Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Consistent, though limited, published data suggests that methotrexate (MTX) improves treatment response in patients treated with pegloticase for uncontrolled (refractory) gout. Recent case series1-3 (25 patients total) showed an 80%-100% response rate in patients co-treated with MTX and pegloticase, versus the 42% response rate reported in clinical trials with pegloticase monotherapy. The current clinical trial prospectively examined efficacy and safety of pegloticase in patients with uncontrolled gout who were co-treated with oral MTX.
Methods: This study included adult patients from 6 sites. Uncontrolled gout was defined as serum uric acid (sUA) ≥6 mg/dL with ≥1 of the following: sUA ≥6 mg/dL despite oral urate lowering therapy (ULT), intolerance to ULT, or functionally limiting tophaceous deposits. Key exclusion criteria included immunocompromised status, G6PD deficiency, severe renal impairment, and MTX contraindication. Oral MTX (15 mg/wk) and folic acid (1 mg/day) were initiated 4 wks prior to the first pegloticase infusion and were continued during pegloticase therapy (8 mg every 2 wks). The protocol originally consisted of 24 wks of co-therapy, but was amended to extend to 52 wks. Primary outcome was the proportion of responders during Month 6 (sUA < 6 mg/dL for ≥80% of time). Analyses were performed on the modified intent-to-treat (mITT) population (patients who received ≥1 pegloticase infusion).
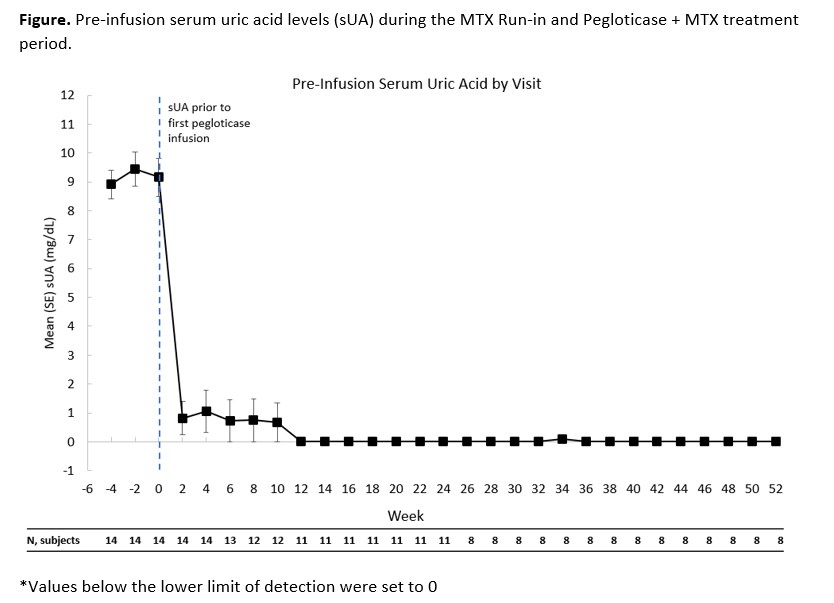
Results: 14 patients made up the mITT population. All patients were male with a mean age 49.3 ± 8.7 yrs. The time since diagnosis of gout was 13.8 ± 7.4 yrs. Mean sUA was 9.2 ± 2.5 mg/dL before the first pegloticase infusion. 12 patients had visible tophi. Eleven patients (78.6%, 95%CI: 49.2-95.3%) were considered 6-month pegloticase responders and 3 non-responders discontinued pegloticase after 2 consecutive sUA levels >6 mg/dL. Of the 11 patients who were responders in month 6, 1 did not extend (pre-protocol amendment), 2 discontinued pegloticase due to meeting their treatment goals (continued on allopurinol; 1 met responder definition during month 12), and 8 continued pegloticase/MTX co-therapy and remained responders at Month 12. Mean sUA over time is displayed in Figure. Gout flares occurred in 13/14 patients (92.9%) in the first 12 weeks and in 2/8 (25%) patients in weeks 36-52. A serious adverse event (AE) of sepsis occurred in 1 patient in the first 6 months; AEs that occurred in >1 patient during co-treatment were diarrhea, nasopharyngitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infection, muscle strain, arthralgia, and hypertension. No new safety issues were observed.
Conclusion: The 6-month response rate of MTX/pegloticase co-therapy was 78.6%. Responders at month 6 who remained on treatment continued to be responders at month 12 with sUA remaining below 1 mg/dL. The MTX/pegloticase co-therapy was well tolerated over this 12 month period with a reduced incidence of gout flares over time.
References
[1] Botson J, Peterson J. Ann Rheum Dis 2019, 78:A1289.
[2] Bessen MY, et al. Int J Clin Rheumatol 2019, 14:238-45.
[3] Albert J, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2019, 71(suppl 10).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Botson J, Peloso P, Obermeyer K, LaMoreaux B, Zhao L, Weinblatt M, Peterson J. A Multicenter, Efficacy and Safety Study of Methotrexate to Increase Response Rates in Patients with Uncontrolled GOut Receiving Pegloticase (MIRROR): 12-Month Results of an Open-Label Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multicenter-efficacy-and-safety-study-of-methotrexate-to-increase-response-rates-in-patients-with-uncontrolled-gout-receiving-pegloticase-mirror-12-month-results-of-an-open-label-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multicenter-efficacy-and-safety-study-of-methotrexate-to-increase-response-rates-in-patients-with-uncontrolled-gout-receiving-pegloticase-mirror-12-month-results-of-an-open-label-study/