Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) has witnessed a substantial change over last the 20 years, with disease remission becoming an achievable goal. Treat-to-target philosophy, which shows improvement in outcome, is the recommended approach to managing RA. This includes regular evaluation of the disease activity and adjusting patient’s therapy as necessary to achieve the target of remission or low disease activity. The American College of Rheumatology recommends five tools for the measurement of disease activity in RA. Patient Activity Score II (PAS II) is one of these validated tools that quantify disease activity using patient-reported outcomes (PROs). Using these tools consistently can help guide therapy plans to achieve treat-to-target approach. We aim to enhance the use of PAS II in a busy rheumatology clinic using animation video and infographics.
Methods: The project was conducted over a 10-month period and was divided into two months pre-intervention period and eight months intervention period. Pre-intervention data about the use of any disease activity measure scale for all RA patients who were seen in the rheumatology clinic were collected. The intervention included distributing infographics (figure 1) and an animation video (see the link below) that explains the project to our rheumatology clinic providers. These were sent through emails and provided on-site our rheumatology clinic providers. The clinic staff received a brief session about the workflow process. PAS II questionnaire (figure 2) was distributed to all RA patients who have confirmed RA diagnosis to complete at the time of check-in. MDCalc (A free medical mobile application) was used by providers to calculate the PAS II score and insert the results in the visit note. The intervention period data about the use of PAS II was collected and compared with the pre-intervention data.
