Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Biomarkers, & Systemic Inflammation (1223–1256)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Most people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are prescribed a TNF inhibitor (TNFi) as their first targeted therapy. A blood-based molecular signature response classifier (MSRC) was shown to predict inadequate response to TNFi therapies, before treatment initiation.1 Identification of likely inadequate responders has the potential to reduce the time spent on trial-and-error approaches for treatment selection. Incorporating this test into clinical workflows could result in improved patient outcomes, reduced patient burden and potentially reduced disease progression.2,3 In a treat-to-target treatment approach, 3-months post treatment initiation is an important decision point for assessment of response;4 therefore, further validation of the MSRC at timepoints earlier than 6 months are warranted
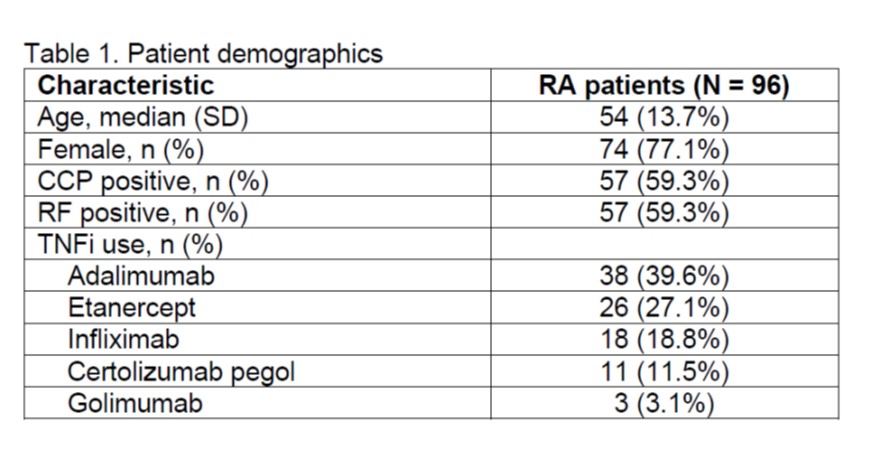
Methods: The MSRC uses data collected at baseline before starting targeted therapy, including gene expression features, laboratory tests (anti-CCP) and clinical metrics (sex, BMI, patient global assessment) to determine if patients have a molecular signature predictive of inadequate response to TNFi. The MSRC was used to evaluate RA patients (N=96) from the CERTAIN study5 who were initiating a TNFi as their first targeted therapy. None of these patients were included in previous MSRC validation studies, and only baseline and 3-month follow-up visit data were available. MSRC prediction of inadequate response were compared to treatment response, ACR50, reported at 3 months. Odds ratios and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) were used to evaluate the ability of the MSRC test to predict inadequate response to TNFi therapy at 3 months.
Results: Of the 96 RA patients described in Table 1, 51.0% (49/96) had a molecular signature of non-response. An ACR50 response at 3 months to a TNFi therapy was observed in 20.8% (20/96) of patients. Patients were stratified according to detection of a molecular signature of non-response to TNFi therapy with an AUC of 0.63. Patients with a molecular signature of non-response were 3 times less likely to satisfy the ACR50 response criterium at 3 months compared to patients lacking the molecular signature (odds ratio 3.0, 95% confidence interval 1.1-8.8).
Conclusion: The MSRC identified RA patients who did not fulfill the ACR50 response criteria to TNFi therapies by 3 months post-treatment initiation. Minimal response to treatment at 3 months is indicative of poor treatment response targets at later timepoints.6,7 Thus, MSRC test results received prior to treatment could support targeted therapy treatment selection in treat-to-target management strategies.
References:
1. Mellors T et al. Network and Systems Medicine 2020
2. van Nies JA et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2014
3. Schipper LG et al. Arthritis Res Ther 2010
4. Aletaha D et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2016
5. Pappas DA et al.. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2014
6. Aletaha D. J Autoimmun 2020;
7. Norvang V et al. RMD Open 2018
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cohen S, Mellors T, Zhang L, Jones A, Connolly-Strong E, Pappas D, Kremer J, Withers J, Akmae V. A Molecular Signature Response Classifier Predicts the Likelihood of Non-response to TNF Inhibitor Therapies in RA at 3 Months [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-molecular-signature-response-classifier-predicts-the-likelihood-of-non-response-to-tnf-inhibitor-therapies-in-ra-at-3-months/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-molecular-signature-response-classifier-predicts-the-likelihood-of-non-response-to-tnf-inhibitor-therapies-in-ra-at-3-months/