Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with lupus. Since the kidney biopsy is invasive, better, more predictive biomarkers of kidney injury are warranted.
Methods: Clarified urine samples from biopsy proven LN patients with differing degrees of disease activity, as scored using the renal components of SLEDAI, and healthy controls, were subjected to a 7000-plex aptamer based proteomic screen. The screening cohort included 15 LN patients with active LN, 6 with inactive LN, 9 healthy controls, and 6 LN patients with serial pre-flare and post-flare urine collections, at an average interval of 3 mo. Heatmaps, gene enrichment analyses and Volcano plots were generated using R. Man Whitney U test or Wilcoxon Rank Sum tests were used for statistical comparisons.
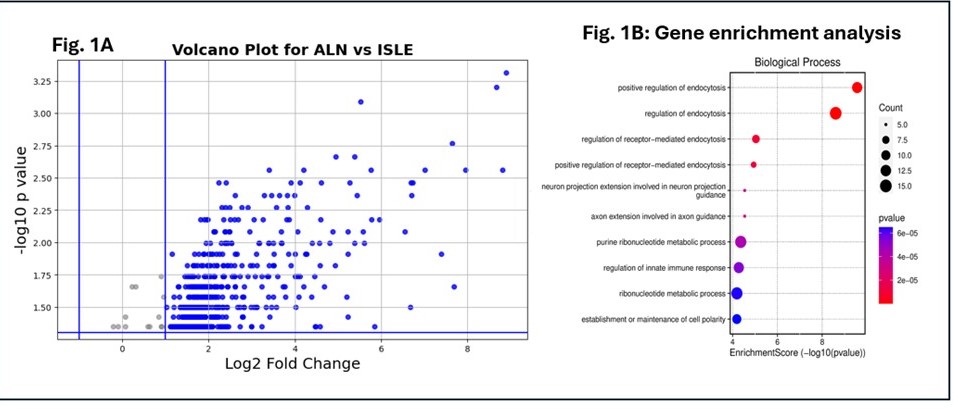
Results: Compared to inactive lupus, 605 proteins were significantly differentially expressed in active LN urine (Fig. 1A), with 279 proteins elevated >2-fold at ROC AUC≥0.80. Gene enrichment analysis implicated several functional pathways including receptor-mediated endocytosis, regulation of immune response, GTPase activity , among others (Fig. 1B). Following treatment, post-flare samples compared to flare samples exhibited 2817 proteins significantly reduced ≥50% (Fig. 2). Comparing renal flare to pre-flare samples. 398 urine proteins were elevated during flare, with ROC AUC >0.90 and p-≤ 0.125 (Fig. 2).
A flare response index (FRI) was computed for each urine biomarker, reflecting its fold-change across pre-flare, through flare, to post-flare intervals. Compared to the FRI of urine albumin (6.5), the top 22 urine biomarkers exhibited FRI > 100 (with the highest reaching ~2000).
Conclusion: These studies implicate several novel urine biomarkers of active LN that are highly responsive to renal flares, compared to albuminuria. Further validation studies are warranted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vanarsa k, Ma Y, Daouk M, Maruvada V, Saxena R, Mohan C. 7000-Plex Proteomic Screen of Urine for Flare Monitoring and Treatment Response Biomarkers in Active Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/7000-plex-proteomic-screen-of-urine-for-flare-monitoring-and-treatment-response-biomarkers-in-active-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/7000-plex-proteomic-screen-of-urine-for-flare-monitoring-and-treatment-response-biomarkers-in-active-lupus-nephritis/