Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0543–0581) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease marked by varied disease activity, underscored by complex immune dysregulation, including altered immune mediators and accumulation of autoantibody (AutoAb) specificities. This study seeks to determine an optimal panel of analytes that distinguish SLE patients with active disease and refine a Lupus Disease Activity Index (L-DAI).
Methods: We procured samples from patients with classified SLE on dates of low disease activity (< 4, range 0-3, n=162) or active disease (≥4, range 4-30, n=162) defined by the hybrid SLEDAI (hSLEDAI). Race/sex/age-matched healthy control (Ctrl) samples (n=81) were also evaluated. Plasma immune mediators (n=33) were evaluated by microfluidic immunoassay and serum AutoAb specificities, including dsDNA, chromatin, Ro/SSA, La/SSB, Sm, SmRNP, and RNP, were assessed by xMAP assay. The L-DAI is the sum of log-transformed, standardized immune mediators, weighted by the Spearman r correlation coefficient of mediator levels vs. either hSLEDAI scores or number of AutoAb specificities associated with clinical disease activity. Log-transformed mediator levels were further evaluated using random forest applied machine learning modeling to determine an optimal subset of analytes to inform the L-DAI.
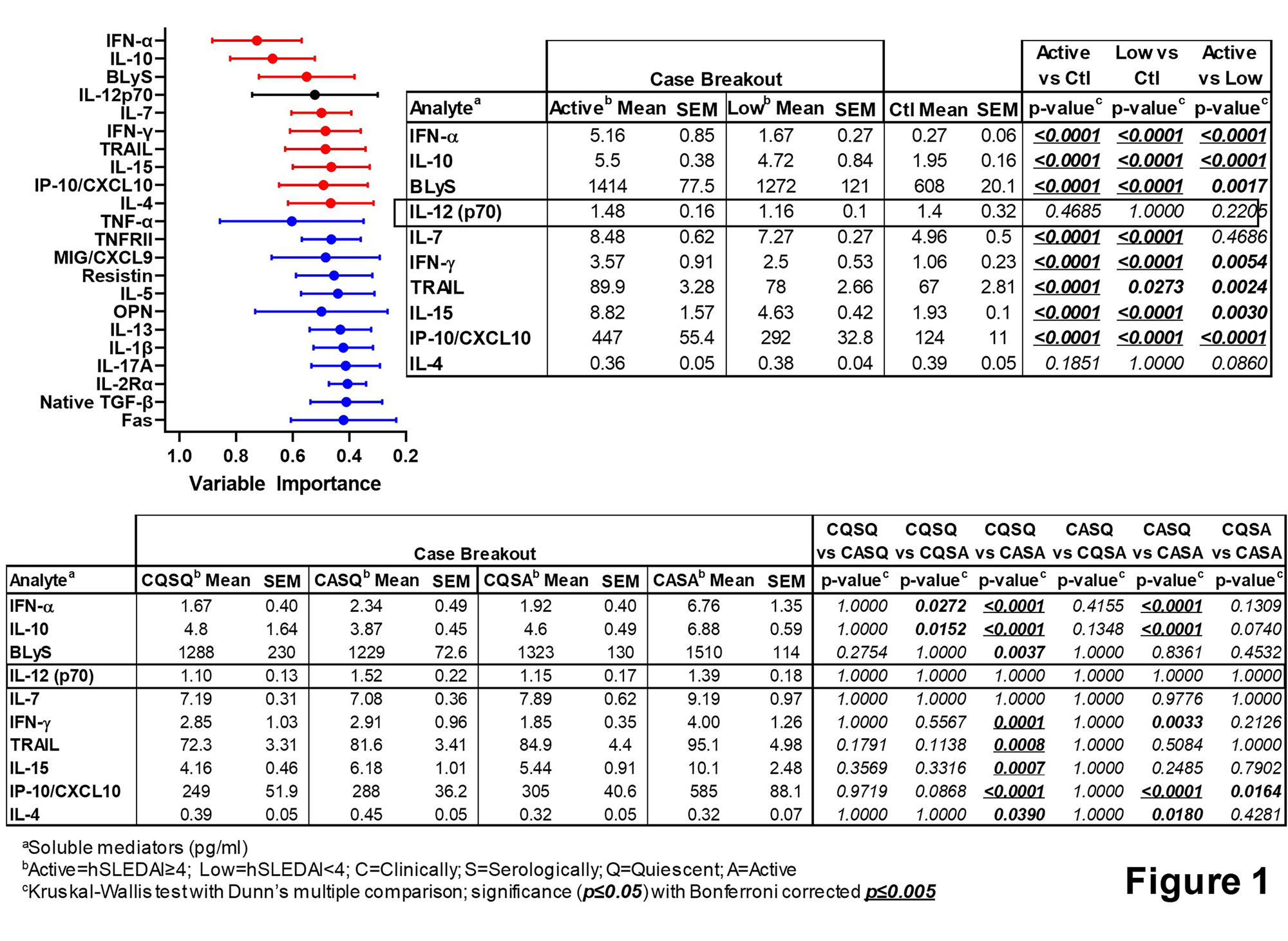
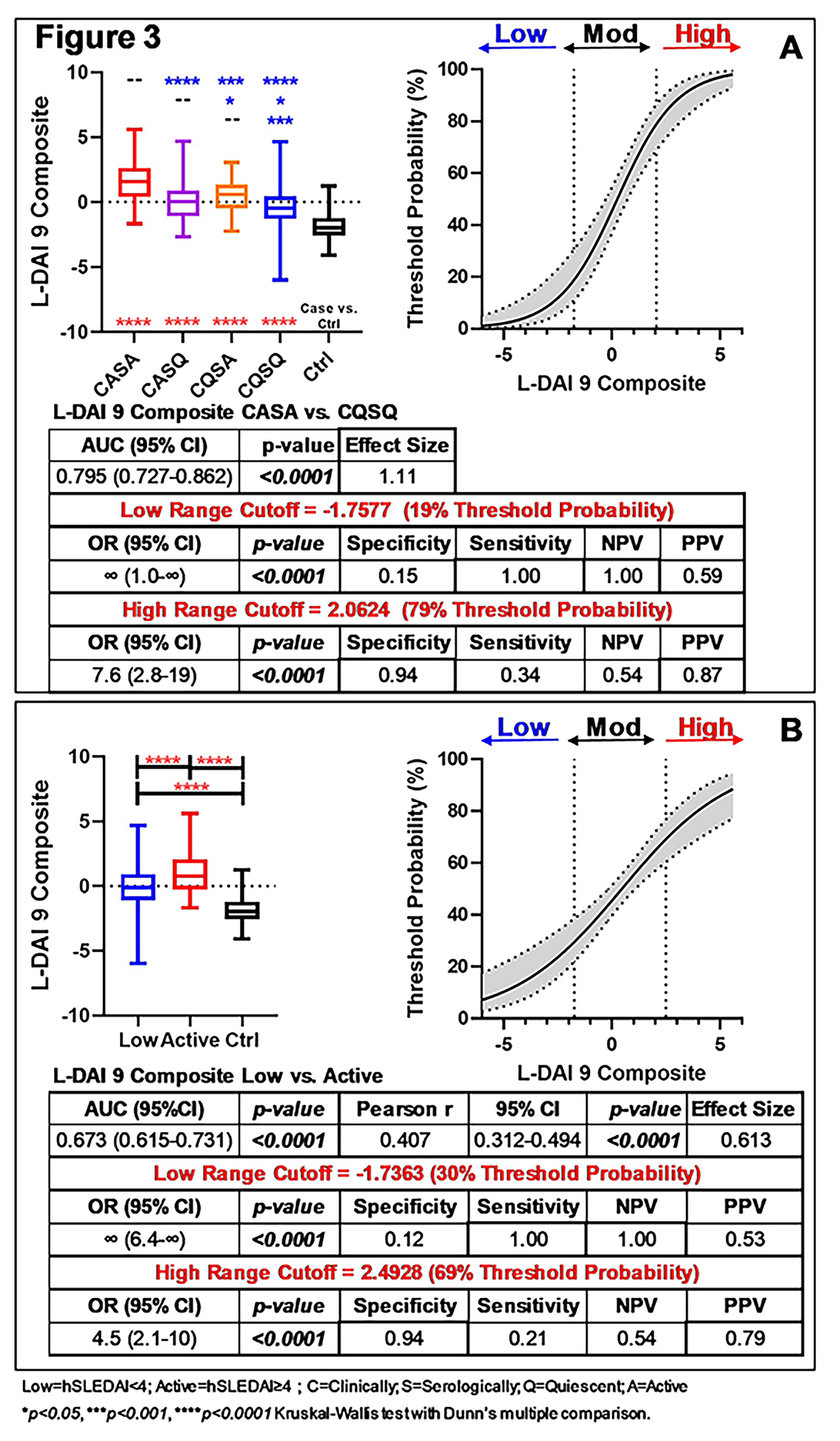
Results: As expected, SLE patients with active disease demonstrated differences in clinical and serologic features, as well as increased use steroids. Random forest modeling of immune mediators comparing low vs. active disease, including clinically and/or serologically active vs. quiescent disease and Ctrls informed a variable importance ranking (Fig. 1, mean ± SD, top 21 mediators shown). Forward selection (adding mediators to top mediator, IFN-α [red]) and backward elimination (subtracting mediators from total [blue]), in combination with univariate analysis (Fig. 1), yielded a combination of 9 mediators (in red, Fig. 