Session Information
Title: Epidemiology and Public Health (ACR): Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Outcomes
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
To investigate the associations of rheumatoid factor (RF) and autoantibodies against citrullinated proteins (ACPA) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease activity.
Methods
We analyzed the association of RF and ACPA on individual and composite measures of disease activity at baseline in four recent randomized controlled clinical trials (RCT) using stratified and matched analyses. Data included one RCT in early RA patients on rituximab, RTX; three on golimumab, GOL, in early and established populations.
Results
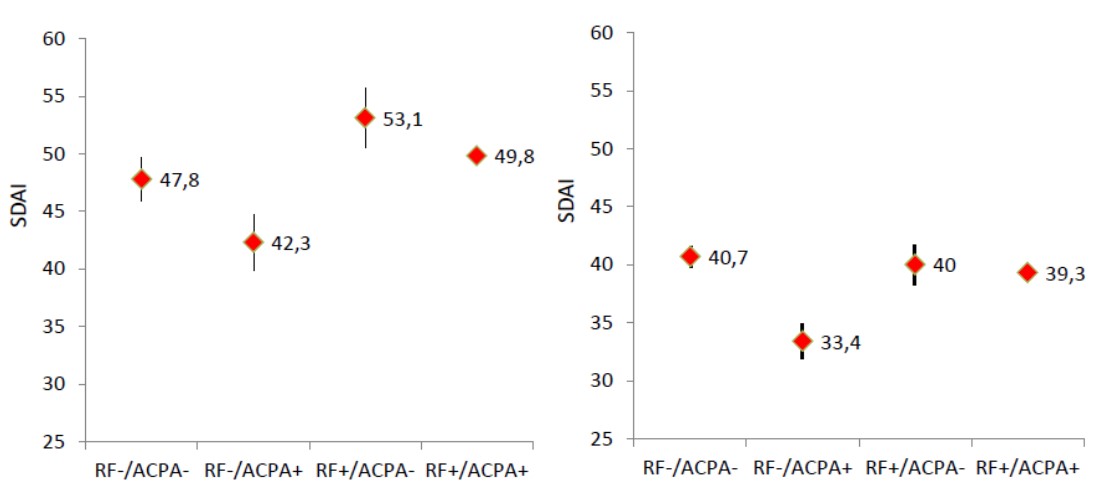
A total of 2118 patients were analyzed in the four studies. In both, the RTX and the pooled GOL cohorts, RF+ patients, regardless of ACPA status, had the highest levels of baseline disease activity, while ACPA+ patients had similar or lower disease activity than ACPA- patients, regardless of RF status (See Figure, using Simplified Disease Activity Index, SDAI).
When patients from the RTX trial were matched for the levels of ACPA, as well as for age, gender, and duration of RA (n=29), SDAI levels were 49.3±14.5 in the presence of high positive RF, and 42.3±12.7 in patients who were RF negative; this was the opposite for ACPA in patients matched for RF levels and the same covariates: high positive ACPA: 45.8±14.8; ACPA negative: 53.1±16.5 (p=0.025). These trends were supported in the respective analyses in the pooled GOL trials (RF high vs. neg.: SDAI of 36.8 vs. 33.1; ACPA high vs. neg.: 37.0 vs. 39.5), although the difference did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusion
The data suggest that the presence of RF rather than ACPA is related to higher disease activity. When matched for RF levels, ACPA had little influence on disease activity, if at all, with the tendency towards lower disease activity for ACPA+ patients.
Figure. Simplified Disease Activity Index at baseline of the rituximab trial (left panel) or the pooled golimumab trials (right panel) by groups of RF/ACPA status.
Acknowledgement. We thank Roche and Janssen for providing anonymised patient level data from their clinical trials.
Disclosure:
D. Aletaha,
None;
F. Alasti,
None;
J. Smolen,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-factor-not-acpa-is-associated-with-disease-activity-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/