Results: Pre-intervention data showed that 4% (1/24) of RA patients had a documented disease activity measure in their charts. Intervention period data showed that 106 RA patients were seen in our clinic and 76% (81/106) had a documented PAS II scale in their charts. Most of them were seropositive 88%. In terms of disease activity, 56% had moderate disease activity, 23% had high disease activity and 21% were in remission or had low disease activity. We noticed that 45% of our RA patients are on biologics and 92% of these patients have PAS II scale in their charts.
Conclusion: We achieved our goal of implementing and maintaining the use of PAS II in a busy rheumatology clinic efficiently through the usage of infographics, simple animation video, PAS II questionnaire paper form, free mobile application, and single educational sessions for rheumatology clinic staff. We believe that our project may be applicable to other busy clinics as it is efficient, cost-effective, and feasible. PROs measures such as PASII, when consistently and judiciously used, may also help facilitate the acquisition of highly expensive biologic treatments that would have encountered extreme health insurance coverage hurdles. Furthermore, regular documentation of disease activity can help researchers who target RA treatments to collect and analyze data more efficiently and more uniformly.
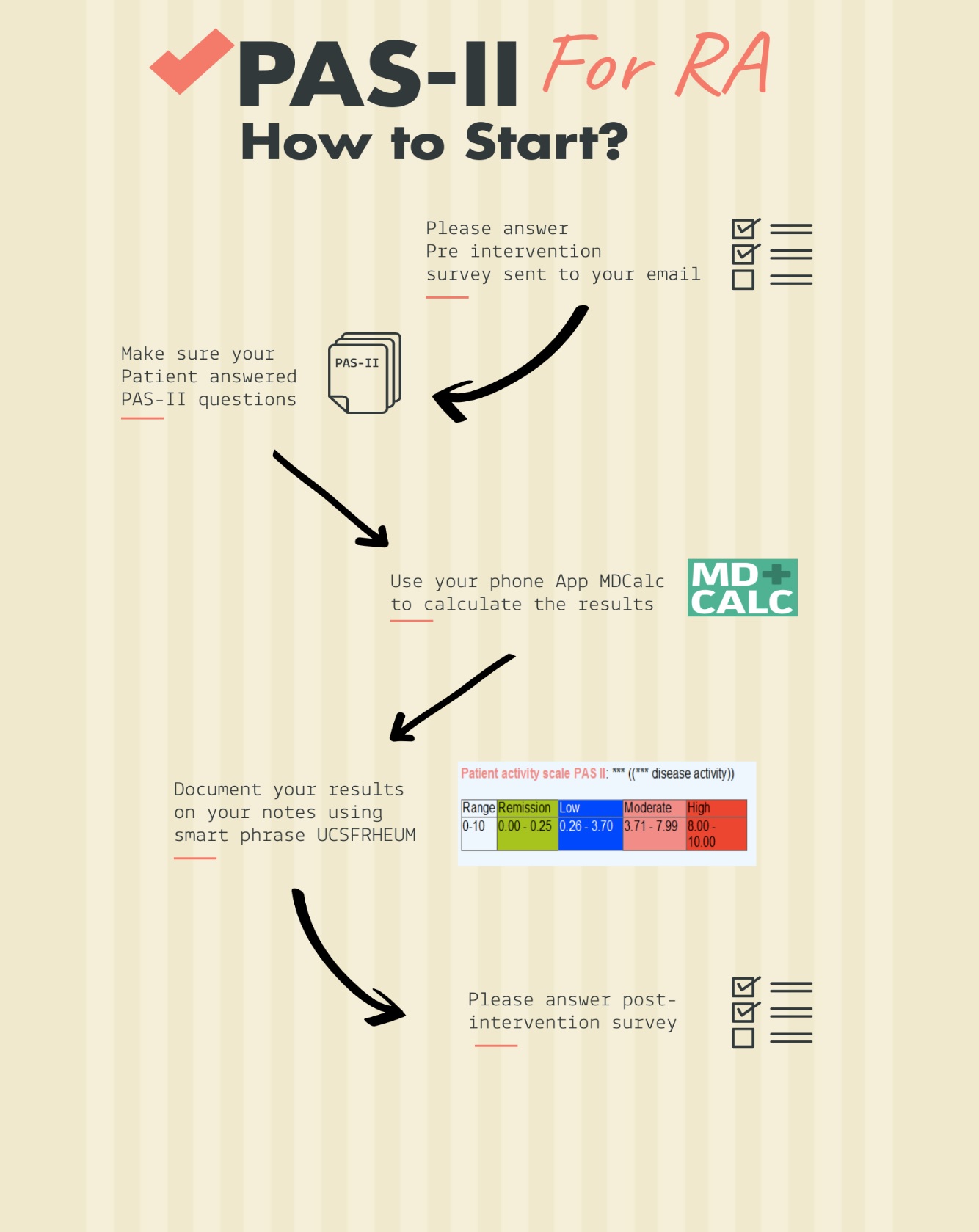 Figure 1. Workflow infographic
Figure 1. Workflow infographic
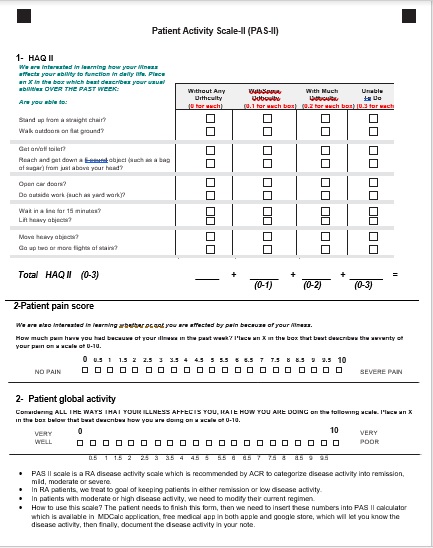 Figure 2: PAS II questionnaire
Figure 2: PAS II questionnaire
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
H.Ali A, Elghafri A, Mohameden M, Sidhu M, Reyes Yuvienco C. A Feasible and Efficient Approach to Implementing Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity Measure in a Busy Rheumatology Clinic: A Quality Improvement Project [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-feasible-and-efficient-approach-to-implementing-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-measure-in-a-busy-rheumatology-clinic-a-quality-improvement-project/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-feasible-and-efficient-approach-to-implementing-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity-measure-in-a-busy-rheumatology-clinic-a-quality-improvement-project/

