Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2437–2469) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease with multisystem involvement and fluctuating activity. Biologic therapies such as Belimumab, Anifrolumab, and Rituximab offer new options for moderate-to-severe or refractory SLE, though comparative data remain limited. This study describes baseline clinical features and compares serologic outcomes over 12 months.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study of SLE patients meeting 2019 ACR/EULAR criteria treated with Belimumab, Anifrolumab, or Rituximab between 2010–2025 at a university hospital. Clinical data and analytical parameters (anti-dsDNA, C3, C4, hemoglobin, leukocytes, lymphocytes, platelets, creatinine, eGFR) were collected. Linear mixed-effects models assessed treatment, time, and their interaction.
Results: A total of 65 patients were included (mean age at diagnosis: 36.1 years; 90.8% female). The most frequent baseline manifestations were articular (90.8%), hematologic (80.0%), or cutaneous (64.6%). Biologic therapies included Belimumab (60.0%), Anifrolumab (26.2%), and Rituximab (13.8%) (see Table 1&2).Therapeutic survival at 12 months was 69.2% for Belimumab, 64.7% for Anifrolumab, and 66.7% for Rituximab. Most discontinuations were due to infections or lack of efficacy. Corticosteroids were used in 88%, 78%, and 83% of Belimumab, Anifrolumab, and Rituximab cases, respectively, with median initial prednisone doses of 7.5, 5, and 10 mg/day. A significant inter-treatment difference was observed for complement C3 levels (p=0.032), with Anifrolumab achieving significantly higher C3 levels than Belimumab at month-1 (p=0.0091) and month-3 (p=0.0097), suggesting faster complement recovery. Rituximab, did not show significant improvements in C3 levels at any time point (see Image 1). For anti-dsDNA, overall treatment effect was not statistically significant (p = 0.13), though time had a significant impact (p=0.01). Belimumab showed a significant intra-group reduction in anti-dsDNA between month 1 and month 12 (p=0.0058), while Rituximab was associated with persistently elevated levels. No statistically significant differences were found between treatments in complement C4 levels (p=0.26), although a marginally significant treatment-by-time interaction (p=0.063) suggests a possible trend toward different temporal profiles among therapies. For the remaining analytical parameters no statistically significant differences were observed.
Conclusion: Anifrolumab demonstrated superior early improvement in C3 complement levels, suggesting a rapid modulation of immune activation, while Belimumab was associated with a significant reduction in anti-dsDNA titers over 12 months, indicating effective serologic control over time. Although C4 and anti-dsDNA levels showed trends toward inter-group differences, these were not statistically conclusive in between-treatment comparisons. Rituximab-treated patients, exhibited persistently elevated anti-dsDNA levels and less consistent complement normalization.These findings support individualized SLE treatment based on serologic response and organ involvement.
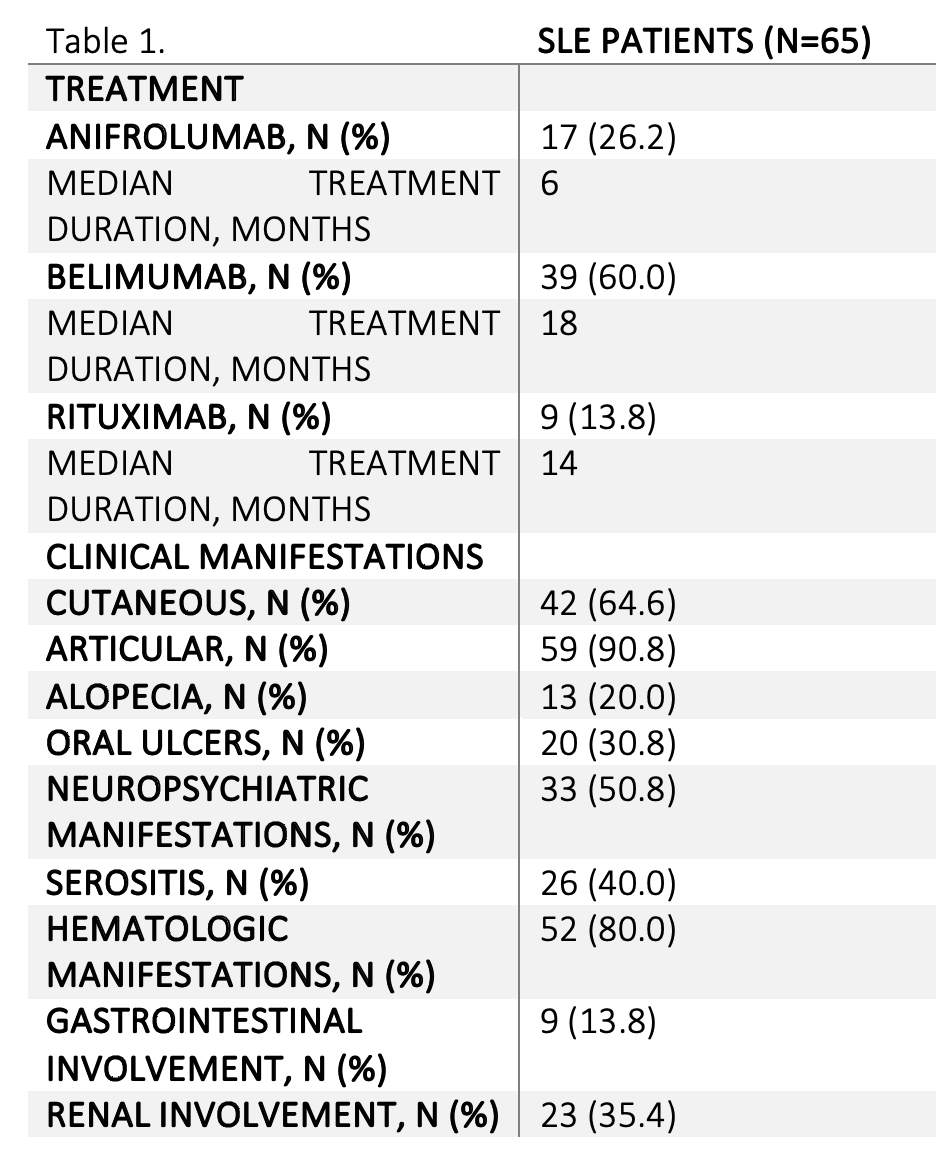 Table 1. Treatment and clinical manifestations of SLE patients
Table 1. Treatment and clinical manifestations of SLE patients
.jpg) Image 1. Changes in numerical parameters according to treatment.
Image 1. Changes in numerical parameters according to treatment.
.jpg) Table 2. Baseline Analytical Characteristics of Patients with SLE
Table 2. Baseline Analytical Characteristics of Patients with SLE
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martínez Calabuig P, Fragío Gil J, González Mazario R, Salvador Maicas L, Sanmartin Martínez M, Lorente Betanzos I, Rueda Cid A, Lerma Garrido J, Martínez Cordellat I, Balaguer Trull I, Gómez Correas B, Campos Fernández C. Comparative Efficacy of Belimumab, Anifrolumab, and Rituximab in SLE: A Retrospective Analysis of Serological and Clinical Outcomes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-efficacy-of-belimumab-anifrolumab-and-rituximab-in-sle-a-retrospective-analysis-of-serological-and-clinical-outcomes-2/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-efficacy-of-belimumab-anifrolumab-and-rituximab-in-sle-a-retrospective-analysis-of-serological-and-clinical-outcomes-2/
