Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: 5T112: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies II: Genetics & Physiology (2834–2839)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Current understanding of why the urate lowering effect of allopurinol varies among individuals with gout is limited. The rs2231142 (Q141K) variant of ABCG2 is associated with inadequate response to allopurinol. The goal of this research was to identify variations in genes grouped by function and how they affect allopurinol response.
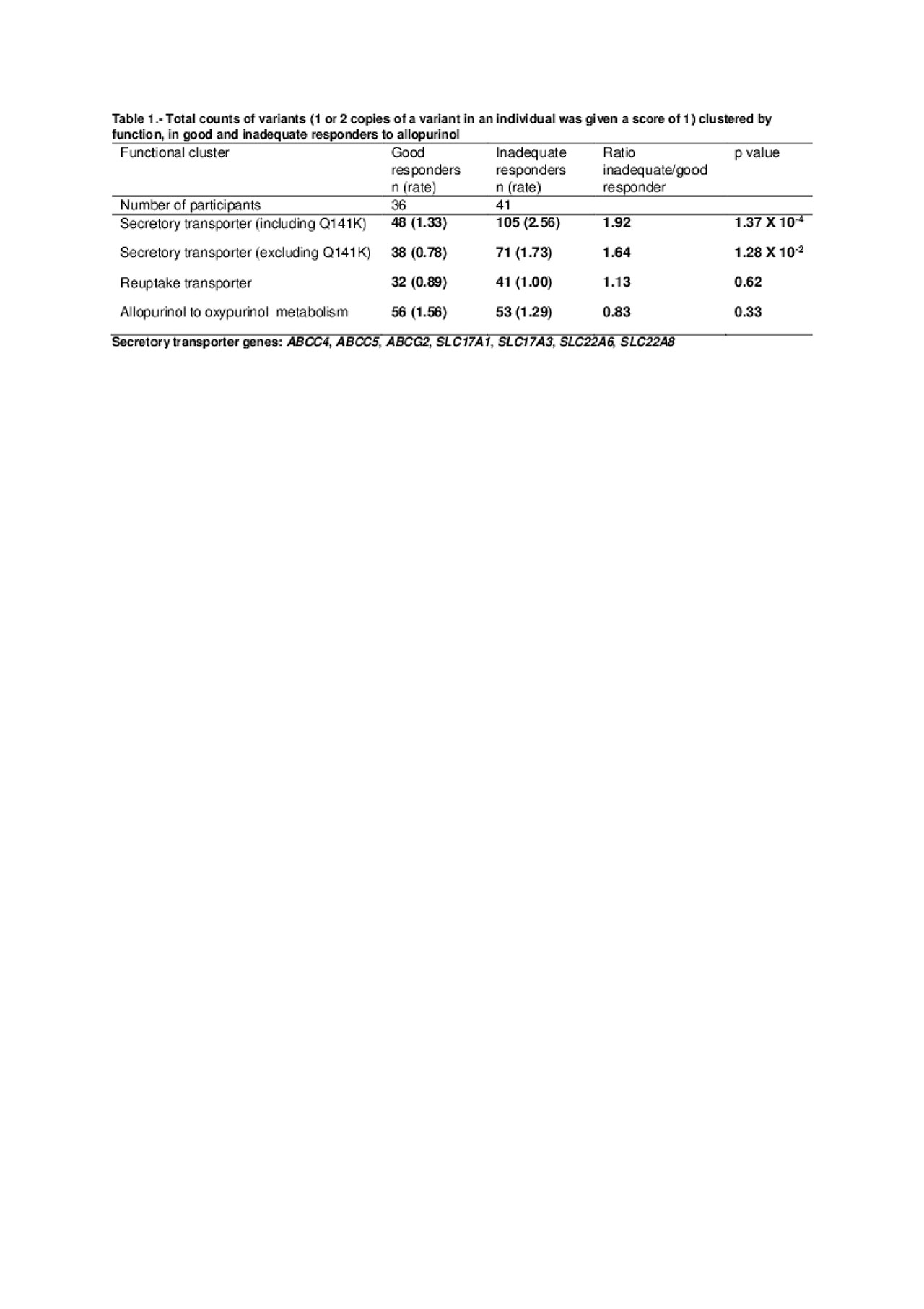
Methods: The exomes of 77 people with gout recruited in New Zealand were sequenced. Gout was defined by American Rheumatism Association classification criteria. Thirty-six participants had a good response to allopurinol, defined as serum urate < 360µmol/L (6mg/dL) with allopurinol dose ≤300mg/day. Forty-one participants had an inadequate response, defined as serum urate ≥360µmol/L with allopurinol dose >300mg/day. Participants with a plasma oxypurinol level < 20µmol/l were excluded due to potential non-adherence to allopurinol treatment. Variants (missense and nonsense) were grouped by the function of candidate causal genes– secretory urate transporters (ABCC4, ABCC5, ABCG2, SLC17A1, SLC17A3, SLC22A6, SLC22A8), reuptake urate transporters (SLC22A12, SLC2A9, SLC22A11) and genes involved in conversion of allopurinol to oxypurinol (AOX1, MOCOS, XDH). The rate of variants within a functional group was compared between good and inadequate responder subsets by Poisson approximation.
Results: A higher rate of variants in secretory urate transporter genes was observed in inadequate responders (105 variants in 41 participants) compared with good responders (48 variants in 36 participants, p=1.37 X 10-4, Table 1). This difference remained significant when the ABCG2 Q141K variant was excluded from analysis (71 variants in 41 inadequate responders versus 38 variants in 36 good responders, p=0.013). No difference was observed in the rate of variants in urate reuptake transporter genes (41 variants in 41 inadequate responders versus 32 variants in 36 good responders, p=0.62) or allopurinol to oxypurinol metabolism (53 variants in 41 inadequate responders versus 56 variants in 36 good responders, p=0.33).
Conclusion: A burden of variants in secretory transporters of urate is associated with inadequate response to allopurinol. There was no evidence that genetic variants relating to reuptake-transport and allopurinol to oxypurinol conversion were associated with inadequate response.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fanning N, Topless R, Frampton C, Cadzow M, Wallace M, Dalbeth N, Merriman T, Stamp L. A Burden of Missense Genetic Variants in Urate Secretory Genes Is Associated with Inadequate Response to Allopurinol in People with Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-burden-of-missense-genetic-variants-in-urate-secretory-genes-is-associated-with-inadequate-response-to-allopurinol-in-people-with-gout/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-burden-of-missense-genetic-variants-in-urate-secretory-genes-is-associated-with-inadequate-response-to-allopurinol-in-people-with-gout/