Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Biomarkers, & Systemic Inflammation (1223–1256)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (BARI) is a JAK1/2 inhibitor approved for the treatment of adults with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and the treatment of adult atopic dermatitis in Europe and Japan. RA-BE-REAL is a 3-year, prospective, observational study of adult RA patients (pts) evaluating adherence to treatment in clinical practice.
The purpose of this abstract is to report the proportion of European pts with RA that discontinue treatment following 3- and 6-months (M) of either BARI, biologic (b)DMARDs or any other targeted synthetic (ts)DMARDs (b/ tsDMARDs) after starting that treatment for the first time. To report the percentage of pts achieving remission and low disease activity (LDA) based on Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) at 6M. To assess changes from baseline in CDAI and to describe changes in patient reported outcomes (PROs) related to quality of life, pain, and physical functioning at 6M.
Methods: The primary endpoint is the discontinuation rate of initial RA treatment for all causes (excluding sustained clinical response) over a 24M period. Two pt cohorts are assessed: cohort A, started treatment with BARI (2mg or 4mg), and cohort B, any biologic or any other tsDMARD (Fig. 1). Treatment initiation and changes are at the discretion of the pt or physician. In this interim analysis we report descriptive baseline, 3M and 6M data.
Results: Between October 2018 and March 2020, 1074 adult RA pts were enrolled from France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and UK. At time of enrollment 50.9% of pts in cohort A and 31.2% of pts in cohort B commenced treatment as a monotherapy (Table 1). A similar proportion of pts in cohort A (52/392 pts; 13.3%) and cohort B (59/425; 13.9%) discontinued treatment at 3M. At 6M pts in cohort A (63/336; 18.8%) were less likely to have discontinued their initial RA treatment than pts in cohort B (93/370; 25.1%) (Fig.2A). At 6M a higher percentage of cohort A pts had achieved CDAI remission (cohort A; 25.6%, cohort B; 18.5%) (Fig.2B). Pts in cohort A experienced a greater decrease in disease activity as assessed by CDAI with a mean reduction in disease activity scores of -13.9 (-11.8 for pts in cohort B) (Table 2). With respect to PROs, a similar improvement from baseline in HAQ-DI, pain (VAS), and EQ-5D-5L scores was observed for both cohorts (Table 2).
| Cohort A Baricitinib (n=509) |
Cohort B b/tsDMARDs (n=565) |
|
| Concomitant use of csDMARDs n (%) | ||
| with any csDMARD | 250 (49.1) | 389 (68.8) |
| as a monotherapy | 259 (50.9) | 176 (31.2) |
| Age in years (SD) | 59.1 (13.2) | 57.0 (13.9) |
| Disease duration in years (SD) | 10.0 (9.1) | 8.9 (9.6) |
| Oral GCCs at time of enrollment n (%) | ||
| Yes | 218 (42.8) | 249 (44.1) |
| No | 291 (57.2) | 316 (55.9) |
| b/tsDMARDs treatment any time before enrollment n (%) | ||
| Naive | 245 (48.1) | 344 (60.9) |
| 1 b/tsDMARD | 67 (13.2) | 57 (10.1) |
| 2 b/tsDMARDs | 110 (21.6) | 79 (14.0) |
| >2 b/tsDMARDs | 87 (17.1) | 85 (15.0) |
| Footnote: Data presented side-by-side for descriptive purposes only. csDMARD; conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, GCCs; glucocorticoids, SD; standard deviation | ||
Conclusion: Overall, these observational study results highlight that pts receiving baricitinib are less likely to discontinue treatment and more likely to achieve remission than pts receiving a biologic or any other tsDMARDs.
