Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Homozygote (HM)/compound heterozygote (CH) and digenic (DG) mutations in proteasome subunits cause the autoinflammatory syndrome CANDLE, or proteasome-associated autoinflammatory syndrome (PRAAS). Inflammation is mediated by type I interferon (IFN I) due to proteotoxic distress, partially through protein kinase R (PKR) activation1. Patients (pts) with heterozygous (HZ) loss of function PSMB9 mutations are described2. We report five pts with heterozygote PSMB8 mutations and severe disease.
Methods: Pts with elevated IFN scores or clinical features of an interferonopathy were enrolled in an IRB-approved natural history protocol. We characterized clinical and immunological phenotype, measured IFN I score and performed targeted genetic analysis. We studied monocytes in culture and assessed the mutation’s effect on proteosome in HeLa cells and patients’ T cell blasts.
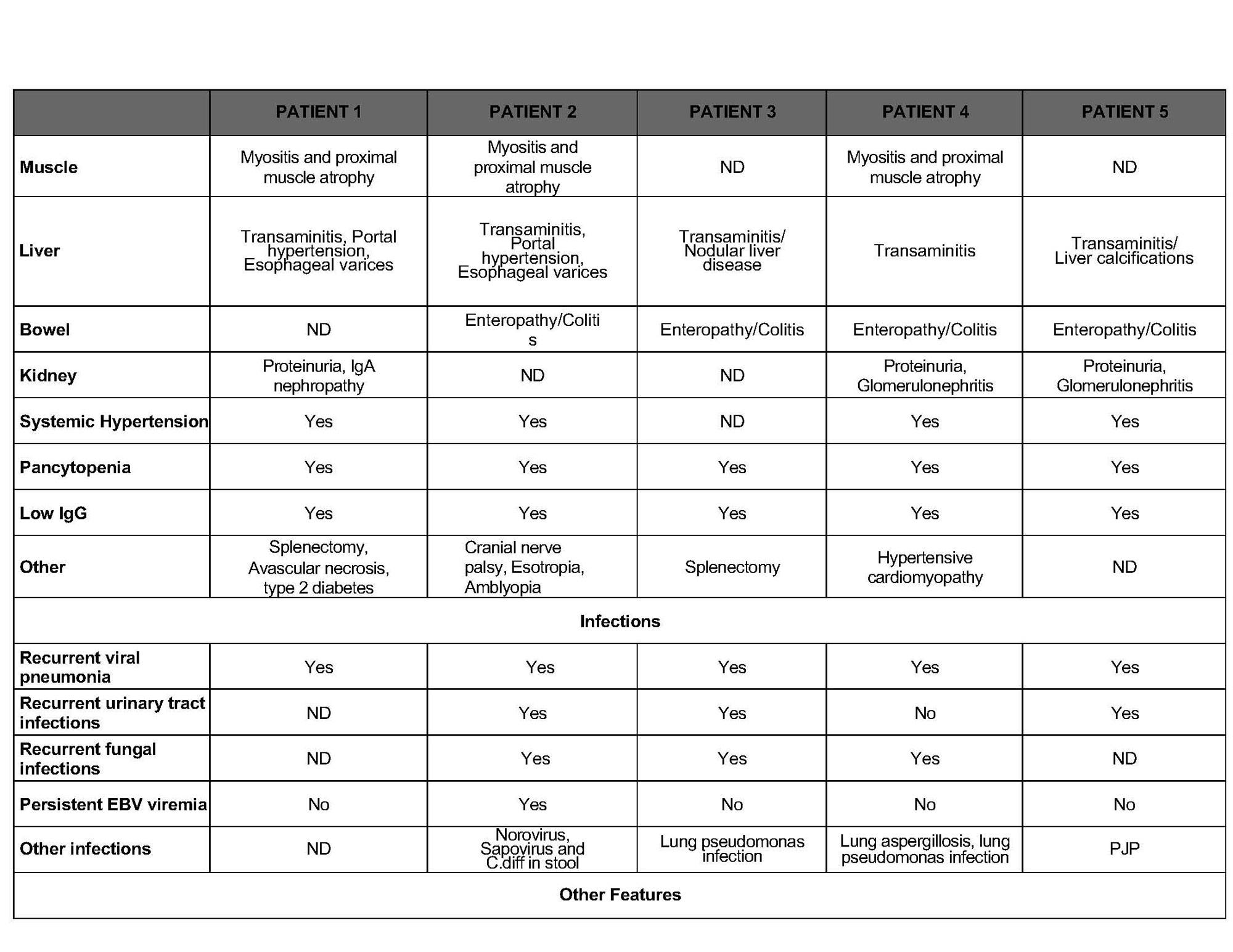
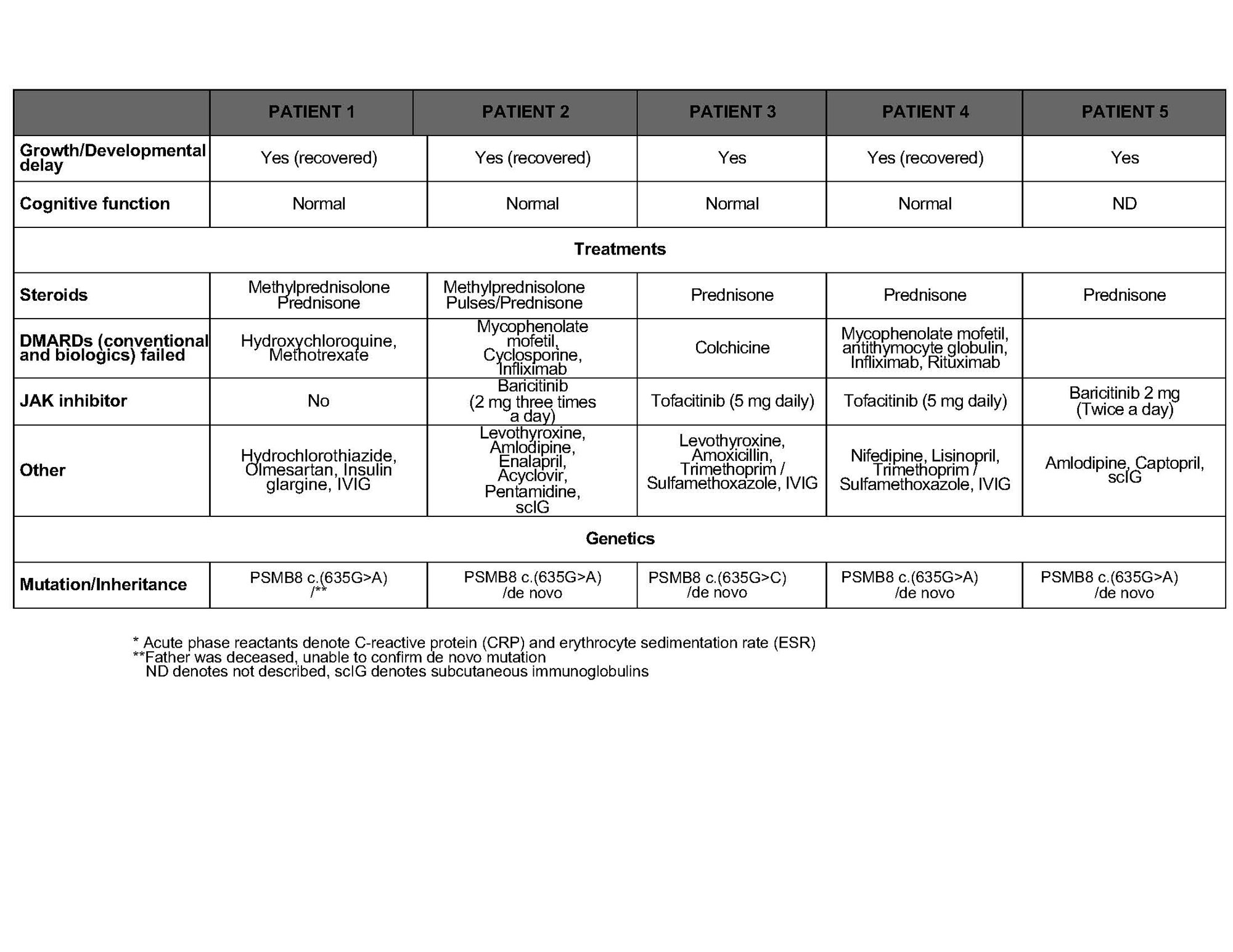
Results: All had heterozygotes PSMB8 mutations p.Gly209Arg due to base pair change c.635G >A (n=4), or c.635G >C (n=1). Clinical features are listed in the Table. All had perinatal onset of CANDLE-like symptoms, fevers, neutrophilic panniculitis, myositis, systemic inflammation and elevated IFN I score. Other features include lymphopenia, hypogammaglobulinemia, chronic infections, portal hypertension, colitis and proteinuria that are rare or absent in HZ or CH PSMB8. All required high-dose steroids. One died at 25 from variceal bleed. Treatment with JAK inhibitors, baricitinib (n=2), and tofacitinib (n=2) improved systemic inflammation and allowed tapering of the steroids. However, cytopenia (n=5) and recurrent infections are ongoing (n= 4). One has persistent lung aspergillosis, two had pseudomonas lung infections, one had PJP and one has persistent EBV viremia and norovirus/sapovirus in the stool. All are on replacement immunoglobulins. Functional assays showed that intracellular protein