1) that best informed the L-DAI. The L-DAI 9, whether weighted by hSLEDAI or number of AutoAbs, significantly (p≤0.05) differentiated SLE patients with Low vs. Active disease, including clinically/serologically active/quiescent disease (vs. Ctrls, Fig. 2), with strong correlation between the weightings (Spearman r=0.990, p< 0.0001). An average composite L-DAI differentiated SLE patients with low, active, and clinically/serologically active/quiescent disease (vs. Ctrls, Fig. 3). There was enhanced distinction of low/moderate/high risk regions for active disease after application of decision curve analysis, with large ( >0.8) Cohen’s effect size and AUC=0.795 (p< 0.0001) in distinguishing clinical/serologic active/quiescent disease activity, and significant correlation (Spearman r=0.407, p< 0.0001) with concurrent clinical disease activity (hSLEDAI scores) (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: We have refined the L-DAI to characterize SLE patients with active clinical and/or serological disease vs. those with low/quiescent disease. Treat-to-target approaches using a sensitive and objective biomarker surrogate for clinical disease activity has the potential to help improve clinical disease management and prevent organ damage in SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Munroe M, Blankenship D, DeFreese D, Holloway A, Purushothaman M, DeJager W, Macwana S, Guthridge J, Kamp S, Redinger N, Aberle T, Chakravarty E, Arriens C, Li Y, Zeng H, Dezzutti S, Izmirly P, Thanarajasingam U, Kamen D, Buyon J, James J, Jupe E. A Refined Disease Activity Immune Index Informed by Select Immune Mediators That Characterizes Clinical Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-refined-disease-activity-immune-index-informed-by-select-immune-mediators-that-characterizes-clinical-disease-activity-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-refined-disease-activity-immune-index-informed-by-select-immune-mediators-that-characterizes-clinical-disease-activity-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/