Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) are systemic autoimmune diseases affecting muscles, skin, lungs, joints, and several other organs; many patients are refractory to available therapy, highlighting the need for novel treatments. BMS-986353 is an investigational CD19-directed autologous chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy being studied in autoimmune diseases. We present the first report on the tolerability and efficacy of BMS-986353 in patients with severe refractory IIMs from Breakfree-1 (NCT05869955).
Methods: Patients with IIM with severe muscle involvement (manual muscle test [MMT]-8 < 130) despite treatment with glucocorticoids and ≥2 immunosuppressants (ISTs) were treated with a single BMS-986353 infusion of 10×106 CAR T cells following lymphodepletion. All patients discontinued IIM-specific therapies and steroids (≥5 mg prednisone equivalent, except when directed for adrenal insufficiency) before lymphodepletion. Primary endpoint was safety.
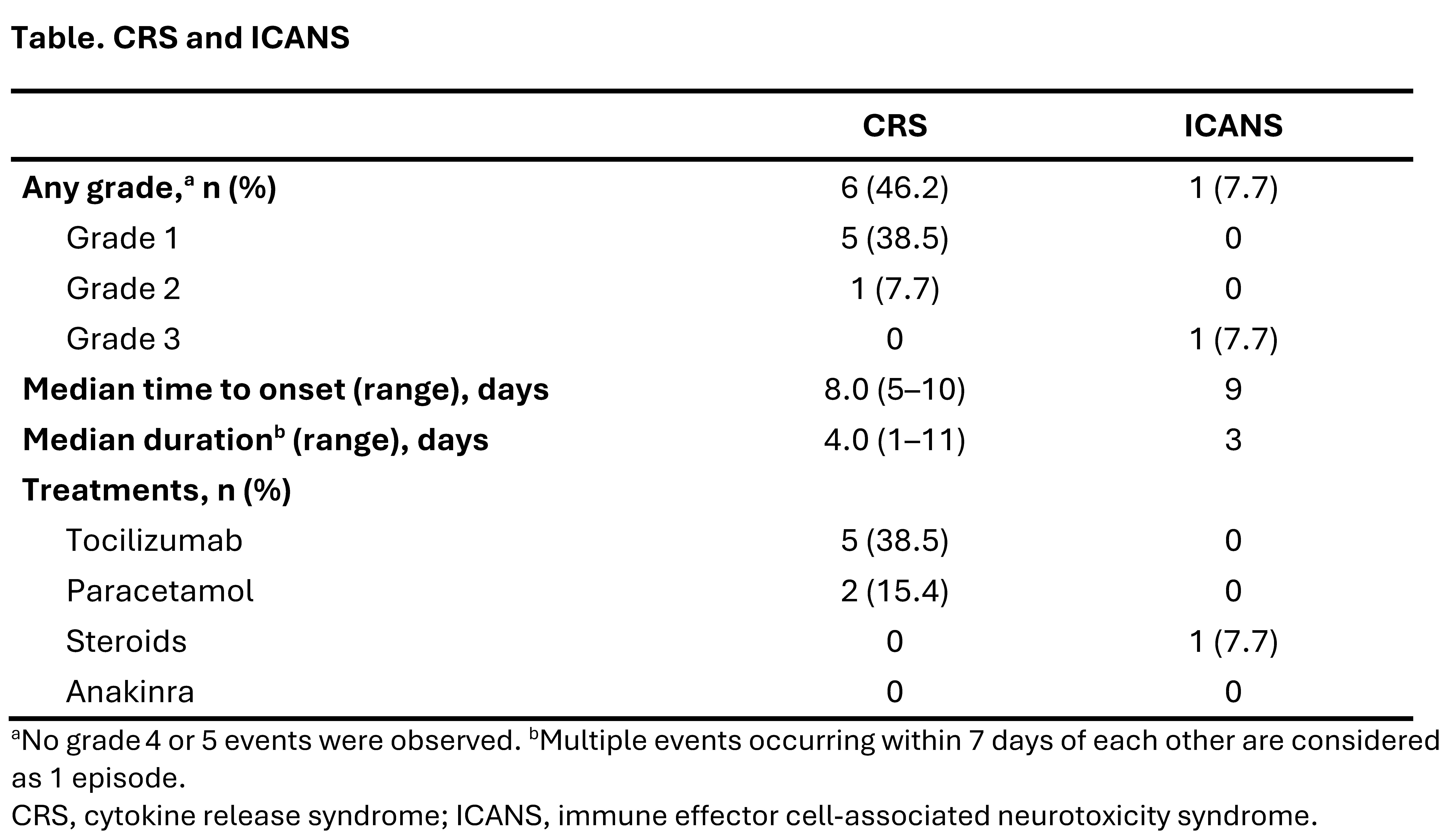
Results: As of August 14, 2025, 13 patients were evaluable for safety. Before enrollment, patients received a median 6 (range 3–9) prior ISTs. Eleven patients were evaluable for efficacy (antisynthetase syndrome, n=3; DM, n=3; PM, n=2; immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy [IMNM], n=3), with median baseline MMT-8 score of 121 (range 72−133). Median follow-up was 87 days (range 4–375).Six of 13 (46.2%) patients developed low-grade (Gr) cytokine release syndrome (Gr 1, n=5; Gr 2, n=1; Table). One patient had immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (Gr 3) characterized by decreased level of consciousness and aphasia, which resolved in 3 days with dexamethasone. Two transient hematologic treatment-emergent adverse events of Gr ≥3 (neutropenia, n=1; anemia, n=1) were reported. There were no prolonged cytopenias (lasting >28 days) or treatment-emergent serious infections.
