Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-RD presents various clinical manifestations, making it challenging to assess treatment responses. B-cell depletion agents such as Rituximab (RTX) are used in refractory cases. This study aimed to evaluate the prescribing patterns in clinical practice and the role of IgG4 levels, IgG4/IgG1, and IgG4/IgG ratios for treatment response evaluation.
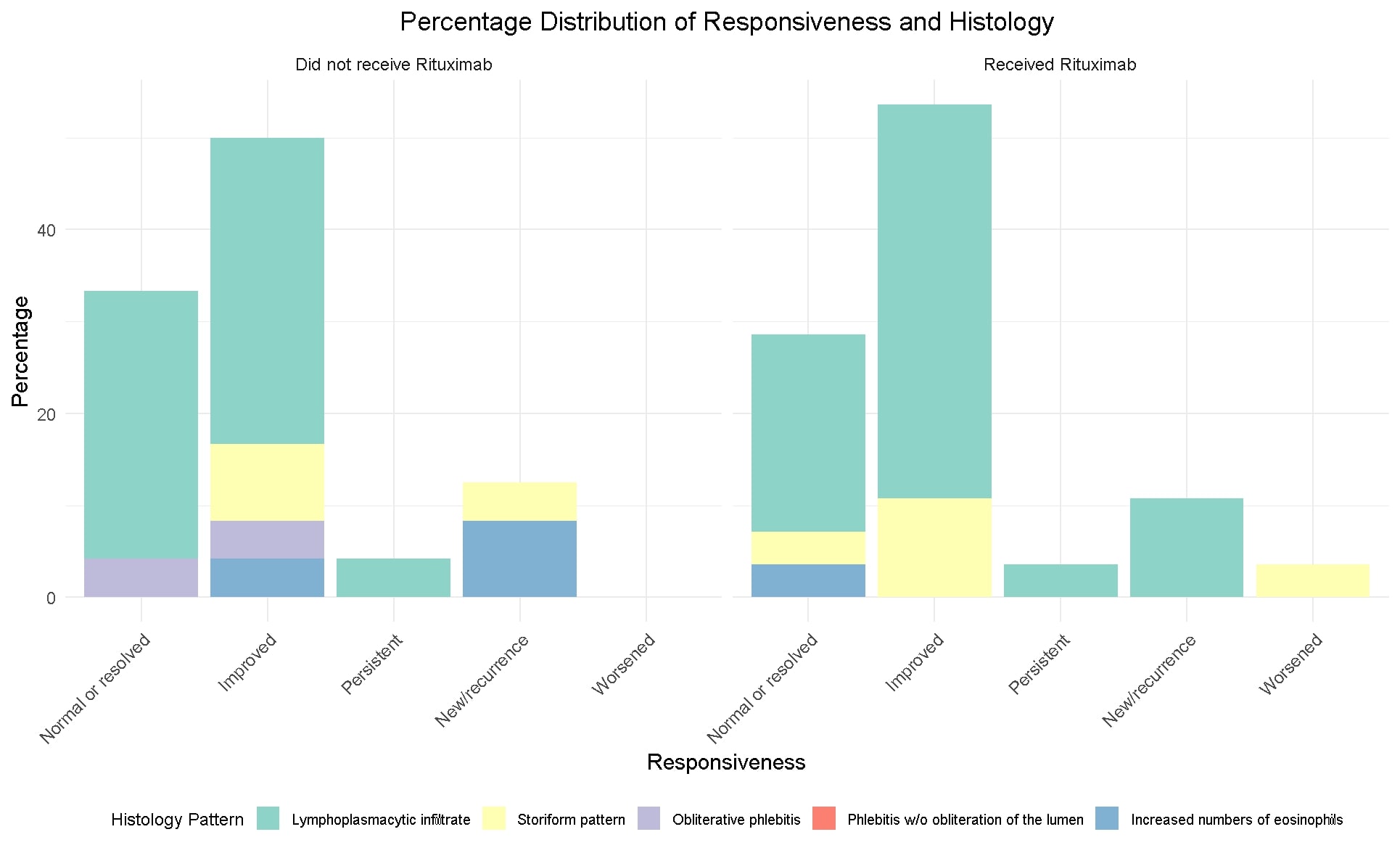
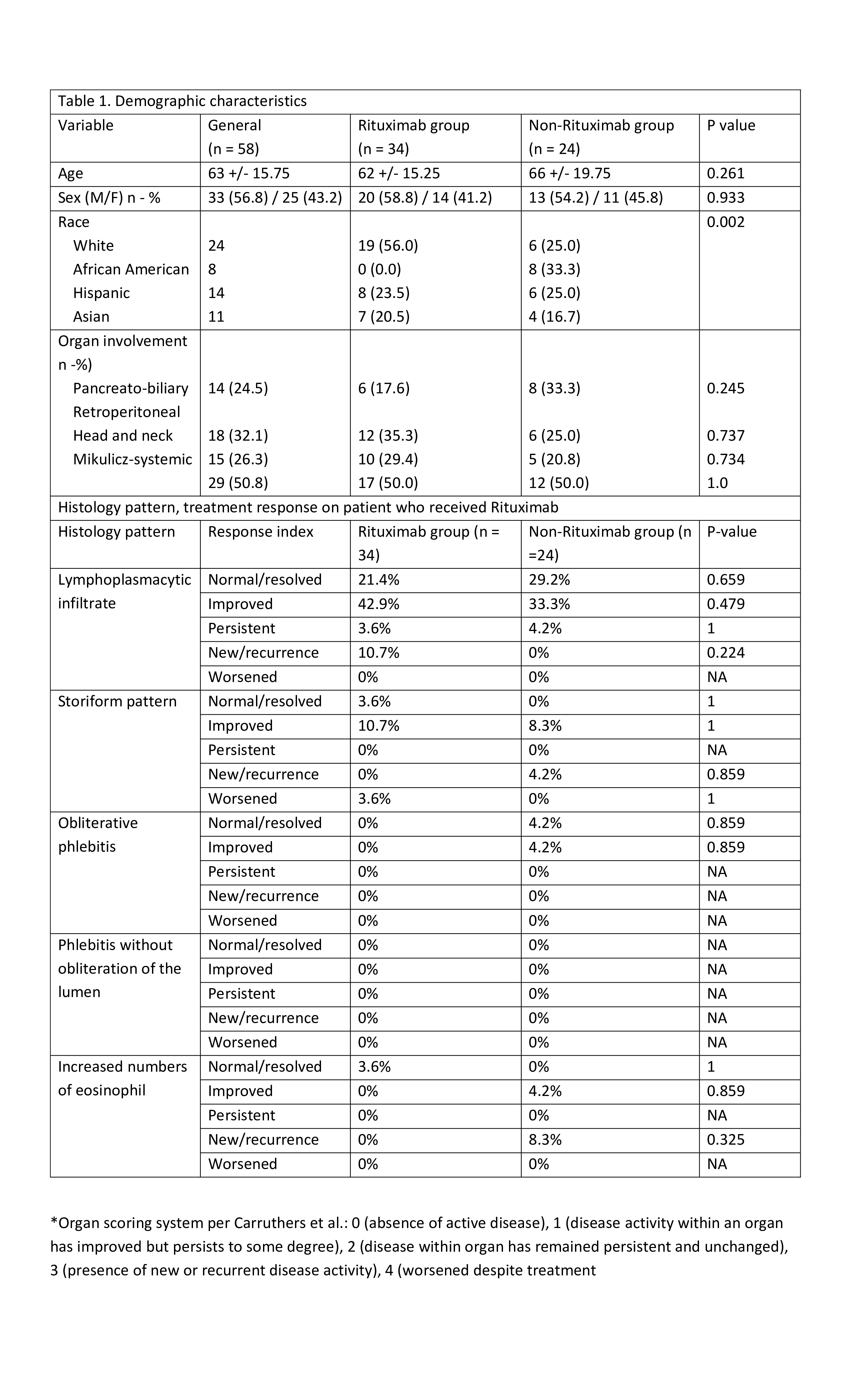
Methods: This is a second retrospective analysis of the IgG4-RD Northwell Health cohort. 64 medical charts were reviewed to confirm the IgG4RD diagnosis, based on biopsy, IgG4 levels and imaging. Demographic, clinical data with organ involvement, histological, serological markers (IgG4 levels, IgG4/IgG, and IgG4/IgG1 ratios) and treatment history were collected. Carruthers’ 2012 resolution criteria assessed treatment response (Table 1). We compared responses for every ethnic group, histological patterns, serological profiles, and between RTX and non RTX groups. Histological patterns were compared on responsiveness score between patients who received RTX and those who did not at 3 months.
For statistical analysis, we analyzed normality using visualization of Q-Q plots. Due to the right skewness in antibody values, we applied a log transformation for statistical analyses. Independent sample t-tests for numerical variables, Fisher’s exact test for small sample sizes, and the chi-squared test for larger samples were used. Paired sample t-tests were conducted to evaluate differences in IgG4, IgG4/IgG, and IgG4/IgG1 values from baseline to the end of the study. ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was utilized to compare antibody values among racial groups, contingent on a significant result. We performed ANOVAs to assess the relationship between race, clinical response and antibody values at the end of treatment, adjusted for baseline values.
