Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The optimal treatment for lupus nephritis is challenging due to its heterogeneity and the lack of prognostic factors favoring one immunosuppressive drug over another. While cyclophosphamide-based regimens improve renal outcomes, significant drug-related adverse effects, particularly serious infections and gonadal failure, limit its use as induction therapy for some patients. This study compares the efficacy and safety of intravenous cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, and tacrolimus as induction treatments for lupus nephritis and to validate the potential use of CXCL10 as a treatment response biomarker.
Methods: This 24-week randomized, open-label, prospective, parallel-arm study enrolled 82 patients diagnosed with clinical or biopsy-proven lupus nephritis (LN) between November 2022 and April 2024 from a tertiary care center in eastern India. Patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive intravenous cyclophosphamide (CYC), mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or tacrolimus (TAC), in combination with hydroxychloroquine, steroids, and ACE inhibitors. All participants fulfilled the 2019 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The primary objective was to evaluate the renal response (complete or partial) at week 24 of induction therapy. Continuous data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median with interquartile range (IQR). Fisher’s exact test was used to assess the statistical significance of differences in renal response among the three groups. Serum CXCL10 was measured at baseline and post-treatment using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method according to the manufacturer’s instructions. A p-value of < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
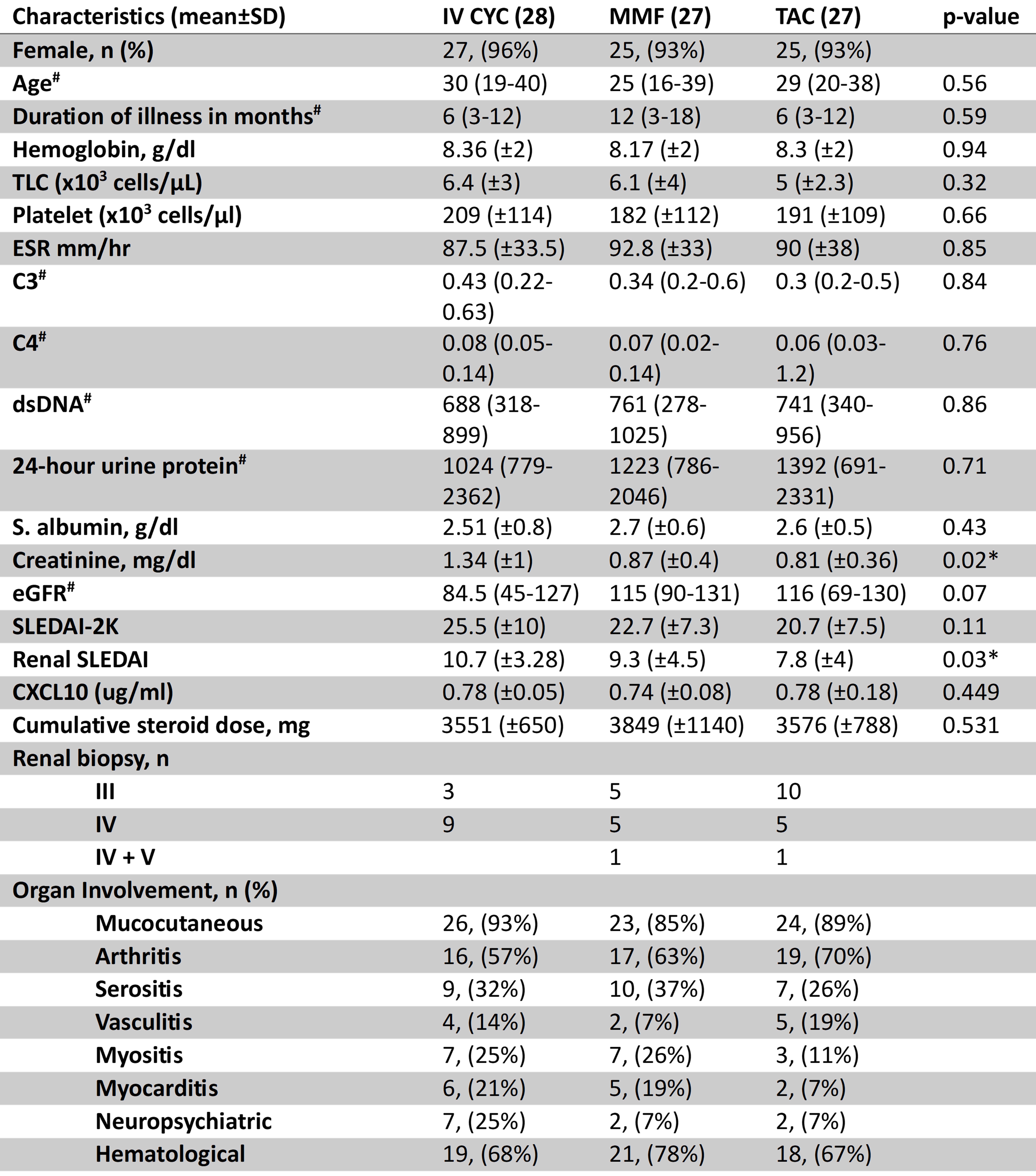
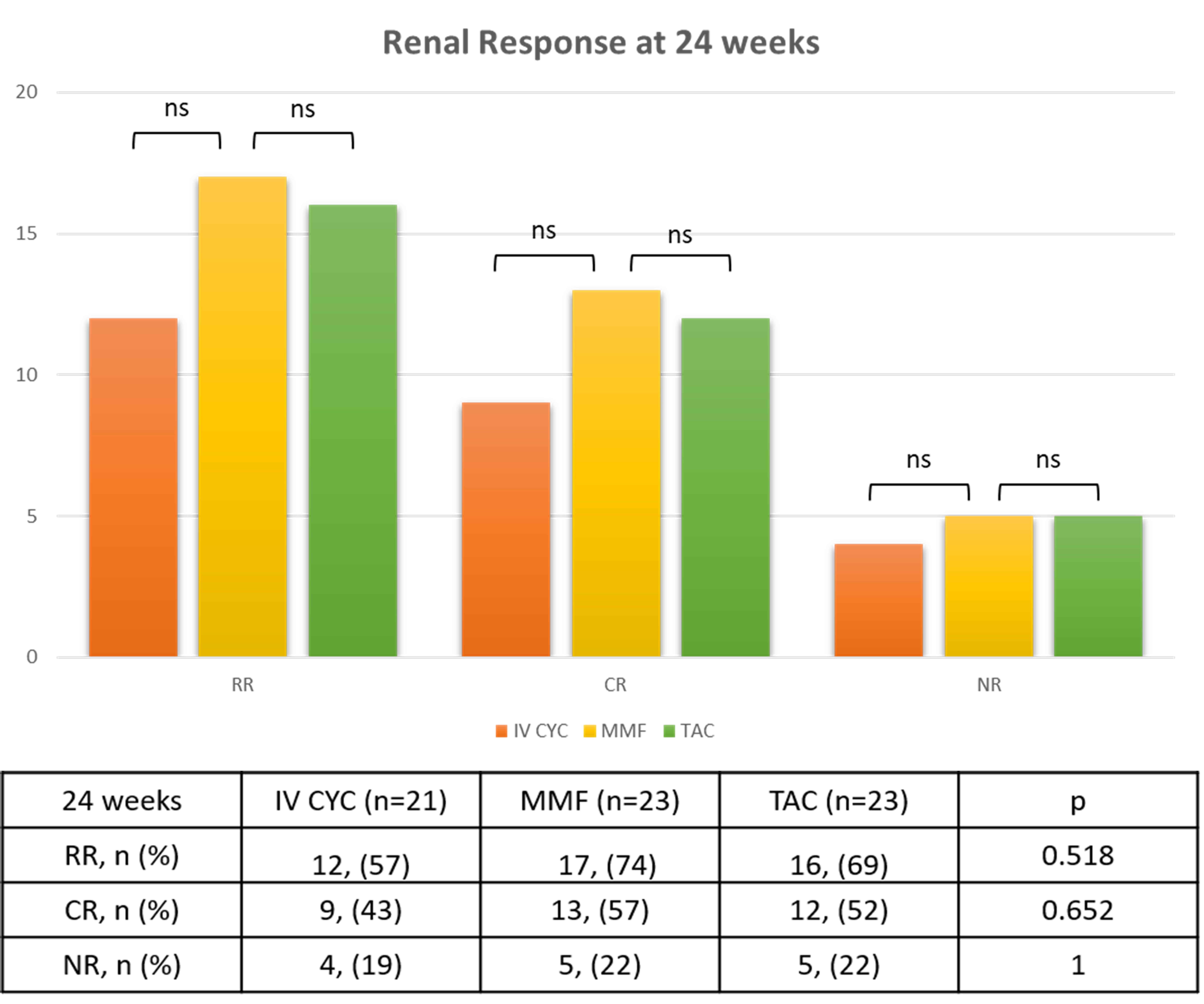
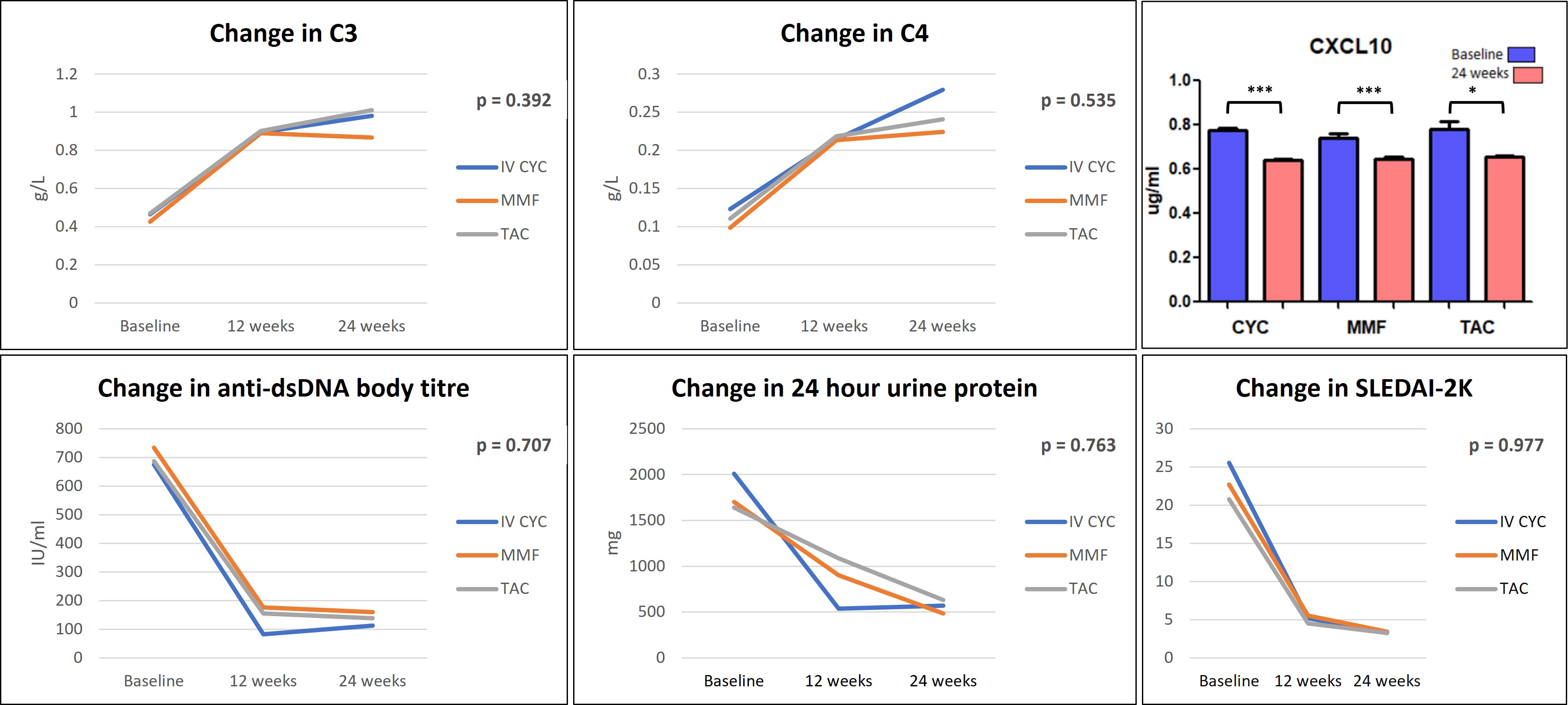
Results: Twenty-eight patients received intravenous CYC whereas MMF and TAC arms included 27 patients each. Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics were comparable among the treatment groups, except for serum creatinine and renal SLEDAI which were significantly higher in CYC group (Table I). Renal response rates (complete or partial) at week 24 were, 57% (12 out of 21 patients) in CYC group, 74% (17 out of 23 patients) in MMF group, and, 69% (16 out of 23 patients) in TAC group (Figure I). There was no significant difference in renal response at 6 months among the treatment groups (p = 0.518). CYC group demonstrated early reduction in 24-hour urine protein. Serum CXCL10 was significantly reduced post-treatment in all three groups (p < 0.05) (Figure II). Four patients died in the CYC group due to serious infections.
