Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Cytokines (e.g. interleukin [IL]-2, -4, -7, -15, -21) involved in lymphocyte development, function and homeostasis are known to signal through JAK. Objectives were to characterize changes in natural killer (NK) cell counts following tofacitinib treatment and evaluate the relationship between NK counts and rates of infection and malignancy.
Methods: Lymphocyte subset data, enumerated by flow cytometric analyses, were pooled from 3 double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 2 (P2) studies (two monotherapy and one background methotrexate [MTX]) in MTX inadequate responders, and from a sub-study of an ongoing long-term extension (LTE) study (study is ongoing; database not locked). RA patients (pts) received tofacitinib (1 to 30 mg twice-daily [BID]) or placebo for 6 to 24 weeks in P2 and tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID for 22 months (median) in LTE. 928 and 161 pts contributed NK cell data in P2 and LTE, respectively. Correlations between baseline or nadir NK cell count and serious infection (SIE, any infection that requires hospitalization for treatment or parenteral antimicrobial therapy), herpes zoster (HZ) and malignancy (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer) were assessed by sub-dividing NK cell data into deciles and calculating incidence rate (events/100 pt years) of adverse events for each decile.
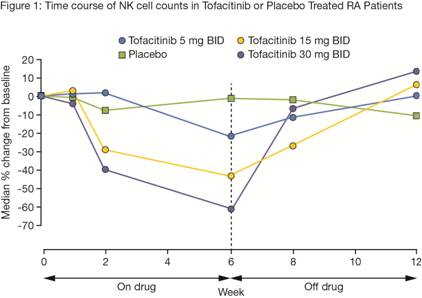
Results: Following tofacitinib administration, NK cell counts decreased in a dose-dependent manner by Week 2 (Figure 1). Median NK cells counts returned to baseline 2 to 6 weeks after treatment discontinuation (dc). At the 5 mg BID dose, pts with the largest (>90th percentile) decrease in NK cell counts recovered from ~70% below baseline to ~18% by 6 weeks after treatment dc (n=4). The estimated median decrease for 5 mg BID at Week 24 was ~35%. Cross-sectional analyses in different groups of pts showed similar median NK cell count in the LTE (141 cells/µL) compared to pre-treatment baseline (135 cells/µL). No clear association between baseline or nadir NK cell counts (predominantly collected within first 6 months of treatment) and the incidence of SIE, HZ or malignancy (Figure 2) was seen over the period of observation (median duration 1.9 years).
Conclusion: Tofacitinib treatment is associated with a dose-dependent decrease in NK cell counts. No association between baseline or nadir NK cell counts and the incidence of SIE, HZ or malignancy was observed. Long-term lymphocyte subset data are being collected in the ongoing LTE study to confirm these relationships.
Disclosure:
R. van Vollenhoven,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
5;
Y. Tanaka,
Abbvie, Chugai, Astellas, Takeda, Santen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Pfizer, Janssen, Eisai, Daiichi-Sankyo, UCB Japan, GlaxoSmithKline, and Bristol-Myers-Squib,
5,
Abbvie, Chugai, Astellas, Takeda, Santen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Pfizer, Janssen, Eisai, Daiichi-Sankyo, UCB Japan, GlaxoSmithKline, and Bristol-Myers-Squib,
8,
Abbvie, Chugai, Astellas, Takeda, Santen, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Pfizer, Janssen, Eisai, Daiichi-Sankyo, UCB Japan, GlaxoSmithKline, and Bristol-Myers-Squib,
9;
R. Riese,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
M. Lamba,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
T. Kawabata,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
T. Hirose,
Pfizer Japan Inc,
1,
Pfizer Japan Inc,
3;
S. Toyoizumi,
Pfizer Japan Inc,
3;
A. Hazra,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
S. Krishnaswami,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-nk-cell-count-and-important-safety-events-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-tofacitinib/