Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: CT-P17 is a recombinant human monoclonal antibody that was developed as the first biosimilar adalimumab with high concentration (100 mg/mL) and citrate-free formulation. The purpose of this study was to compare the pharmacokinetics (PK), safety, and immunogenicity of the CT-P17 auto-injector (AI) and CT-P17 pre-filled syringe (PFS) after a single subcutaneous (SC) injection of 40 mg (100 mg/mL) in healthy subjects.
Methods: Healthy subjects aged 18 to 55 years (N=193) were randomized in 1:1 (98 subjects in the CT-P17 AI and 95 subjects in the CT-P17 PFS treatment groups) to receive 40 mg of either CT-P17 by AI or PFS. The primary objective of this study was to demonstrate PK similarity in terms of area under the serum concentration-time curve (AUC) from time zero to infinity (AUC0-inf), AUC from time zero to the last quantifiable concentration (AUC0-last), and maximum serum concentration (Cmax) of CT-P17 via AI versus CT-P17 via PFS in healthy subjects. Secondary objectives were to evaluate additional PK parameters, safety and immunogenicity.
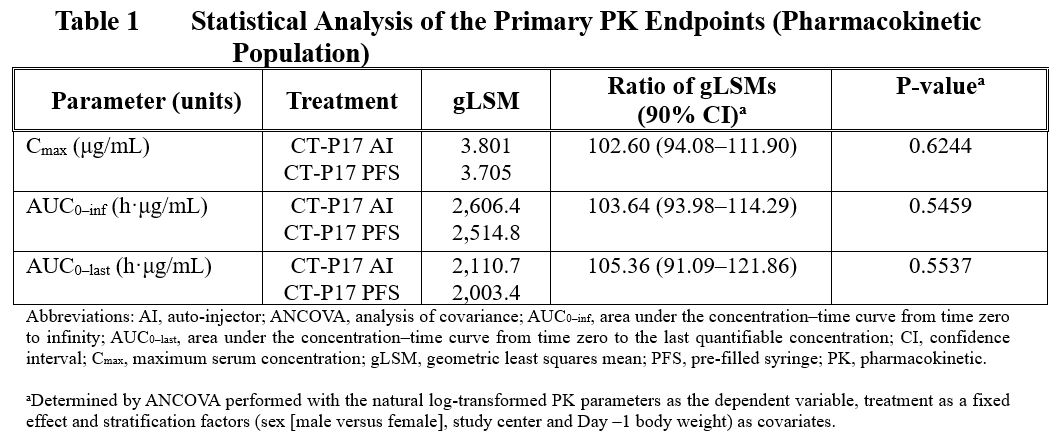
Results: Demographics and baseline characteristics were similar between the 2 treatment groups. Following a single SC administration of CT-P17 via AI in healthy subjects, mean peak and total systemic exposure (Cmax, AUC0-inf, and AUC0-last) were equivalent with those of CT-P17 via PFS, since the 90% CIs of the geometric least squares mean ratios were within the predefined equivalence margin of 80% to 125% (Table 1). Median Tmax occurred at 132 hours for both treatment groups. Means of secondary PK parameters (t1/2, λz, CL/F, Vz/F and %AUCextrap) were also comparable between the treatment groups.
Mean serum CT-P17 concentrations observed through 71 days post-dose were comparable between the treatment groups (Figure 1).
