Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1124–1154) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hemay005 is an orally active selective PDE4 inhibitor under clinical development for treating chronic inflammatory diseases. Hemay005 significantly inhibits the activation of T lymphocytes, which play a vital role in the pathogenesis of psoriatic diseases. It also inhibits Th1-type pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-12, and IL-23. Improvements in the side effect /efficacy ratio vs Apremilast are anticipated to improve the efficacy of Apremilast, which was side effect limited at doses >30mg.
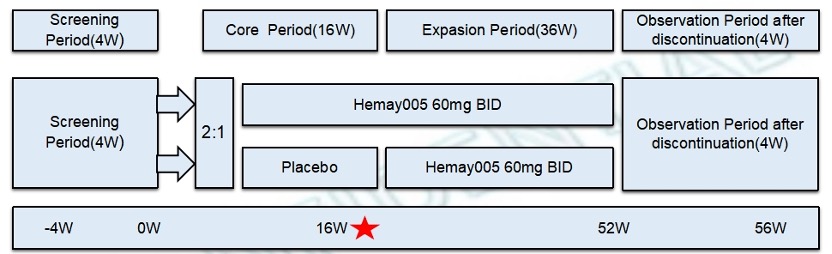
Methods: This phase III, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study randomized adults (2:1) to Hemay005 or placebo according to the Study Design Fig 1 with the primary efficacy endpoint at 16 weeks.
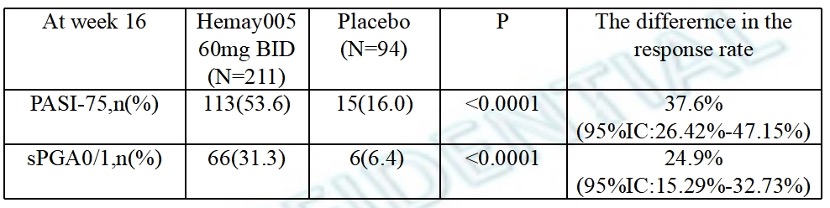
Results: Efficacy: Based on FAS, the proportion of subjects with sPGA score of cleared (0) or almost cleared (1) with a decrease ≥2 points (i.e., sPGA improved) at Week 16 Efficacy Results are shown in Table 1.
Safety: During the double-blind core treatment, drug-related AEs were reported in 141 (66.8%) in the test group and 37 (39.4%) in placebo, respectively (P< 0.0001). Drug-related AEs with an incidence ≥10% in either the test or placebo group includednausea (test group vs placebo group: 23.2% vs 1.1%), diarrhea (11.4% vs. 1.1%), and vomiting (10.0% vs 0). The incidences of all these events had statistically significant differences between groups (P< 0.05), being significantly higher in the test group than in the placebo group. The severity of drug-related AEs reported during double-blind treatment phase was primarily Grade 1 or 2. Drug-related AEs ≥Grade 3 reported in the test group included hypertriglyceridemia (0.5% each for Grades 3 and 4) and hypokalemia (0.5%, Grade 3); drug-related AEs ≥Grade 3 reported in the placebo group included soft tissue infection (1.1%, Grade 3). A population pharmacokinetics model was developed from the combined PK Phase II and Phase III data sets. The model was consistent with a one-compartment first-order absorption and linear elimination model, with an estimated elimination half-life of 12.28h.
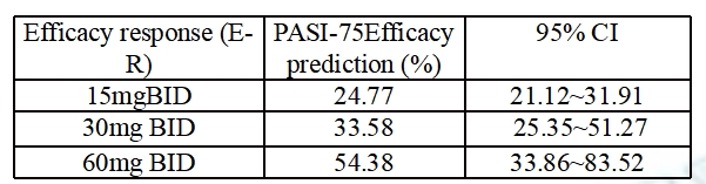
The results showed that the PASI-75 rate at 16 weeks increased with exposure, and the efficacy signal in the 60 mg BID group was greater than in the placebo or low dose groups Table 2. In the safety analysis, the frequency of defecation and vomiting increased significantly with increasing exposure. However, there was no significant correlation between exposure and the incidences of headache, dizziness, or occult blood positive.
Conclusion: Hemay005 has the potential to be the best-in-class oral PDE4 in the management of psoriasis. The results from this study showed that Hemay005 significantly reduced the severity of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis over 16 weeks. Most AEs were mild. The severity of drug-related AEs reported during the double-blind treatment phase was primarily Grade 1 or 2. The most common drug-related AE was gastrointestinal reactions, and E-R analysis showed that the optimal dose of Hemay005 was 60 mg.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jones C, Zhang J, Wang L, Dai X, Wang H, Bi X, Duan X, Meng Z, Tian Z, Xu A, Yang B, Guo S, Li W, Diao Q, Fang H, Liu Y, Fan J, Yan M, Lin S, Zhu M, Hu x, Lin J, Bi M. A Double-blind, Placebo-parallel Controlled Phase III Clinical Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Hemay005 Tablets in Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Plaque Psoriasis in China [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-double-blind-placebo-parallel-controlled-phase-iii-clinical-study-of-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-hemay005-tablets-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-chronic-plaque-psoriasis-in-china/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-double-blind-placebo-parallel-controlled-phase-iii-clinical-study-of-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-hemay005-tablets-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-chronic-plaque-psoriasis-in-china/