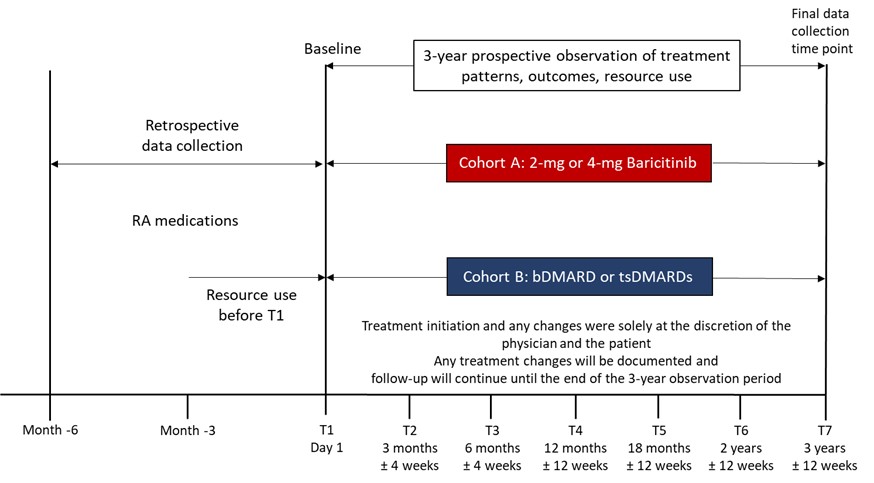 Study Design. Participants entered cohort A or B based on their treatment decision for BARI or another b/tsDMARD, pts in each cohort were with/without concomitant csDMARDs.
Study Design. Participants entered cohort A or B based on their treatment decision for BARI or another b/tsDMARD, pts in each cohort were with/without concomitant csDMARDs.
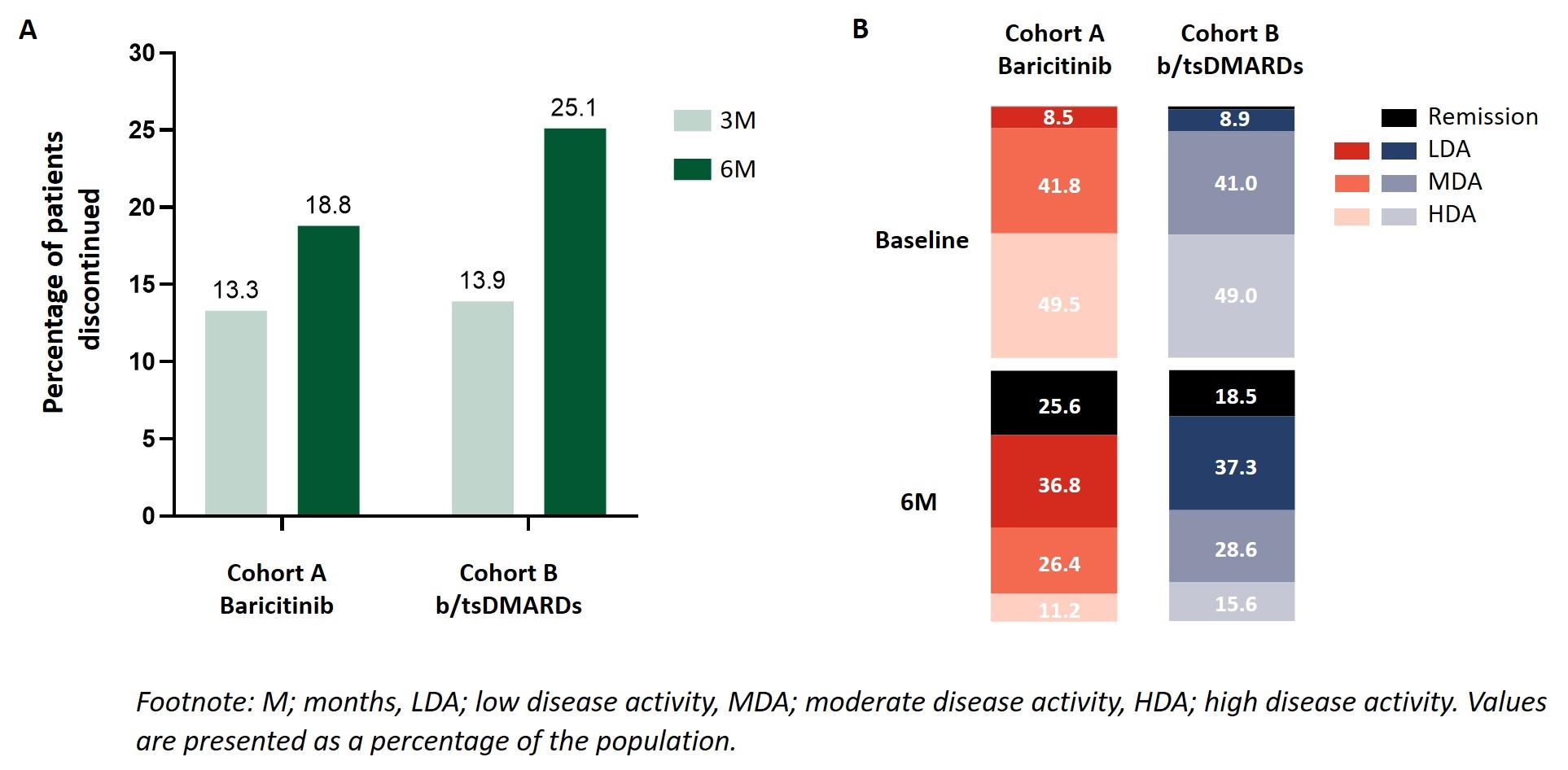 A. Percentage of pts that discontinued initial RA treatment at 3M and 6M, B. Percentage of pts in cohort A and cohort B achieving remission and LDA status at 6M.
