Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: AMG 329 (formerly HZN-1116), a human monoclonal antibody (mAb), binds to soluble and membrane-bound human feline McDonough sarcoma (FMS)-like tyrosine kinase 3 receptor ligand (FLT3L). FLT3L is a hematopoietic cytokine that plays a major role in driving the expansion and survival of conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) and plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), as well as monocytes. This was a first-in-human, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled phase 1 study to evaluate the safety, pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of single and multiple ascending doses of AMG 329 in participants (pts) with cDC- and pDC-mediated rheumatic diseases.
Methods: Pts with stable rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, or Sjögren’s while receiving standard-of-care (SOC) therapy were randomized sequentially to receive a single ascending dose (SAD) or multiple ascending doses (MAD) of AMG 329. AMG 329 doses ranged from a low dose predicted to have a moderate PD effect to a high dose with sufficient safety margin based on model simulation using nonclinical PD and toxicology studies. In the SAD study, pts were enrolled into five cohorts to receive a single dose of AMG 329 or PBO administered subcutaneously (SC), with an additional cohort with AMG 329 or PBO given intravenously. In the MAD study, pts were enrolled into three (low-, mid- and high) ascending dose cohorts to receive multiple SC doses of AMG 329 or PBO. Pts were followed for a minimum of 4 –12 weeks after receiving the final dose with additional follow-up required until repletion of pDC counts. Blood samples were collected for the evaluation of AMG 329 PK and pDC, cDC and monocyte levels. Safety was monitored throughout the study.
Results: A total of 73 pts were randomized: 48 pts in the SAD study (PBO: N=12; AMG 329 groups: N=36 [6/group]), and 25 pts in the MAD study (PBO: N=7; AMG 329 groups: N=18 [6/group]. A total of 35 (72.9%) and 19 (76.0%) pts reported ≥1 adverse event (AE) in the SAD and MAD studies, respectively. The frequency of AEs was balanced between AMG 329 and PBO groups with most being mild/moderate in severity. There were no deaths and no AEs leading to discontinuation.
