Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0280–0305) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are characterized by elevated muscle enzymes, including creatine kinase (CK), aldolase, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). While CK is a relatively specific marker of muscle injury, AST and ALT are also indicators of liver damage, complicating interpretation- particularly in patients receiving potentially hepatotoxic medications. Distinguishing muscle-related enzyme elevations from true liver injury remains a key clinical challenge.We aimed to develop a predictive model for estimating liver enzyme levels based on CK values in IIM patients, assisting in the differentiation between muscle-derived enzyme elevations and true hepatotoxicity.
Methods: This study analyzed data from adult participants in the Rituximab in Myositis (RIM) trial, a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with refractory dermatomyositis (DM) or polymyositis (PM). Patients with known liver disease were excluded. Data on CK, AST, and ALT were collected across 11 visits over 44 weeks. Enzyme values were standardized as multiples of the upper limit of normal (xULN). Concurrent medication use, including potentially hepatotoxic agents such as methotrexate, acetaminophen, and NSAIDS, was documented. All enzyme values were incorporated into a repeated measures mixed model as log₁₀-transformed variables to normalize distributions and satisfy model assumptions. Predicted enzyme levels and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) were derived from the model and subsequently back-transformed to xULN to facilitate clinical interpretation.
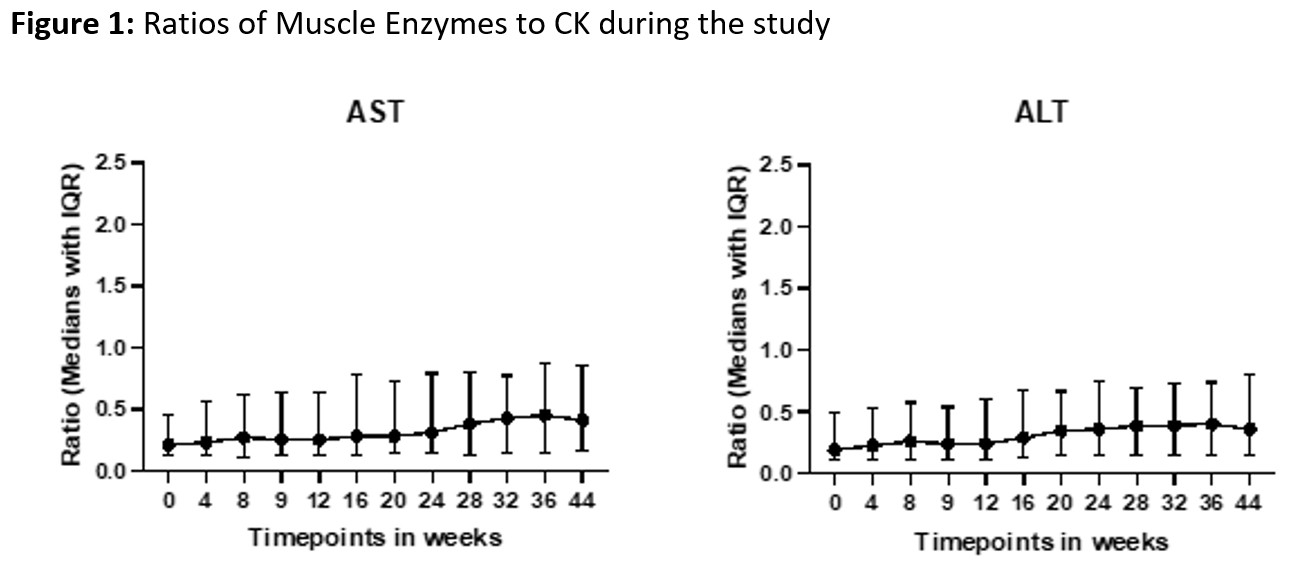
Results: The study included 147 patients (49% DM, 51% PM), with a mean age of 49 ± 11.3 years; 75% were female and 71% were White. Muscle enzyme-to-CK ratios remained stable over time (median range 0.19–0.87), reflecting consistent proportional release (Figure 1). There were no significant differences in CK, AST, ALT, or enzyme-to-CK ratios between patients receiving hepatotoxic medications and those who were not. Similar results were observed in a sub-analysis comparing methotrexate users to non-users (Table 1). ALT and AST levels were predicted from CK using model-derived formulas: ALT = 0.480 × log₁₀(CK) + 0.186 (R² = 0.78) and AST = 0.598 × log₁₀(CK) + 0.204 (R² = 0.82). Expected enzyme levels across CK categories are summarized in Table 2. For example, for CK levels between 2 and 3 times the ULN, the estimated ALT and AST values were 1.0 and 0.96 xULN, respectively. Estimated AST and ALT based on CK levels were similar in DM vs. PM patients.
Conclusion: A CK-based predictive model can allow reliable estimation of AST and ALT in IIM patients, providing a valuable framework for distinguishing muscle-related enzyme elevations from potential liver injury. The use of hepatotoxic medications did not significantly influence liver enzyme levels in this cohort. This model can potentially aid clinicians in interpreting liver enzyme elevations in the context of active muscle disease.
Stability of Muscle Enzyme-to-CK Ratios Over Time in IIM Patients.
Median enzyme-to-CK ratios (AST/CK and ALT/CK) remained consistent throughout the study, supporting proportional enzyme release from muscle.
Comparison of Muscle Enzyme Abnormalities Based on Hepatotoxic Medication Use.
Median values of CK, AST, ALT, and corresponding enzyme-to-CK ratios in patients on hepatotoxic medications versus those not on such medications, including a sub-analysis by methotrexate use. No significant differences were observed between groups.
Model-Predicted AST and ALT Levels Based on CK Values in IIM Patients.
Estimated AST and ALT (in xULN) across CK categories, derived from a predictive model using log₁₀-transformed CK values. Values include means, 95% confidence intervals of the mean, and expected value ranges.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Keret S, Chandra T, Pongtarakulpanit N, Sreerama Reddy K, Wilkerson J, Moghadam-Kia S, Ascherman D, V. Oddis C, Aggarwal R. A Predictive Model for Liver Enzyme Elevations Based on Creatine Kinase in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-predictive-model-for-liver-enzyme-elevations-based-on-creatine-kinase-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-predictive-model-for-liver-enzyme-elevations-based-on-creatine-kinase-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/

.jpg)
.jpg)