Conclusion: The renal response rate at 6 months was comparable among cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, and tacrolimus treatment in lupus nephritis induction therapy, although cyclophosphamide-based regimen was associated with a higher number of deaths due to serious infections.
#Data are expressed as median (interquartile range), *p-value< 0.05 is considered statistically significant
CYC- cyclophosphamide, MMF- mycophenolate mofetil, TAC- tacrolimus, SD- standard deviation, TLC- total leucocyte count, ESR- erythrocyte sedimentation rate, dsDNA- double-stranded deoxy-ribonucleic acid, GFR- glomerular filtration rate, SLEDAI- systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index
Normal values: C3 (0.9 – 1.0) g/dl, C4 (0.2 – 0.4) g/dl, antids-DNA (<100 IU/ml)
RR – Renal response, CR – Complete response, NR – no response
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Amudalapalli A, Shukla A, Maddineni A, Nagar S, Gadde S, BV H, Sahoo R, Patro P. A Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trial Comparing Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Cyclophosphamide, Mycophenolate Mofetil, or Tacrolimus as Induction Therapy in Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-open-label-phase-iii-trial-comparing-efficacy-and-safety-of-intravenous-cyclophosphamide-mycophenolate-mofetil-or-tacrolimus-as-induction-therapy-in-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-open-label-phase-iii-trial-comparing-efficacy-and-safety-of-intravenous-cyclophosphamide-mycophenolate-mofetil-or-tacrolimus-as-induction-therapy-in-lupus-nephritis/