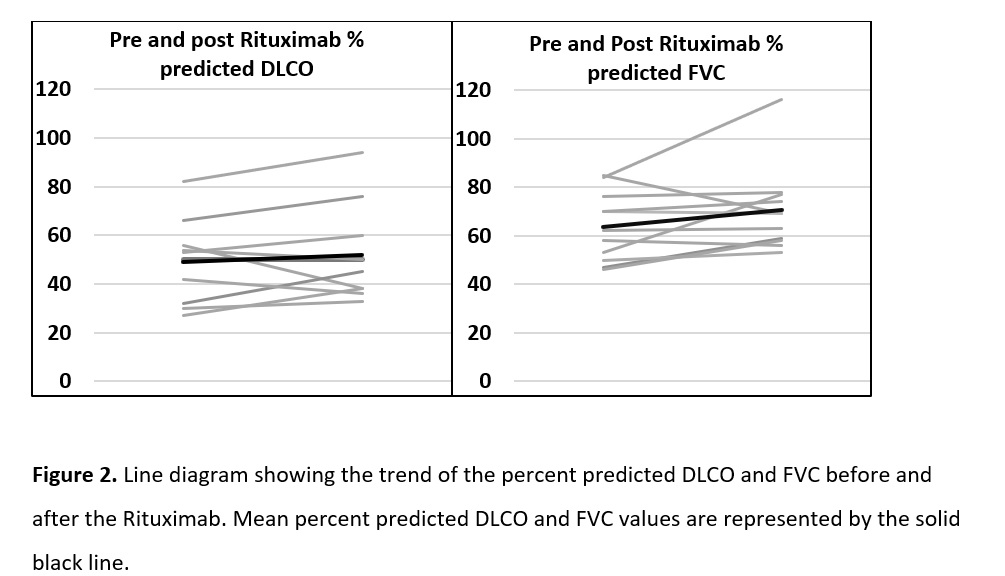
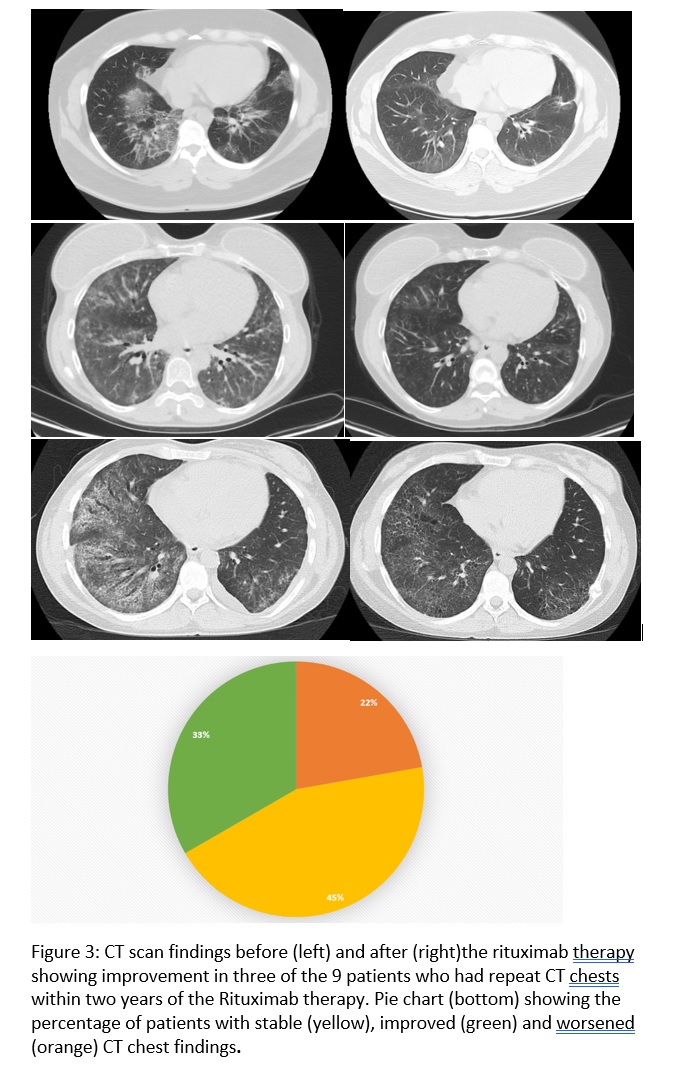
Results: Of the 791 patients in the registry, 14 patients met the criteria for IPAF and received at least one dose of Rituximab. 19 patients were identified who met the criteria for IPAF and did not receive Rituximab to serve as the control group. There were no differences in the baseline demographics. Five patients (45.4%) in the RTX group were improved and 4 (36.3%) remained with stable FVC and DLCO. Accordingly, HRCT scan findings improved in 3 (33%) patients and remained stable in 4 (45%), from 9 patients with available HRCT scans. Frequency of oxygen use, incidence of infection, respiratory related admissions and overall mortality was similar in both the groups.
Conclusion: The majority of patients with IPAF receiving rituximab showed improvement or stability in their pulmonary function. Although both the groups had similar outcomes, all patients in the RTX group had failed multiple immunosuppressive agents, suggesting refractory ILD. We propose RTX as an option for patients with moderate to severe IPAF who progress despite standard immunosuppressive therapy. Further prospective studies are needed to assess the benefit of RTX in this subset of patients with ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sandhu T, Meir L, Ng N, Klein L, Zatakia J, Padilla M, Tassiulas I. A Single-center, Observational, Retrospective, Case Control Study of Rituximab for the Treatment of Interstitial Pneumonia Associated with Autoimmune Features [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-single-center-observational-retrospective-case-control-study-of-rituximab-for-the-treatment-of-interstitial-pneumonia-associated-with-autoimmune-features/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-single-center-observational-retrospective-case-control-study-of-rituximab-for-the-treatment-of-interstitial-pneumonia-associated-with-autoimmune-features/