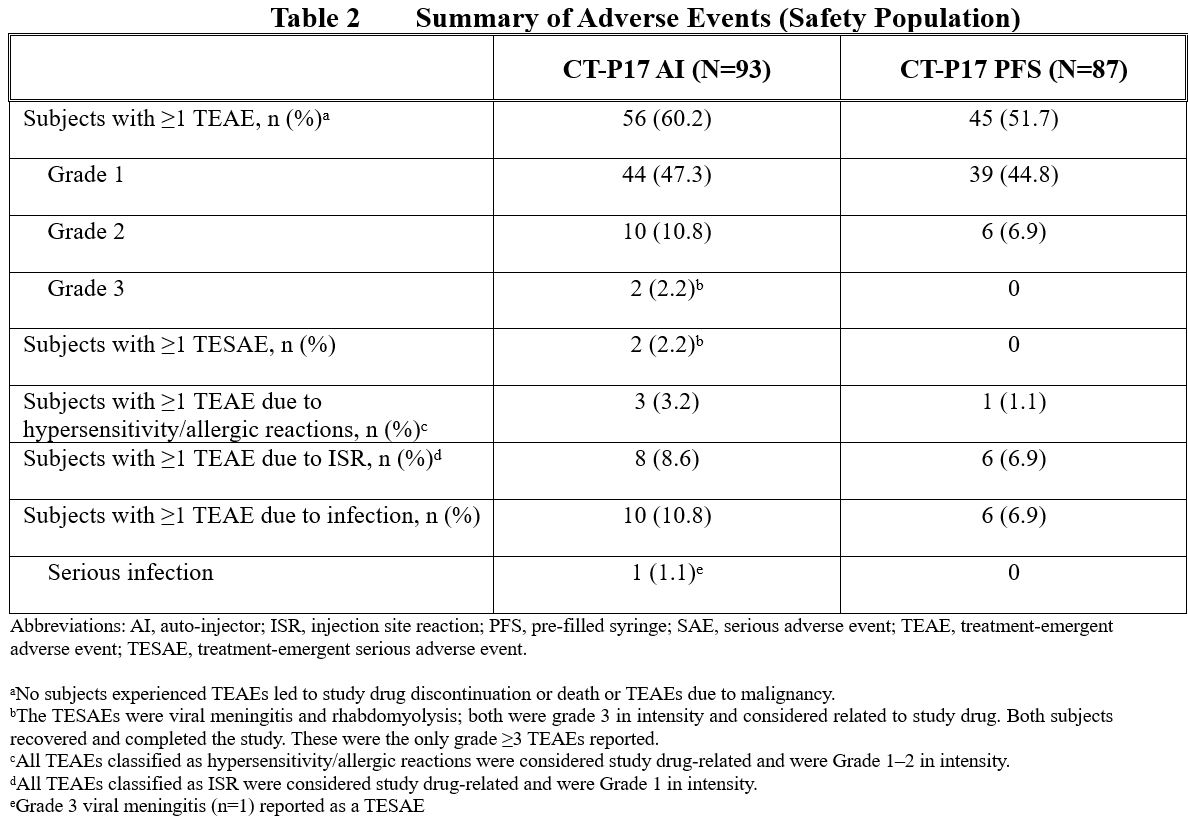
Overall, 56 (60.2%) and 45 (51.7%) subjects reported ≥1 treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) in the CT-P17 AI and CT-P17 PFS treatment groups, respectively (Table 2). TEAEs considered to be related to study drug were reported by 47 (50.5%) and 38 (43.7%) subjects, respectively. The most frequently reported TEAEs were headache (11 [11.8%] and 8 [9.2%] subjects) and injection site reactions (8 [8.6%] and 6 [6.9%] subjects) in the CT-P17 AI and CT-P17 PFS treatment groups, respectively).
Overall, 91 (97.8%) and 85 (97.7%) subjects in the CT-P17 AI and CT-P17 PFS treatment groups, respectively, had ≥1 positive result post-treatment for anti-drug antibodies (ADA) and 81 (87.1%) and 75 (86.2%) subjects, respectively, had ≥1 positive result post-treatment for neutralizing ADA. ADA titers were similar between the treatment groups. In both treatment groups, higher ADA titers were significantly associated with decreased AUC0-inf and AUC0-last (Fisher’s z transformation; p-value <0.0001). Cmax did not correlate significantly with ADA titer.
Conclusion: Mean peak and total exposure were equivalent following administration of high concentration formulation CT-P17 via AI or PFS. Secondary PK parameters and safety, including immunogenicity, were also comparable between the two delivery methods.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Keystone E, Furst* D, Kay J, Choi E, Davidson A, Bae Y, Brimhall D, Lee S, Kim S, Kwak D. A Phase 1, Randomized, Open-label, Parallel Group, Single-dose Study to Compare the Pharmacokinetics and Safety of the Auto-injector and Pre-filled Syringe of CT-P17, a Proposed, Higher Concentration Biosimilar (100 mg/mL) Adalimumab, in Healthy Subjects [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-1-randomized-open-label-parallel-group-single-dose-study-to-compare-the-pharmacokinetics-and-safety-of-the-auto-injector-and-pre-filled-syringe-of-ct-p17-a-proposed-higher-concentration/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-1-randomized-open-label-parallel-group-single-dose-study-to-compare-the-pharmacokinetics-and-safety-of-the-auto-injector-and-pre-filled-syringe-of-ct-p17-a-proposed-higher-concentration/