aggregates were increased consistent with severe proteasome dysfunction. The pts’ monocyte-derived macrophages produce high IL-8, IL-6 upon stimulation like other CANDLE pts compared to controls. In vitro, mutation cause a dominant negative effect with accumulation of proteasome precursors that do not mature. It inhibits compensatory POMP/Beta5 expressions, and disrupts proteosome assembly and maturation in HeLa cells, in a dominant-negative way. In vitro treatment of the T cells with PKR inhibitor and JAKinhibitor decreased Interferon-Stimulated Genes transcription.
Conclusion: We describe 5 pts with HZ dominant negative PSMB8 mutations who expand the spectrum of CANDLE. Like HZ PSMB9 mutations and DN POMP mutations, they have infections suggestive of T cell dysfunction and respond partially to JAKinhibitors. Our report points to the need to evaluate the effect of novel mutations on proteasome functions in patients presenting with neutrophilic rashes and CANDL like presentations.
1Kanazawa, et al. “HZ missense variant of the proteasome subunit β-type 9 causes neonatal-onset autoinflammation and immunodeficiency.” Nature commun. 2021
2 Davidson, et al. PKR is an innate immune sensor of proteotoxic stress via accumulation of cytoplasmic IL-24. Science Immun. 2022
Acknowledgments: This work was supported by DIR at NIAID/NIH.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alehashemi S, Almeida de Jesus A, Papendorf J, Bhuyan F, Uss K, Metpally A, Lin B, Park S, Moura T, Dias R, Dorna M, Kozu K, Sallum A, Campos L, Santen G, Kers J, Teng O, Palmblad K, Huizinga T, Ebstein F, Krüger E, Goldbach-Mansky R. A De Novo Dominant-negative PSMB8 mutation is Linked to a More Severe CANDLE-like Phenotype [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-de-novo-dominant-negative-psmb8-mutation-is-linked-to-a-more-severe-candle-like-phenotype/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-de-novo-dominant-negative-psmb8-mutation-is-linked-to-a-more-severe-candle-like-phenotype/