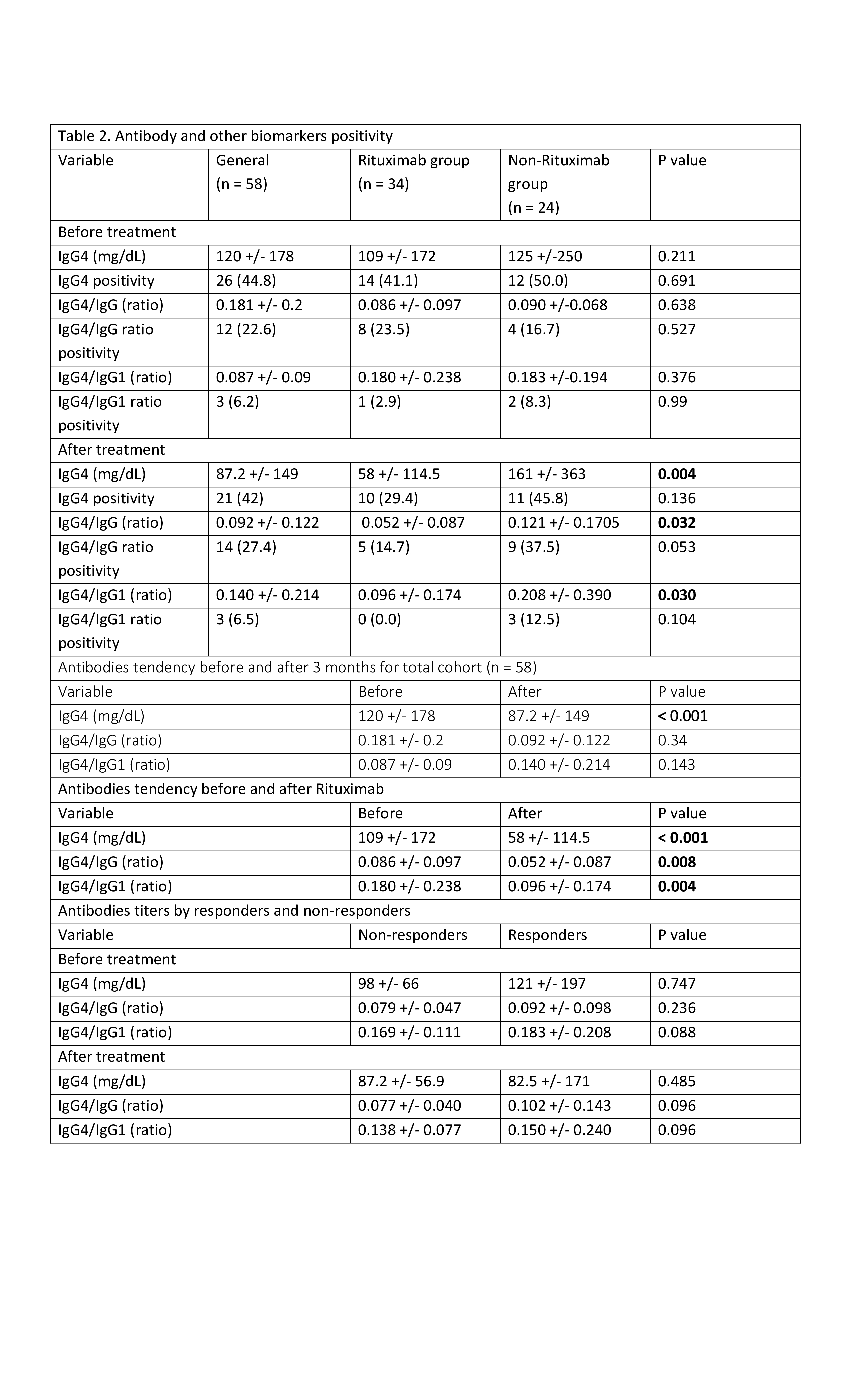
Results: Of 64 patients 6 did not pass entry criteria and 58 patients were included in analysis. Demographic and clinical data are presented in (Table 1). Patient on rituximab retroperitoneum, mediastinum, mesentery (11.6%), and lymphadenopathy (8.12%) were prevalent. The most common histological patterns were storiform (51%) and lymphoplasmacytic (32%). Of 58 patients 49% received RTX and rest on steroids or traditional immunosuppressives (IS). Irrespective of histological patterns response indices were the same in RTX and non RTX groups (Table 1, figure 1). Baseline IgG4 levels, IgG4/IgG1, and IgG4/IgG ratios were non-significant (NS) between RTX and non RTX group. After treatment, in RTX group levels were significantly lower as compared to non RTX with p= 0.004, p = 0.03, and p = 0.032 respectively. Paired analysis showed significant differences in IgG4, IgG4/IgG, and IgG4/IgG1 values from baseline to 3 months after RTX with p= 0.001, p= 0.008, and p= 0.004 respectively (Table 2). Same analysis for total cohort from baseline to the end of the study showed IgG4 levels significantly lower (p = 0.001). When comparing responders and non-responders in either treatment arms there was no significant difference in Ig4, IgG4/IgG1 and IgG4/IgG levels.
Conclusion: While IgG4 levels and ratios (IgG4/IgG and IgG4/IgG1) were much lower after Rituximab, these markers did not distinguish between responders and non-responders
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cho Y, Quintero Villegas A, Means M, Theodoros Z, El Khoury L, Marder G. 2nd Analysis of IgG4-Related Disease in a Diverse Long Island Population: Utilizing Serological and Histological Markers for Assessing Treatment Response [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/2nd-analysis-of-igg4-related-disease-in-a-diverse-long-island-population-utilizing-serological-and-histological-markers-for-assessing-treatment-response/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/2nd-analysis-of-igg4-related-disease-in-a-diverse-long-island-population-utilizing-serological-and-histological-markers-for-assessing-treatment-response/