Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2039–2060) Pediatric Rheumatology – Clinical Poster III: Potpourri
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and Crohn’s disease (CD) are now controlled using immunosuppressive medications. However, disease control comes at the risk of increased infection. It remains unclear if immunosuppressed pediatric patients mount a blunted and/or rapidly waning immune response to the Hepatitis A virus (HAV) vaccine. We conducted a randomized controlled pilot trial to compare vaccine immunogenicity to either pediatric or adult doses of HAV seronegative adolescents, aged 12-15 years, receiving immunosuppressive medications for JIA or CD.
Methods: Participants were recruited from the outpatient Rheumatology and Gastroenterology clinics at a single center. Demographics, diagnosis, and current treatments were obtained from health records.19 participants, confirmed to be HAV seronegative, were randomized such that 10 were assigned to receive HAV Pediatric 80 antigen units and 9 HAV 160 antigen units. Serum samples were analyzed using the Elecsys anti-HAV assay.All serum samples were tested at 4-time points; pre-vaccine dose 1 (t1), ~ 28 days post-vaccine dose 1 (t2), pre-vaccine dose 2 (t3) and ~ 28 days post-vaccine dose 2 (t4).Participants were considered seropositive if they achieved a threshold of ≥ 20 IU/L anti-HAV. Descriptive statistics and a Wilcoxon rank test was used to analyze the data.
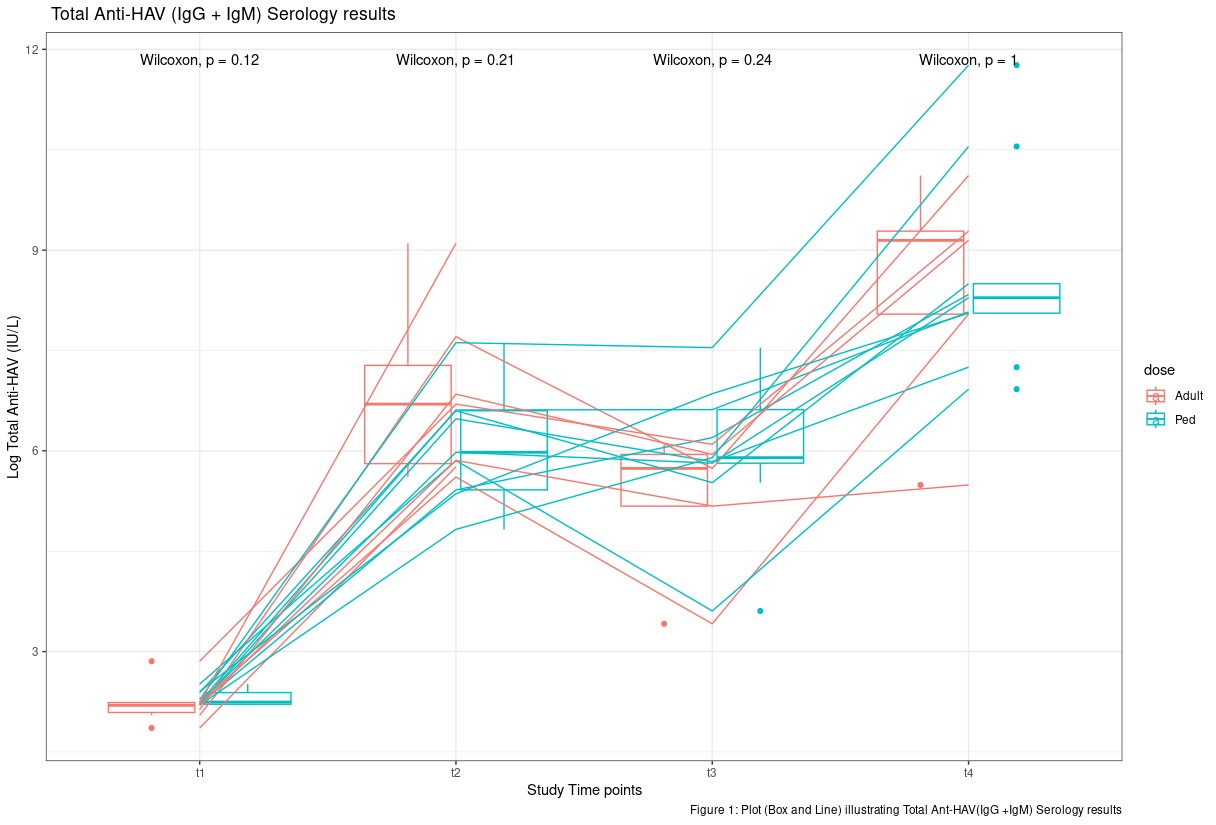
Results: 16/19 participants completed the 2-dose regimen (each dose 6 months apart). 10/6 were female/male; aged 13.32 ± 1.29 years (mean ± SD); diagnosed with CD (3/16) or JIA (13/16). Seven patients were treated with DMARDs and 2 with TNF-alpha Inhibitor monotherapy. Three patients were treated concomitantly with Methotrexate/Sulfasalazine and 4 with methotrexate/TNF-alpha Inhibitors. All participants (16/16) mounted a seropositive response ~ 28 days after vaccine dose 1 (t2) that was maintained at t3 and t4. Figure 1 illustrates individual (lines) median, and interquartile ln transformed values (box plot) for both dose assignments over the study time points. Serological response between participant’s assigned to pediatric vs adult doses were not statistically significant (p < 0.05) at all time points; however, participants receiving the adult vaccine appeared to have a higher median serology value 28 days post-vaccine dose 2. Adverse events were reported by 2/16 participants after the first dose. All adverse events resolved without sequelae. No serious adverse events were reported.
Conclusion: This is the first randomized controlled trial that compares the immunogenicity of pediatric vs. adult doses of HAV vaccine in immunosuppressed pediatric patients. We found no statistical difference in the serological response to Pediatric or Adult vaccine formulations. However, our results support evidence of the immunogenicity of HAV vaccine in immunosuppressed CD and JIA patients. Uniquely, this trial provides a preliminary pragmatic approach that will inform future studies and vaccination guidelines on the comparative benefits of both formulations. Future studies with longer follow up time frame, larger sample sizes and healthy controls will need to be conducted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Githumbi R, Kuhn S, Osiowy C, DeBruyn J, Fritzler M, Johnson N, Vanderkooi O, Schmeling H. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Two Hepatitis a Vaccine Doses Among Adolescents with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Crohn’s Disease on Immunosuppressive Therapy: A Pilot Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-controlled-trial-of-two-hepatitis-a-vaccine-doses-among-adolescents-with-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-and-crohns-disease-on-immunosuppressive-therapy-a-pilot-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-controlled-trial-of-two-hepatitis-a-vaccine-doses-among-adolescents-with-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-and-crohns-disease-on-immunosuppressive-therapy-a-pilot-study/