Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster I: COVID-19 & Vaccination (0084–0117)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
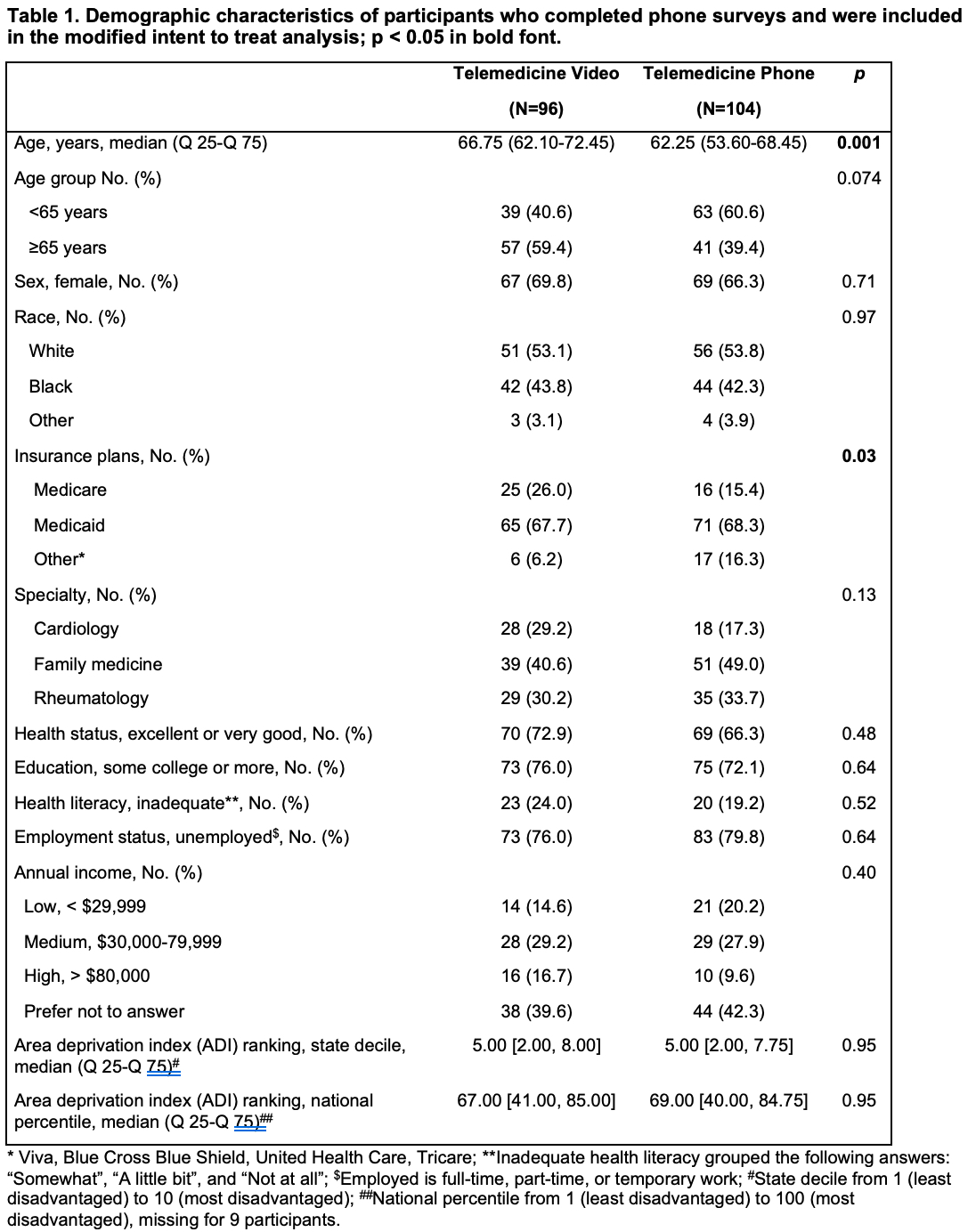
Background/Purpose: The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a significant shift to home-based telemedicine including video and phone-only visits in many medical specialties. However, patients may be agnostic about the relative value and satisfaction with one form of telemedicine compared to another. Thus, the goal of our study was to determine if patient satisfaction with phone-only visits was noninferior to video visits in rheumatology and two other medical clinics at a large tertiary referral center in the Deep South, a region which is home to many socioeconomically disadvantaged older individuals.
