Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Bench to Bedside
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We reported previously (Ramsey-Goldman et al., Arthritis Rheumatol 2020) that score > 0.8 of a multianalyte assay panel (MAP) with algorithm predicts fulfillment of a 4th ACR criterion 9-18 months (median 12) after enrollment in patients with probable systemic lupus erythematosus (pSLE). We continued to follow pSLE to better evaluate transition to classifiable SLE.
Methods: pSLE, defined as fulfilling 3 ACR criteria, were followed at academic lupus centers. At enrollment, 35 (38%) of the 92 pSLE fulfilled SLICC criteria. CB-CAPs – C4d bound to erythrocytes (EC4d) and B-cells (BC4d) – were measured by quantitative flow cytometry, serum C3 and C4 by turbidimetry, and autoantibodies by ELISA. Anti-dsDNA positivity was confirmed by immunofluorescence (IFA). MAP index consists of an algorithm with CB-CAPs and autoantibodies (Dervieux et al., J Immunol Methods 2017). Initial decision analysis with Youden index showed that MAP > 0.8 and EC4d > 20 mean fluorescence intensity units (MFI) reflected the optimal cutoffs for transition to ACR classifiable SLE; the same cutoffs were used for analysis of all follow-up visits. Time to fulfillment of ACR criteria was evaluated by Kaplan-Meier analysis; associations were analyzed by log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards model and are expressed as hazards ratio (HR).
Results: Of the 92 pSLE, 74 had 1 or 2 follow-up visits 9-35 months after enrollment for a total of 128 visits. Overall, 28 pSLE (30.4%) transitioned to ACR classifiable SLE: 16 (57%) in the 1st year and 12 (43%) in the 2nd. The clinical or laboratory features that defined fulfillment of ACR criteria are in Table 1. Use of hydroxychloroquine and immunosuppressants was similar in those who did and did not transition to SLE. Of the 17 subjects who accrued hematological criteria during the study (11 as the sole criterion and 6 as one of the new criteria), a minority were on immunosuppressants: 6 at enrollment, 5 at the 1st visit, and 3 at the 2nd. Neither SLICC criteria nor individual biomarkers were significantly associated with transition to SLE (Table 2). Only MAP > 0.8 had significantly high HR for transition to SLE; EC4d > 20 MFI, low complement, and anti-dsDNA were not significant (Table 2).
Conclusion: The majority of pSLE transitioned within a year. MAP > 0.8 predicted disease evolution into classifiable SLE better than other biomarkers or fulfillment of SLICC criteria.
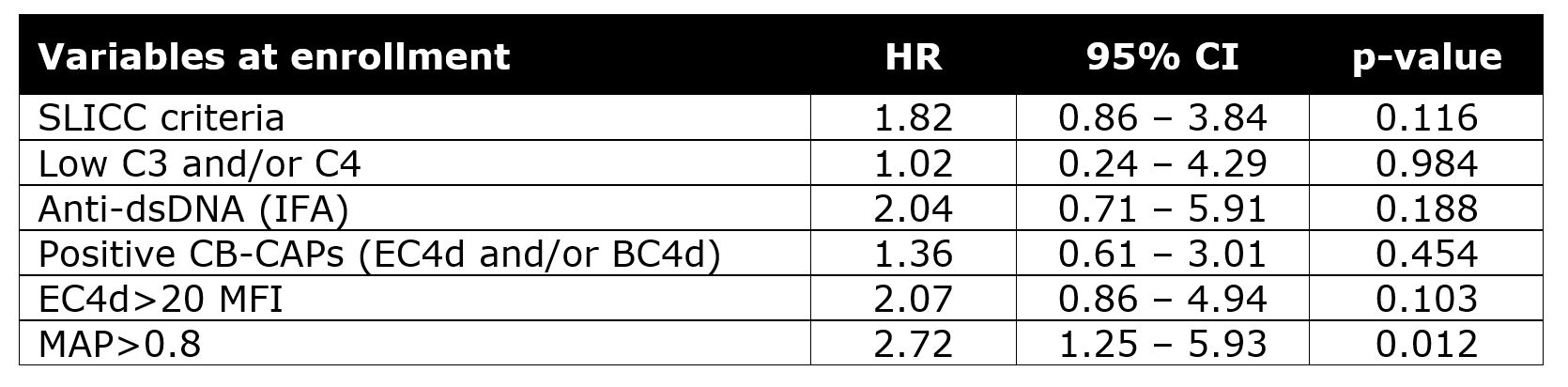 Table 2. Hazard ratio (HR) of variables measured at enrollment in predicting fulfillment of ACR classification criteria in the pSLE population. Data of 128 follow-up visits (n=127 for MAP) that occurred 9 to 35 months after enrollment were analyzed. CB-CAPs: cell-bound complement activation products; MAP: multianalyte assay panel with algorithm; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence intervals.
Table 2. Hazard ratio (HR) of variables measured at enrollment in predicting fulfillment of ACR classification criteria in the pSLE population. Data of 128 follow-up visits (n=127 for MAP) that occurred 9 to 35 months after enrollment were analyzed. CB-CAPs: cell-bound complement activation products; MAP: multianalyte assay panel with algorithm; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence intervals.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ramsey-Goldman R, Alexander R, Arriens C, Narain S, Massarotti E, Wallace D, Saxena A, Collins C, Putterman C, Kalunian K, Sace A, LaFon R, Ligayon J, Conklin J, Weinstein A. A Multianalyte Assay Panel (MAP) with Algorithm Containing Cell-Bound Complement Activation Products (CB-CAPs) Is Superior to Anti-dsDNA and Low Serum Complement Levels in Predicting Transition of Probable Lupus to ACR Classified Lupus Within 2 Years [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multianalyte-assay-panel-map-with-algorithm-containing-cell-bound-complement-activation-products-cb-caps-is-superior-to-anti-dsdna-and-low-serum-complement-levels-in-predicting-transition-of-pro/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multianalyte-assay-panel-map-with-algorithm-containing-cell-bound-complement-activation-products-cb-caps-is-superior-to-anti-dsdna-and-low-serum-complement-levels-in-predicting-transition-of-pro/

