Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease characterized by infiltration of the synovium by inflammatory cells that destroys the cartilage and the bone adjacent to the joint. The thickened synovium, called pannus, causes swelling of the joint with excess of synovial fluid (SF) production. A large number of proteins involved in inflammation and immune response have been identified in SF from RA patients (SF-RA). The aim of this study was to determine the effects of synovial fluids (SF) from RA patients (SF-RA) on surface phenotype, co-stimulatory activity, viability and cytokine production of monocytes, as a model for the interaction between SF and synovial tissue macrophages in RA.
Methods
Purified monocytes from healthy donors were incubated with individual specimens of SF-RA obtained from twelve RA patients with active knee arthritis and then analyzed by flow cytometry for ILT4 and CD86 expression, co-stimulation ability, rate of spontaneous apoptosis and TNFα, IL-1β and IL-10 production. Comparative analysis was carried out with serum from RA patients and medium alone.
Results
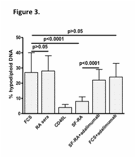
Downmodulation of ILT4 and upmodulation of CD86 expression (Figure 1), together with increased ability to co-stimulate CD4+ T cells for IFNγ and TNFα production, was observed in monocytes incubated with SF-RA (SF-RA monocytes) compared with control cells, even under condition of activation by CD40L (Figure 2). A reduction of spontaneous apoptosis was observed in SF-RA monocytes compared to control cells. Adalimumab increased the rate of SF-RA monocytes apoptosis, whereas no significant influence of adalimumab was detected in control monocytes. The TNFα and IL1β response, but not that of IL-10, to LPS was greater in SF-RA monocytes compared with control cells (Figure 3).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that soluble factors present in SF-RA could function as so-called damage-associated molecular patterns and contribute to increase the effectiveness intra-articular of the immune response and inflammation by increasing monocyte numbers and pro-inflammatory activity.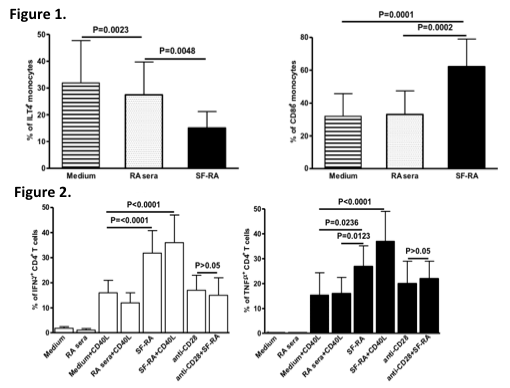
Disclosure:
M. S. Chimenti,
None;
A. Bergamini,
None;
E. Baffari,
None;
E. Ballanti,
None;
A. Musto,
None;
P. Conigliaro,
None;
R. Perricone,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-fluid-from-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-modulates-the-immunophenotype-and-viability-of-monocytes/