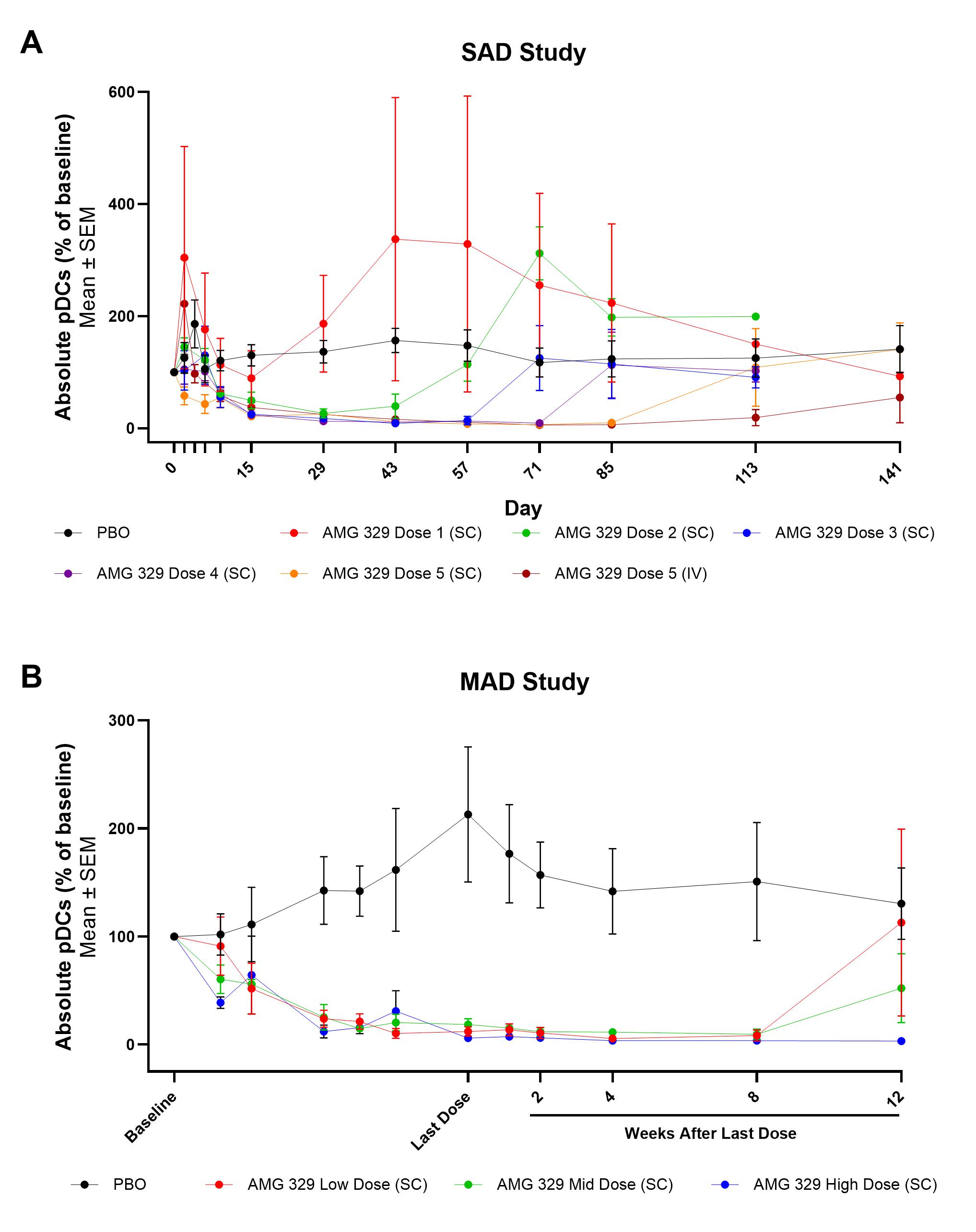
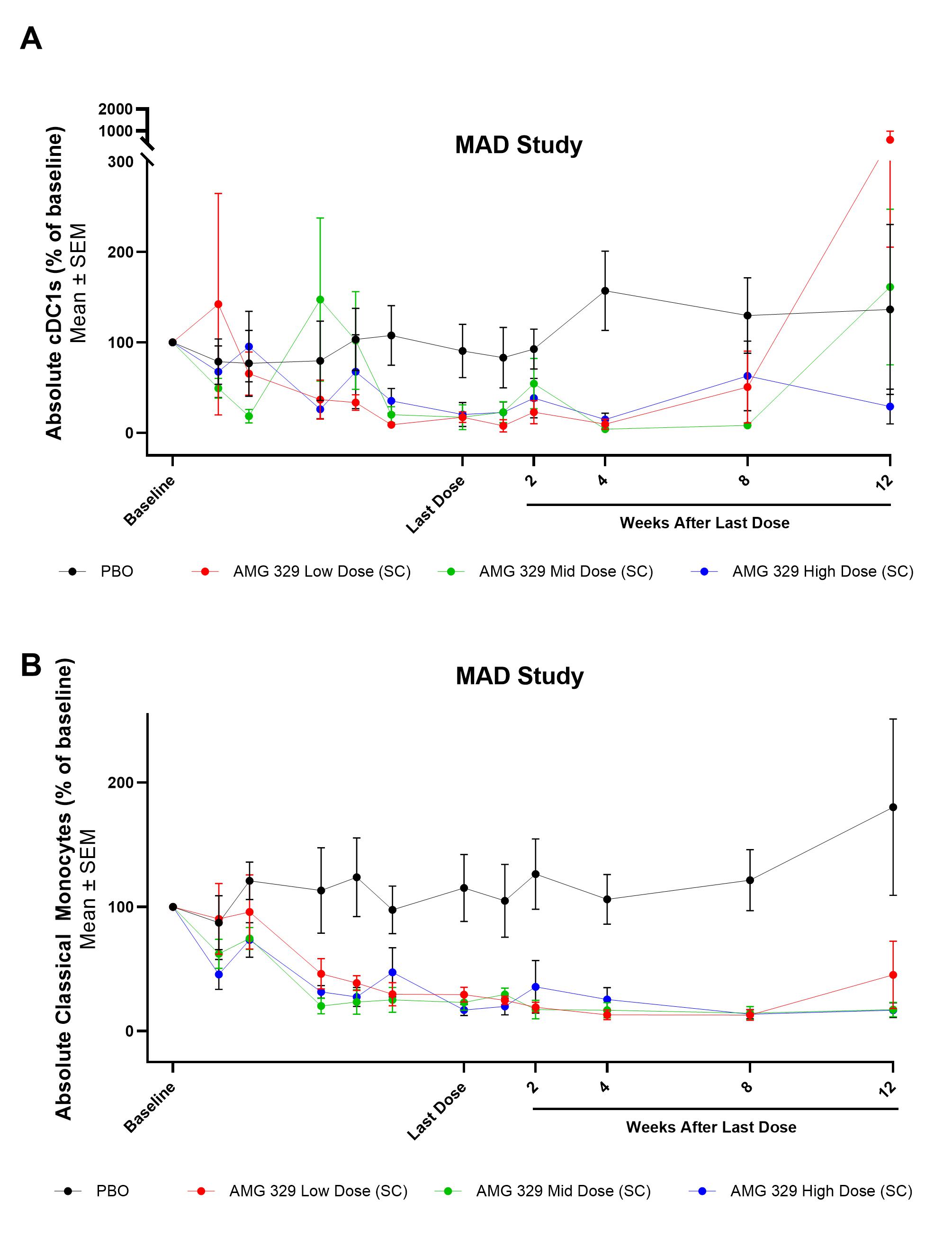
In both studies, exposures of AMG 329 increased approximately in a dose-proportional manner with increasing dose levels. The terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) values were similar in SAD and MAD studies and ranged from 17–27 days across dose levels, within the range of a typical mAb. Rapid reductions in pDCs, cDCs and monocytes were observed for pts in both the SAD and MAD studies receiving AMG 329. In the MAD study, reductions in pDC levels were evident by Day 9 and reduced by >80% for all groups receiving the last dose of AMG 329; pDC levels returned to near baseline levels during the follow-up period.
Conclusion: When added to SOC therapy, AMG 329 had an acceptable safety profile in adult pts with stable cDC- and pDC-mediated rheumatic diseases. The PK profile of AMG 329 is consistent with a typical mAb. Reductions in pDCs, cDCs and monocytes were observed that lasted up to 12 weeks following the highest dose in the MAD cohort. These data support further clinical investigation of AMG 329 in patients with autoimmune diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kivitz A, Cohen S, Lau-Kilby A, Sun Y, Huang J, Jana A, Kim S, Wu Y, Yang Q, Zhao L. A Phase 1, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Single and Multiple Ascending Doses of AMG 329, a Monoclonal Antibody, in Conventional and Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell-Mediated Rheumatic Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-1-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study-to-evaluate-the-safety-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-single-and-multiple-ascending-doses-of-amg-329-a-monoclonal-antibody-in/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-1-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study-to-evaluate-the-safety-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-single-and-multiple-ascending-doses-of-amg-329-a-monoclonal-antibody-in/