Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: There is a lipid paradox in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): despite low lipids influenced by systemic inflammation, there is an increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) disease. Our aim was to describe doses of statins needed to obtain recommended lipid goals in patients with inflammatory joint disease (IJD), including RA, ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Further, to evaluate if baseline systemic inflammation and lipid levels were associated with statin dose (conventional vs. intensive) needed to obtain guideline recommended low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) goal in patients with IJD.
Methods : CV risk stratification was performed at the first consultation in a preventive cardio-rheuma clinic in 202 patients (RA: n=124, AS: n=52, PsA: n=26). The patients were classified to either primary or secondary CV prevention with lipid lowering (LL) treatment, or to have low risk with no indication for medical intervention. LL treatment was initiated with statins and adjusted until at least two lipid targets were achieved. Any side effects/intolerance was recorded. Intensive LL treatment was defined as rosuvastatin ≥ 20 mg, atorvastatin and simvastatin ≥ 80 mg, and conventional LL treatment was defined as all lower doses.
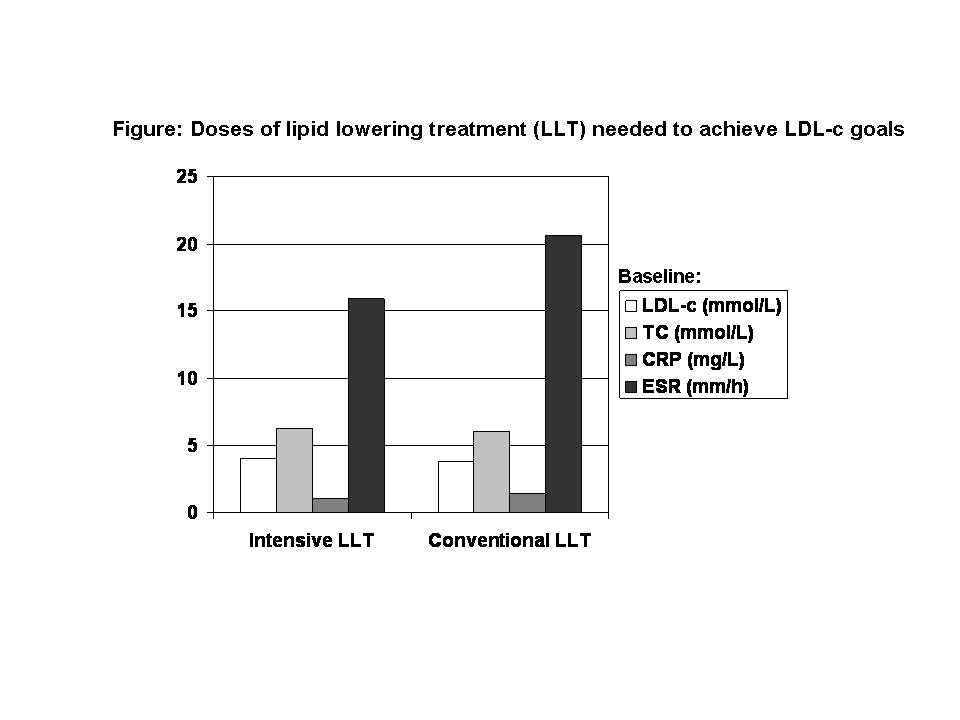
Results: Type or dosage of statins and number of dose adjustments to obtain lipid goals were similar in patients with RA, AS and PsA. There was equal need for change of statin medication across the 3 IJD’s due to intolerance/adverse event(s). In a univariate analysis neither systemic inflammation (CRP/ESR: p-value 0.10 and 0.11, respectively) nor lipid levels (LDL-c/total cholesterol (TC): p-value 0.17 and 0.34, respectively) at baseline were associated with the dose of statin needed to achieve LDL-c targets (Figure).
Conclusion: Systemic inflammation or lipid levels did not influence statin dose (conventional or intensive) needed to obtain guideline recommended lipid targets in CV prevention. Whether the background inflammation in IJD patients over time influences the CV risk reduction related to statins is yet unknown.
SHAPE * MERGEFORMAT
|
Figure: Doses of lipid lowering treatment (LLT) needed to achieve LDL-c goals
|
|
Baseline:
|
Disclosure:
S. Rollefstad,
None;
E. Ikdahl,
None;
T. K. Kvien,
None;
T. R. Pedersen,
Pfizer, Merck-Schering Plough, AstraZeneca,
5;
I. Holme,
Pfizer, Merck/Schering Plough, AstraZeneca, Roche,
5;
A. G. Semb,
Merck/Schering-Plough, Abbott, BMS, Pfizer/Wyeth, Genentech and Roche,
5.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-inflammation-in-patients-with-inflammatory-joint-disease-does-not-influence-statin-dose-needed-to-obtain-low-density-lipoprotein-cholesterol-goal-in-cardiovascular-prevention/