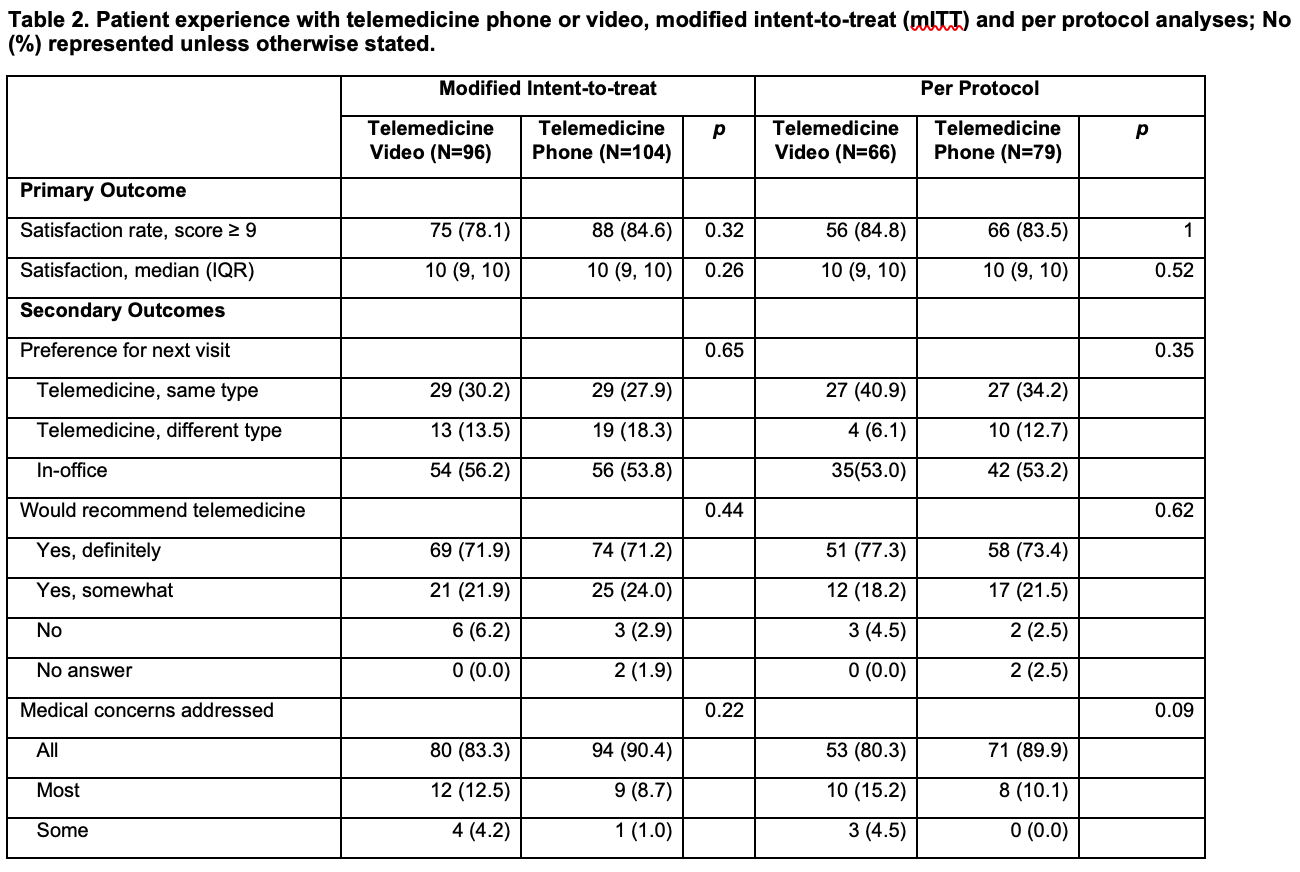
Methods: We conducted a parallel group, randomized (1:1), single-blind, noninferiority trial comparing satisfaction rates for two telemedicine delivery methods: phone-only (intervention group) and video visits (standard group). Adults, age >= 60 years or with public insurance (Medicare/Medicaid) were recruited from rheumatology, family medicine, cardiology clinics. The primary outcome was visit satisfaction rate (9 or 10 on a 0-10 satisfaction scale). Noninferiority was determined if satisfaction with phone-only (intervention) versus video visits (comparator) was no worse by a -15% noninferiority margin. We performed modified intent-to-treat (mITT) and per protocol analysis. We also examined preference for the next visit type, whether patient concerns were addressed during the visit, and whether patients recommended telemedicine.
Results: A total of 200 participants (87.3%), including 96 assigned to video group and 104 assigned to phone-only group, completed surveys on average 2.7 (3.4) days post-visit. A third of the participants were recruited from the rheumatology clinic. This population defines the modified intent-to-treat (mITT) analysis. Overall, participants who completed the surveys were predominately women (N=136, 68%), 86 (43%) were Black with a mean age in the early sixties consistent with the inclusion criteria, and the majority had at least some college education (N=148, 74%) (Table 1).The satisfaction rates were higher than anticipated in both groups (78.1% for video vs 84.6% for phone-only) and not significantly different, (p = 0.32) (Table 2). In the mITT analysis, phone-only visits were noninferior by an adjusted difference of 3.2% (95% CI, -7.6% to 14%). In the per protocol analysis, phone-only were noninferior by an adjusted difference of -4.1% (95% CI, -14.8% to 6.6%) (Figure 1). The proportion of participants who indicated they preferred the same type of telemedicine visit as their next clinic visit were similar (30.2% versus 27.9% video versus phone-only group, p = 0.78) and a majority said their medical concerns were addressed and would recommend a telemedicine visit.
Conclusion: Among a group of diverse, medically at-risk patients seen in rheumatology and two other medical clinics the satisfaction rate for phone-only was noninferior to video visits. Our findings provide added data on patients’ acceptance and satisfaction with different types of telemedicine in populations of concern, which can inform clinical, regulatory, and administrative context of telemedicine and related reimbursement policies for medical care of patients with chronic diseases during and beyond the COVID-19 era.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Danila M, Sun D, Jackson L, Cutter G, Jackson E, Ford E, DeLaney E, Mudano A, Foster J, Rosas G, Curtis J, Saag K. A Randomized Trial Showing No Differences in Patient Satisfaction with Telemedicine Delivered by Phone or Video During COVID-19 in Rheumatology and Other Medical Specialty Clinics [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-trial-showing-no-differences-in-patient-satisfaction-with-telemedicine-delivered-by-phone-or-video-during-covid-19-in-rheumatology-and-other-medical-specialty-clinics/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-trial-showing-no-differences-in-patient-satisfaction-with-telemedicine-delivered-by-phone-or-video-during-covid-19-in-rheumatology-and-other-medical-specialty-clinics/