Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), frequently continue to suffer from morning symptoms despite treatment with conventional therapies 1,2. Routine morning administration of tofacitinib results in peak drug concentrations several hours after peak cytokine release and disease symptoms. A product designed to be taken at bedtime and exhibiting a delayed and extended release profile that releases tofacitinib late in the night providing maximum tofacitinib concentrations in the early morning hours, could provide an enhanced opportunity to address morning symptoms.
T19 is a novel, three-dimensionally (3D) printed tablet being developed for delayed- and extended- release (DR/ER) of tofacitinib and engineered to provide peak tofacitinib concentrations concurrent with the circadian rhythm of early morning endogenous cytokine release and disease symptoms.
Methods: T19 was manufactured by a 3D printing technology called “Melt Extrusion Deposition” (MEDÒ). A total of 24 participants were enrolled in the Phase I, randomized, open-label, single-dose, three-period, three-sequence crossover study to compare the pharmacokinetics (PK) between T19 and the reference listed drug (LD, Xeljanz XRÒ). Participants were randomized 1:1:1 to receive two formulations of T19 (Z001101 & Z001091; designed to provide differing degrees of delayed release) or LD in the three sequences. T19 was administered orally at bedtime (approximately 22:00) following a standard dinner at approximately 18:00.
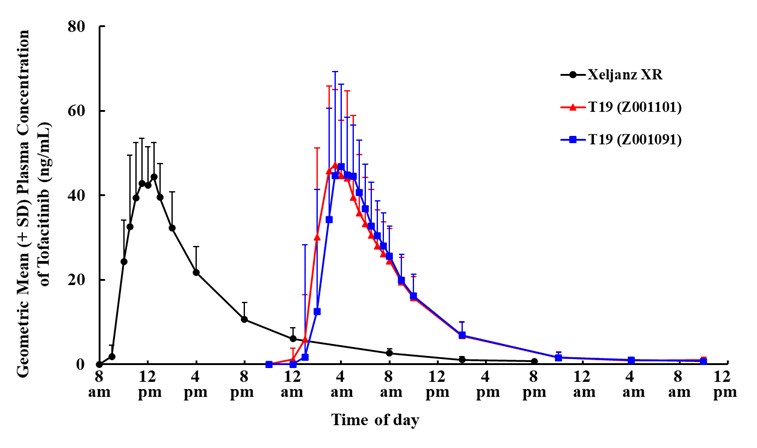
Results: Following administration of T19 and Xeljanz XRÒ, both formulations of T19 exhibited a delayed time of maximum plasma concentration (Tmax), as expected. Under fasting conditions, the median Tmax was 5.5-6.0 h with a range of 3.0-10.0 h for T19, whereas the median Tmax was 4.5 h (2.5-5.0 h) for the LD. The Tmax of the T19 formulations were significantly different as compared to the LD (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, p < 0.001).
A statistical analysis of relative bioavailability between the formulations demonstrated that the exposure of T19 was similar to that of LD. The area under the concentration-time curve (AUCinf) and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of T19 were within the desired bioequivalence range (80% to 125%) relative to LD. The ratio (T19/LD) and 90% confidence intervals of adjusted geometric means for AUCinf and Cmax were 105.46 (102.03, 109.38) and 116.95 (104.92, 130.35) for Z001101, and 104.04 (100.81, 107.38) and 130.89 (113.49, 150.95) for Z001091, respectively. Geometric mean concentration-time profiles of T19 and LD after single-dose administration are shown in Figure 1.
Conclusion: The PK results demonstrate that T19 achieved the desired product design properties of delayed- and extended-release, as exhibited by the pharmacokinetic profiles and providing peak plasma concentrations in the early morning hours when morning symptoms are most present. The bioequivalence of exposure (AUC) and Cmax observed suggests a potential pharmacokinetic bridge to Xeljanz XRÒ, providing a basis for a 505(b)(2) application for the indications similar to the LD, XeljanzÒ and a potential therapeutic option for the patients with morning symptoms.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhou Y, Ji M, wang l, Deng F, Cheng S, Li X, Zhang Y. A Novel Oral 3D-Printed Delayed- and Extended-Release Tofacitinib (T19) for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Related Inflammatory Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-novel-oral-3d-printed-delayed-and-extended-release-tofacitinib-t19-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-related-inflammatory-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-novel-oral-3d-printed-delayed-and-extended-release-tofacitinib-t19-for-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-related-inflammatory-diseases/