Of the 11 efficacy-evaluable patients, 7 (63.6%) achieved a major response and 3 (27.3%) a moderate response based on Myositis Response Criteria—Total Improvement Score (MRC-TIS). All 11 patients experienced a rapid and significant improvement in muscle strength; median increase in MMT-8 score from baseline was 22.0 points at day 85 (n=6) and 27 points at day 169 (n=3). One patient with IMNM with a >10-year disease duration and minimally elevated baseline creatine kinase had an improved MMT-8 without achieving ≥moderate MRC-TIS response (Figure 1). Ten of 11 efficacy-evaluable patients remained off IIM-directed therapy at last follow-up, with 1 patient empirically restarting IVIG for elevated creatine kinase despite improvement in MMT-8 score.
All patients had robust CAR T cell expansion and achieved complete peripheral blood B-cell depletion (Figure 2). IIM-related autoantibody levels decreased post-infusion.
Conclusion: Findings from Breakfree-1 demonstrate a manageable safety profile, robust CAR T cell expansion, complete B-cell depletion, and promising efficacy of BMS-986353 without IIM-directed therapies in >90% of patients with severe refractory IIMs.
Medical writing: Sameen Yousaf, PhD (Caudex, an IPG Health company), funded by BMS.
.jpg) Figure 1. MRC-TIS (A) and MMT-8 (B) following BMS-986353 infusion in efficacy-evaluable IIM population.
Figure 1. MRC-TIS (A) and MMT-8 (B) following BMS-986353 infusion in efficacy-evaluable IIM population.
ASyS, antisynthetase syndrome; IMNM, immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy; M, month.
.jpg) Figure 2. CAR transgene levels (A) and peripheral blood B cell depletion/reconstitution (B) in evaluable IIM population.
Figure 2. CAR transgene levels (A) and peripheral blood B cell depletion/reconstitution (B) in evaluable IIM population.
Transgene levels refer to the number of genetic copies of the engineered CAR construct present in a patient’s blood, as measured by droplet digital PCR.
CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; PT, pre-treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aggarwal R, Korman D, Wiesendanger M, Majithia V, De Langhe E, Schmalzing M, Griffith M, Koehler P, Schiller J, Mougiakakos D, Cherry M, Nash R, Azzi J, Ayala E, Vandenberghe P, Topp M, Gutman J, Feist E, Desai A, Melton A, Wozniak A, Ou S, Harnois M, Thorpe J, Jarugula P, Ide T, Koegel A, Kramer N. Promising Early Outcomes With BMS-986353, a CD19-directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Severe Refractory Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: Safety and Efficacy Findings From the Ongoing Phase 1 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/promising-early-outcomes-with-bms-986353-a-cd19-directed-chimeric-antigen-receptor-t-cell-therapy-in-severe-refractory-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-safety-and-efficacy-findings-from-the-ongoin/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/promising-early-outcomes-with-bms-986353-a-cd19-directed-chimeric-antigen-receptor-t-cell-therapy-in-severe-refractory-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-safety-and-efficacy-findings-from-the-ongoin/