Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster IV
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Dazodalibep (DAZ), a non-antibody biologic antagonist of CD40L, led to higher/durable response rates vs. placebo (PBO) in a double-blind, Phase 1b trial of patients (pts) with active RA (1). We continued assessment of DAZ in a Phase 2 study of safety, efficacy, and response duration of 4 dosing regimens of DAZ in pts with RA.
Methods: This double-blind study (NCT04163991) included adult pts with active moderate-severe RA (DAS28-CRP > 3.2, ≥ 4 tender and ≥ 4 swollen joints), positive for serum RF and/or ACPA with inadequate response to MTX, conventional/biological DMARDs or anti-TNFα, with no prior treatment with B-cell depleting agents. Pts were randomized equally to 5 cohorts to receive 4 infusions of DAZ or PBO (in 2, 3 and 4, PBO was given on dosing days when DAZ was not administered):
1: DAZ 1500 mg IV Q2Wx3, last dose 4W after
2: DAZ 1500 mg IV Q8Wx2
3: DAZ 3000 mg IV Q8Wx2
4: DAZ 3000 mg IVx1
5: PBO IV Q2Wx3, last dose 4W after
The primary endpoint (EP) was the change from baseline (BL) in DAS28-CRP at Day (d) 113. Secondary EPs included proportion with clinical remission (CR) by DAS28-CRP < 2.6 at d113, time-to-rescue medication, change from BL in RF/ACPAs at d113, treatment-emergent adverse events (AE), serious AE (SAE) and AE of special interest (AESI). Pts were followed until d309.
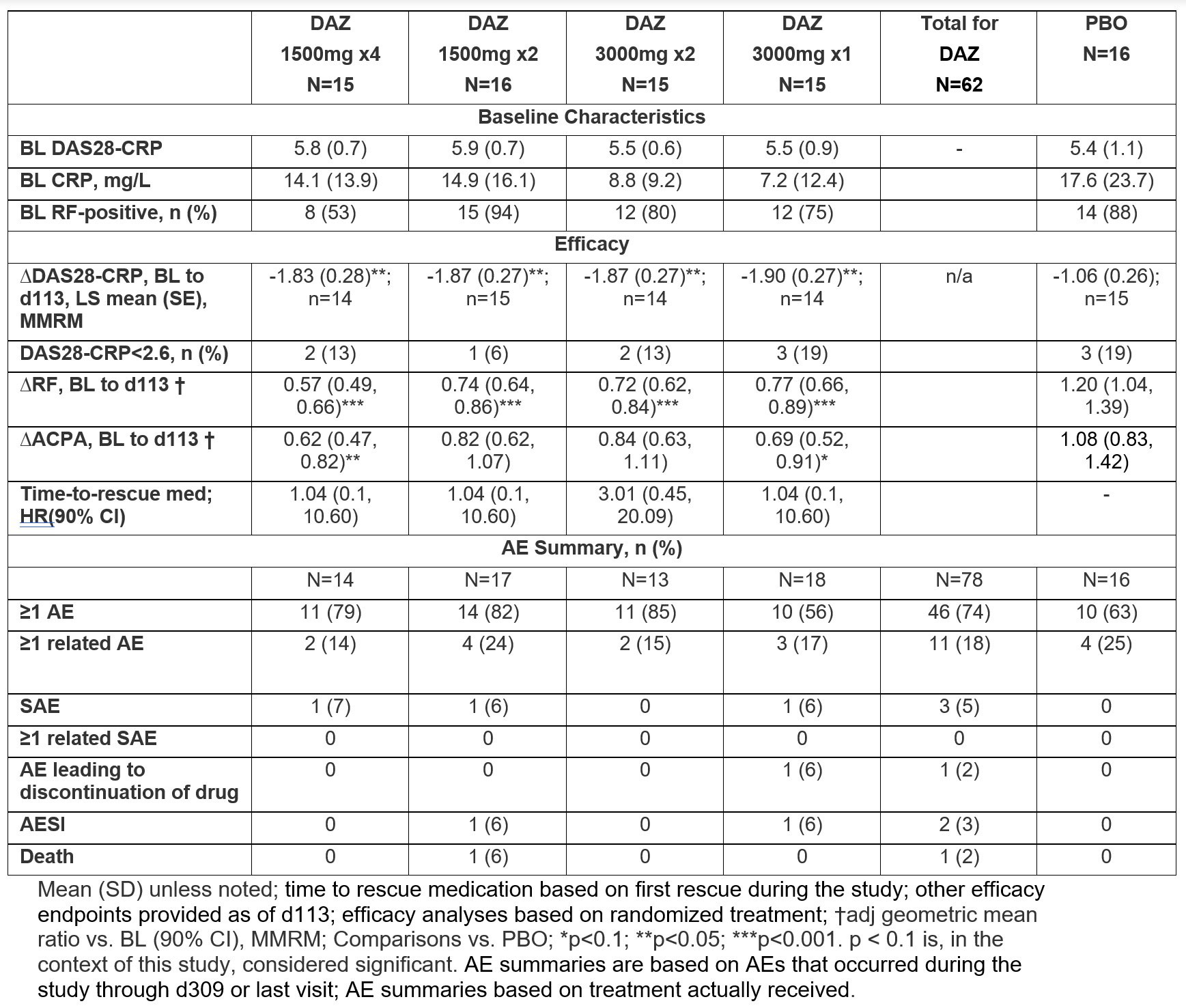
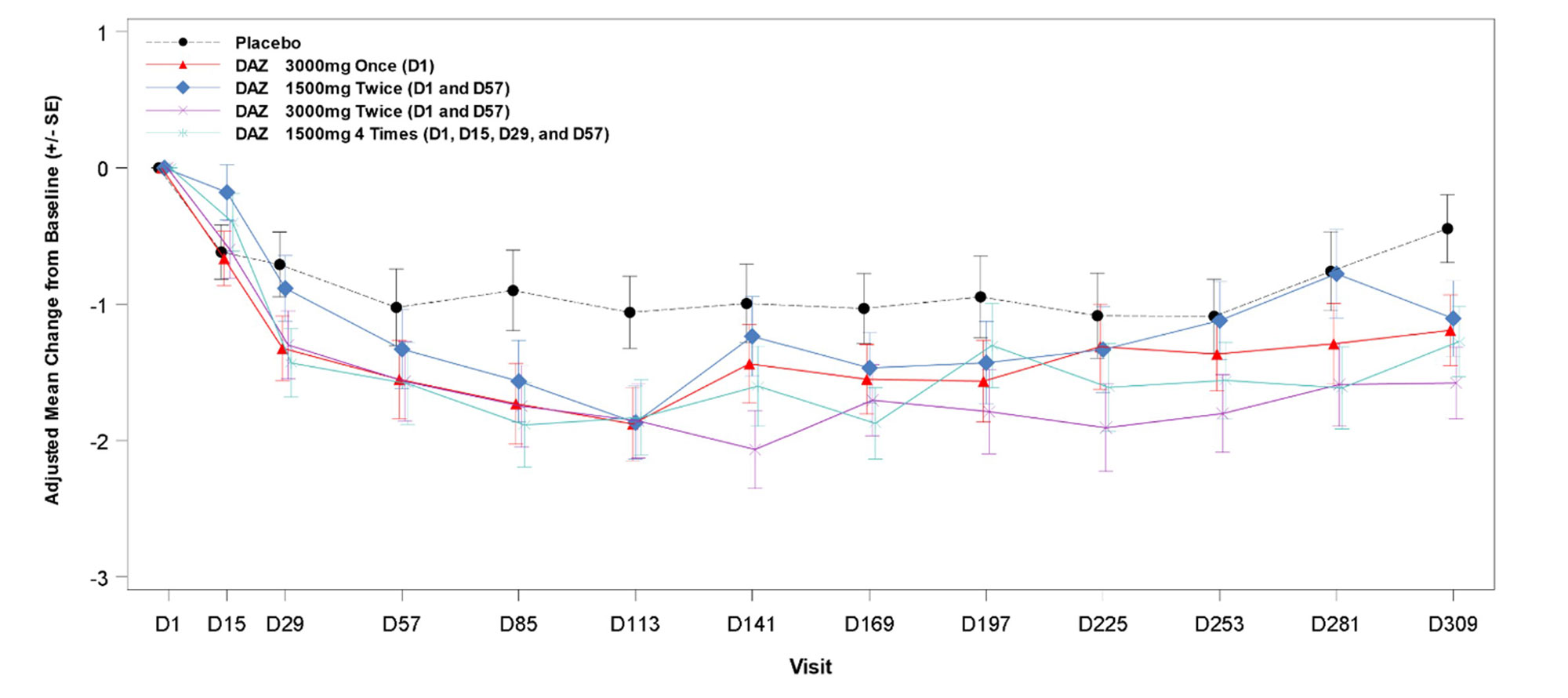
Results: A total of 78 pts were randomized and received study medication, with 73 (94%) having completed treatment and 65 (83%) having completed the study follow-up to d309. At BL, the mean (SD) age was 56 (13) yrs, and 80% were female. Demographics/disease characteristics were generally similar across arms, except for RF+ proportion and mean CRP. Significant reductions in DAS28-CRP were observed at all doses of active drug at d113 vs. PBO (table). Significant reductions were also observed at all doses at d309; in cohort 3, significant reduction was observed at all post-dose timepoints after d113 (figure). RF levels decreased significantly vs. PBO starting d57 to d113 (p≤0.0035) for all doses. There was a similar trend with ACPA levels that was significant in cohorts 1 and 4. DAS28-CRP CR rates were low and similar in all groups, but fewer DAZ pts had high disease activity (DAS28-CRP >5.1) at d113. Few patients received rescue medication (none before d113), and time-to-rescue medication did not differ between DAZ and PBO.
