Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases II
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Behçet’s disease (BD) is a chronic and recurrent vascular inflammatory disease with major manifestations including oral ulcers, genital ulcers, skin damage and ophthalmitis, and it can also affect the nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, joints, and other vital organs. PDE IV inhibition is an approved therapy for BD. Hemay005 is a novel PDE IV inhibitor for treating chronic inflammatory diseases. Hemay005 significantly inhibits the activation of T lymphocytes, which play a vital role in the pathogenesis of Bechet’s disease. It also inhibits Th1 type pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-12, and IL-23. Improvements in the side effect /efficacy ratio vs Apremilast are anticipated to improve on the efficacy of Apremilast, which was side effect limited at doses >30mg.
Methods: This was a multi-centre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-parallel-controlled, phase II clinical study. The study included four periods: a screening period, a 12-week core treatment period, a 12-week extension treatment period, and an off-drug observation period. All subjects completed the extension treatment period, followed by a 4-week off-drug observation period. It was planned to enrol a total of 252 patients, with randomization at 2:2:1:1 ratio. The study was terminated early as the efficacy objective was achieved after 90 patients were recruited. The Area under the curve (AUC) for the number of oral ulcers in BD patients from baseline to Week 12 was the primary efficacy endpoint. Adverse Events were also recorded as primary safety endpoint.
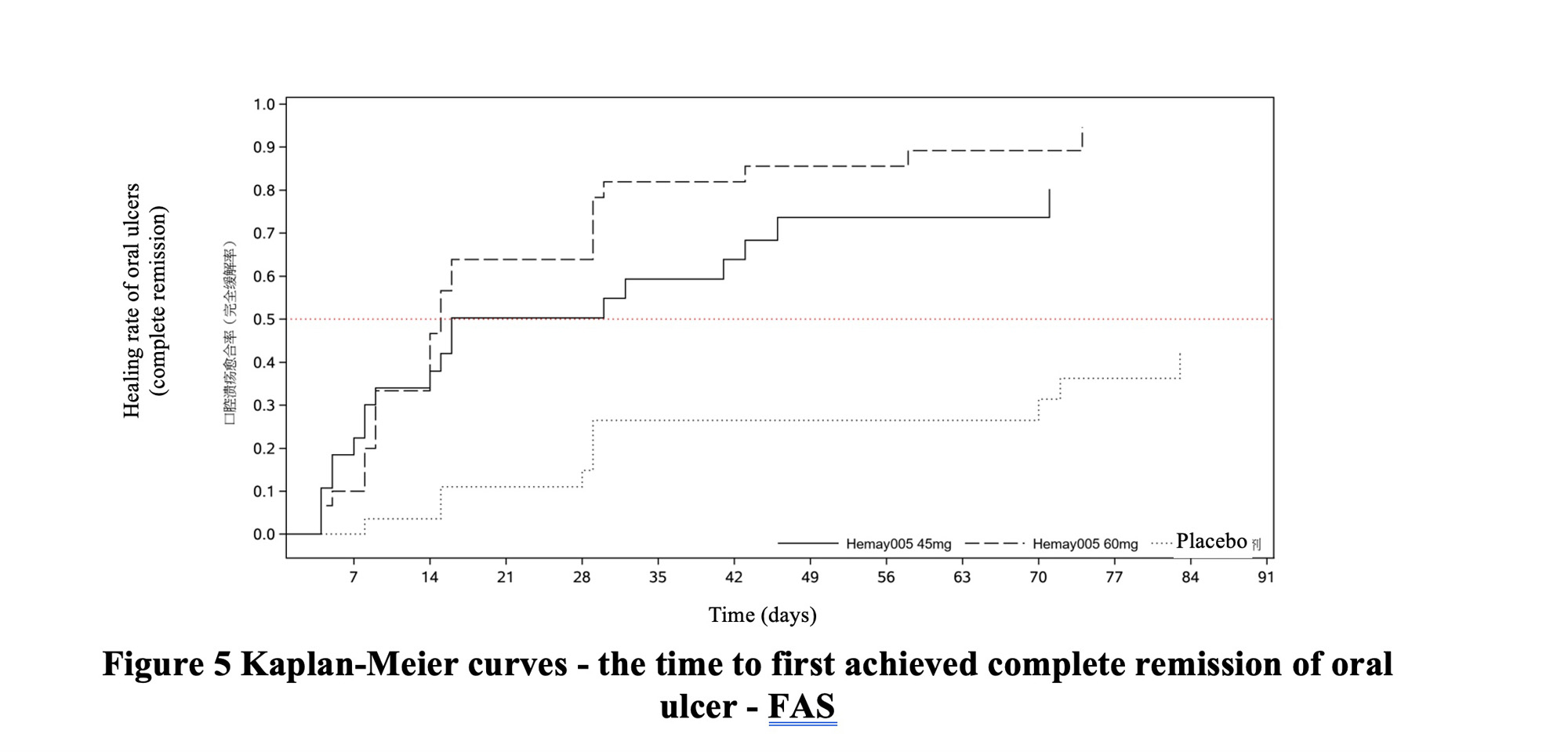
Results: Overall, 90 subjects were recruited; 29 subjects were assigned to Hemay005 tablet 45 mg BID group, 31 to Hemay005 tablet 60 mg BID group, and 30 to placebo group. Results based on the FAS showed that the Hemay005 60 mg BID (1-sided, P <0.0001) and 45 mg BID (1-sided, P <0.0001) were statistically different from placebo in reducing the AUCs for the number of oral ulcers from baseline to Week 12. Analysis of the median healing time of oral ulcer estimated by KM was 16 days in 45 mg BID group, with 95% CI (8, 46); 15 days in 60 mg BID group, with 95% CI (9, 29); and the median healing time could not be estimated by KM method in placebo group Fig 1.
In the safety data set; (patients who received one dose or more of the drug or placebo), the incidence of TEAEs related to the study drug and leading to discontinuation of medication were higher in the 45 mg BID ( 6.9%) and 60 mg BID (6.7%)groups than that in the placebo group (0.0%) during the core treatment period. Most TEAEs reported during the core treatment period were mild; the incidence of severe TEAEs was dose-related, 3.3%, in the 60 mg BID and 0% in the 45 mg BID and placebo groups, respectively. No SAEs related to drug were reported throughout the study.
Conclusion: Hemay005 60 mg BID and 45 mg BID for 12 weeks effectively reduced the AUC for the number of oral ulcers from baseline to Week 12 in BD patients. The study drug was safe and well-tolerated. A phase Ⅲ clinical trial in patients with Bechet’s disease is underway.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jones C, Li Z, Zhang Z, Wu J, Shi G, Zheng W, Tang J, Wang X, Dai L, Chen L, Li Y, Wu L, Wang Y, Liu S, Ke Y, Lin J, Zhang Z, Hu J, Dang W, Yin S, Tang X, Zhu M, Lin J, Jones R, Wan W, Hu x. A Phase II Clinical Study to Investigate the Efficacy and Safety of Hemay005 Tablets in Patients with Active Behçet`sDisease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-ii-clinical-study-to-investigate-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-hemay005-tablets-in-patients-with-active-behcetsdisease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-ii-clinical-study-to-investigate-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-hemay005-tablets-in-patients-with-active-behcetsdisease/