A. Percentage of pts that discontinued initial RA treatment at 3M and 6M, B. Percentage of pts in cohort A and cohort B achieving remission and LDA status at 6M.
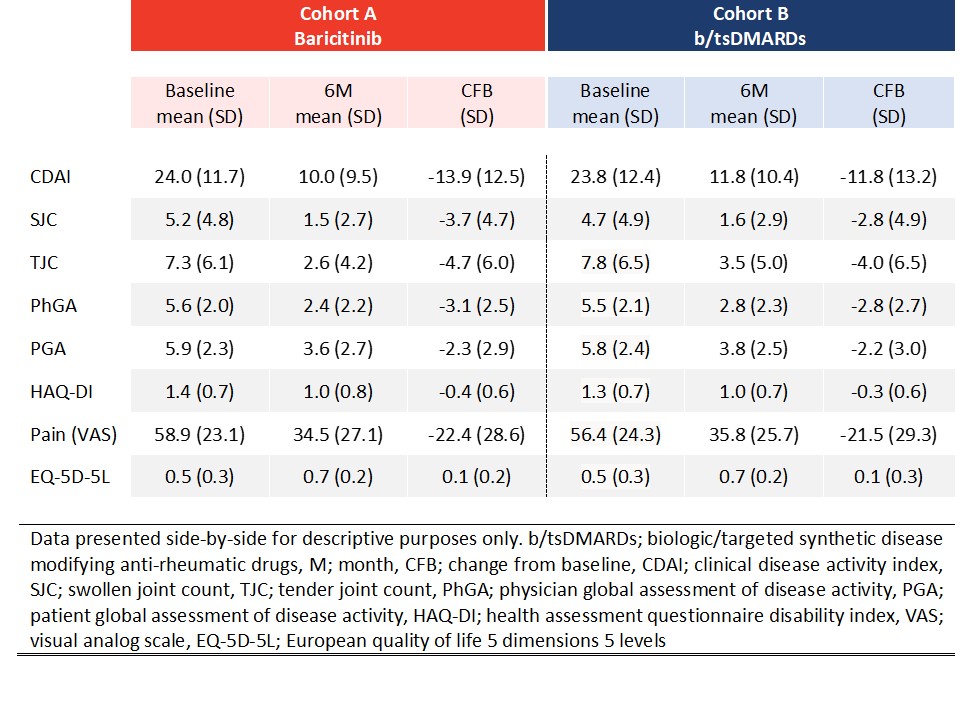 Observed means (baseline, 6M) and change from baseline in clinical characteristics for pts enrolled in RA-BE-REAL.
Observed means (baseline, 6M) and change from baseline in clinical characteristics for pts enrolled in RA-BE-REAL.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Burmester G, Fautrel B, Alten R, Matucci-Cerinic M, Salmon J, Holzkaemper T, de la Torre I, Lopez-Romero P, Fakhouri W, Gentzel-Jorczyk A. A Multinational, Prospective, Observational Study in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving Baricitinib, Targeted Synthetic or Biologic Disease-Modifying Therapies: 6-Month Effectiveness and Patient Reported Outcome Data from the European Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multinational-prospective-observational-study-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-baricitinib-targeted-synthetic-or-biologic-disease-modifying-therapies-6-month-effectiveness-and-pat/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multinational-prospective-observational-study-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-baricitinib-targeted-synthetic-or-biologic-disease-modifying-therapies-6-month-effectiveness-and-pat/