The % of pts with ≥1AE was higher with DAZ vs. PBO (74% vs. 63%). There were 4 SAEs in 3 pts in DAZ groups vs. 0 in PBO: 1 nephrolithiasis, 1 COVID-19 infection, and 1 pt hospitalized for COVID-19 who died from unknown cause 2d after discharge (232d after last dose); all SAEs were deemed by investigators to be unrelated to study drug. In total, 11/62 (18%) vs. 4/16 (25%) pts had ≥1AE deemed related to DAZ and PBO, respectively.
Conclusion: DAZ reduced DAS28-CRP and RF significantly vs. PBO at d113 in all dose regimens. Safety and tolerability were consistent with previous observations. Treatment effects at d113 and the prolonged duration of responses support the possibility of long dosing intervals.
References:
1. Karnell JL, Albulescu M, Drabic S, Wang L, Moate R, Baca M, et al. A CD40L-targeting protein reduces autoantibodies and improves disease activity in patients with autoimmunity. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(489).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kivitz A, Wang L, Alevizos I, Gunsior M, Falloon J, Illei G. A Phase 2, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Mechanistic Insight and Dosage Optimization Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Dazodalibep (VIB4920/HZN4920) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Having Inadequate Response to Conventional/Biological DMARDs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-2-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-mechanistic-insight-and-dosage-optimization-study-of-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-dazodalibep-vib4920-hzn4920-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthr/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-2-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-mechanistic-insight-and-dosage-optimization-study-of-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-dazodalibep-vib4920-hzn4920-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthr/