Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Basic Science (0944–0947)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:15AM-9:30AM
Background/Purpose: Dysregulated endothelial cell (EC) function and altered (lympho)angiogenesis crucially contribute to synovial pathology in inflammatory arthritis. Additionally, endothelium plays a key role in the positional identity of sublining synovial fibroblasts and their pathogenic expansion in RA. Here, we utilized single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to characterize the diversity of synovial vascular and lymphatic ECs and functionally annotate synovial ECs across inflammatory arthritides.
Methods: We obtained synovial tissue from 12 knees, 8 wrists, 8 metacarpophalangeal and one sternoclavicular joint from 14 RA, 5 SpA, 3 PsA and 3 patients with undifferentiated arthritis (UA, 2 mono-, 1 polyarthritis) using ultrasound-guided synovial biopsy. We dissociated synovium into a single cell suspension through a combined mechanical-enzymatic dissociation. Additional tissue was formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded for immunohistology (Krenn synovitis score, pathotype). We created scRNA-seq libraries with 10x Genomics Chromium and sequenced them on NovaSeq6000 (min. 50’000 reads/cell). We mapped the reads to the reference genome GRCh38.p13 (transcripts from GENCODE Release 32) and analysed the scRNA-seq data with R/Bioconductor tools, including quality control, filtering, graph-based clustering, manual and computational cell-type annotation, differential abundance (DA), and differential state analysis. We visualized data using iSEE.
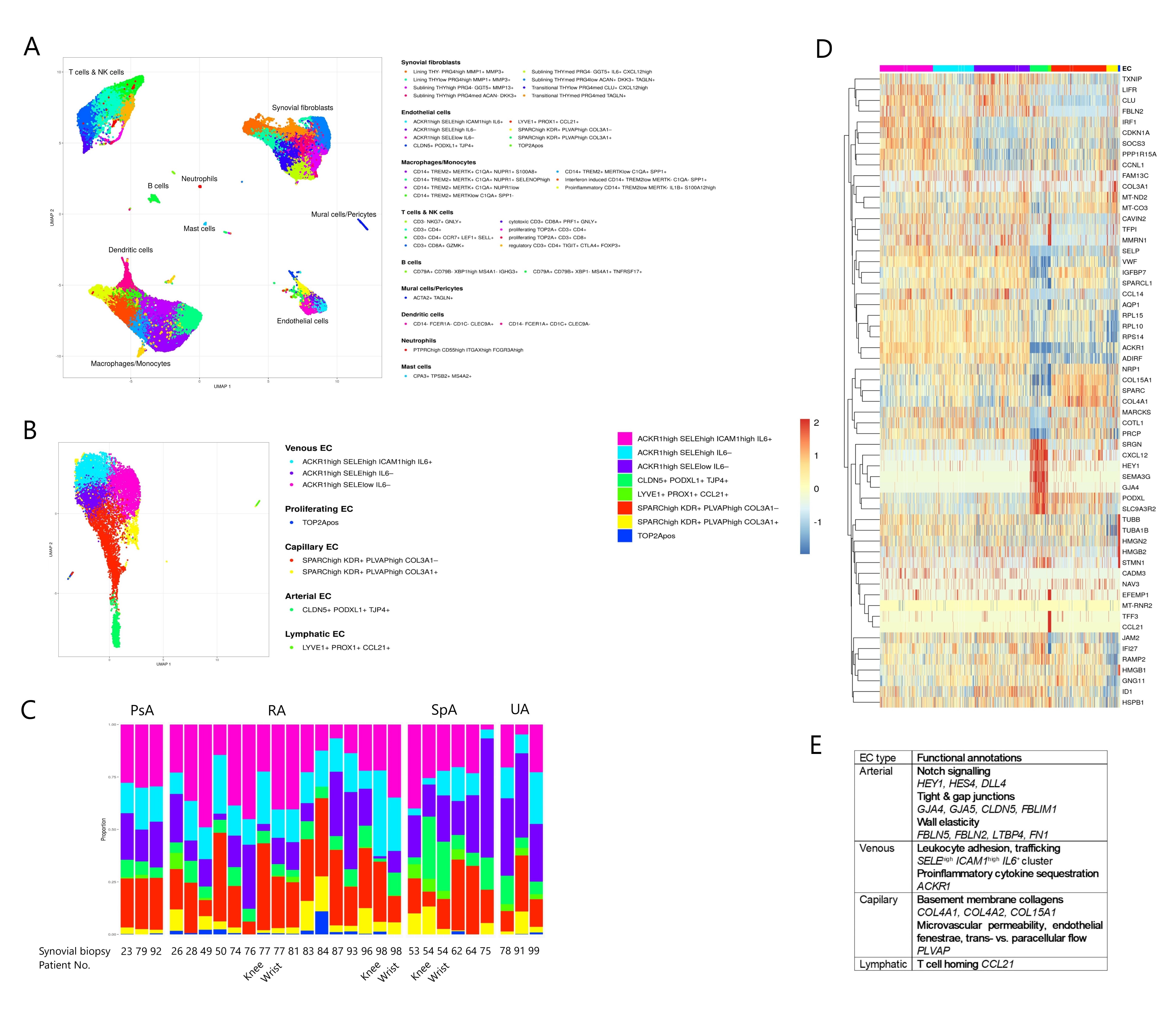
Results: Our dissociation protocol yielded highly viable (median 90%) single-cell suspensions from which we generated 107’438 high quality synovial single cell profiles. We could classify synovial pathotypes in 86% of the samples (24% diffuse myeloid, 29% lympho-myeloid, 33% pauci-immune). Krenn synovitis score ranged from 2 to 8 (median 4), suggesting a moderate inflammation in most synovia. ScRNA-seq analysis identified 6 principal and 4 minor synovial cell populations forming 38 distinct synovial cell clusters (Fig 1A). PECAM1+ ECs (n=10’231) represented 4-15% (25Q-75Q, median 9%) of all synovial cells, comprising 8 distinct cell subpopulations: ACKR1high SELEhigh ICAM1high IL6+ venous ECs, ACKR1high SELEhigh IL6– venous ECs, ACKR1high SELElow IL6– venous ECs, COL3A1+ and COL3A1– SPARChigh KDR+ PLVAPhigh capillary ECs, highly proliferative TOP2A+ ECs, CLDN5+ PODXL1+ TJP4+ arterial ECs and lymphatic LYVE1+ PROX1+ CCL21+ ECs (Fig 1B). EC subpopulations were heterogeneously distributed across patients (Fig 1C), but none of the EC subpopulations was significantly enriched in RA, PsA and SpA synovia in our patient cohort. We defined synovial pan-endothelial and subtype-specific EC markers (Fig 1D) and identified genes that infer the core EC subtype-specific functions (Fig 1E).
Conclusion: We created a comprehensive single-cell atlas of synovial ECs in patients with inflammatory arthritis. Our EC dataset comprises more than 10’000 EC profiles, representing a reference dataset for annotating synovial ECs and guiding EC subtype-specific functional studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Edalat S, Gerber R, Houtman M, Micheroli R, Buerki K, Izanc N, Burja B, Kuret T, Sodin-Šemrl S, Ciurea A, Distler O, Ospelt C, Pauli C, Robinson M, Frank-Bertoncelj M. A Single-cell Atlas of Human Synovial Endothelial Cells in Inflammatory Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-single-cell-atlas-of-human-synovial-endothelial-cells-in-inflammatory-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-single-cell-atlas-of-human-synovial-endothelial-cells-in-inflammatory-arthritis/