Session Information
Date: Wednesday, October 29, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment II (2693–2698)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:45AM-12:00PM
Background/Purpose: Plasma biomarkers may play a role in understanding kidney health in patients with lupus, particularly in terms of early detection of lupus nephritis (LN), monitoring for disease progression, and predicting treatment responses. Deucravacitinib is a first-in-class, oral, selective, allosteric tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor that has shown clinical efficacy in the 48-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 PAISLEY SLE study (NCT03252587).1 In this post hoc analysis, we investigated circulating proteins associated with kidney dysfunction at baseline (BL) by analyzing proteomic profiles of patients with higher BILAG renal scores and urine protein-to-creatinine ratios (UPCRs) in PAISLEY SLE and assessed the impact of deucravacitinib on these biomarkers throughout the course of the study.
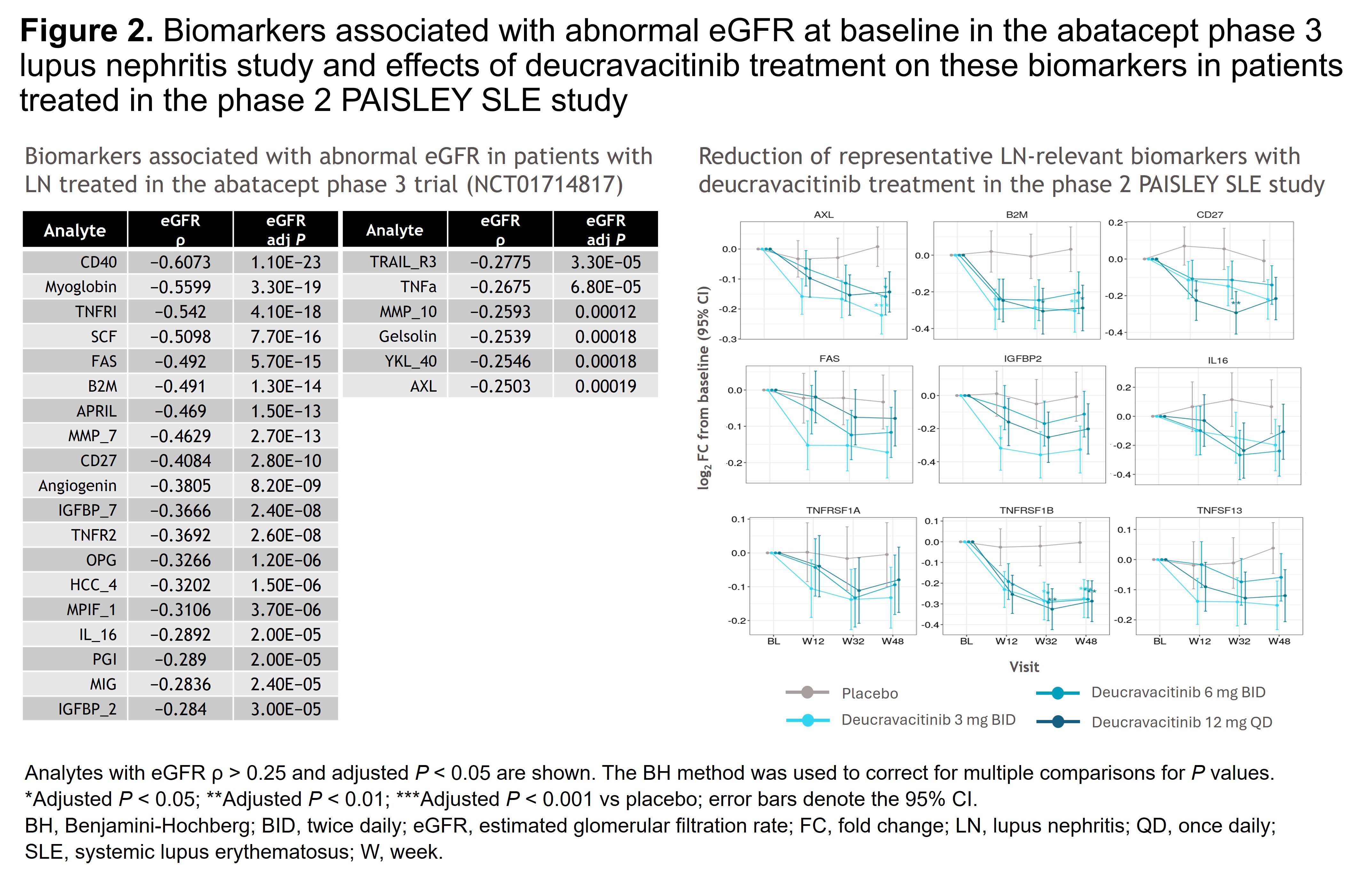
Methods: Patients with SLE were randomized 1:1:1:1 to placebo (n = 90) or deucravacitinib 3 mg twice daily (BID; n = 91), 6 mg BID (n = 93), or 12 mg once daily (n = 89). Proteomic profiles of 1187 clinical samples, collected longitudinally from 351 patients at BL and 268 patients at W12, W32, and W48, were evaluated using Olink Explore HT assays. Using DREAM, genome-wide statistical analyses were conducted to identify differentially expressed proteins associated with a higher BILAG renal score and UPCR at BL and W32. Pharmacodynamics in the intent-to-treat population were analyzed using linear mixed-effects models adjusted for stratum and batch. Pathway enrichment analyses using the Gene Ontology database identified biological pathways that were significantly represented among differentially expressed proteins. Protein biomarkers associated with low estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) identified at BL in the phase 3 abatacept LN study (NCT01714817) were also evaluated for changes throughout the PAISLEY SLE study.
Results: Plasma proteins significantly associated with higher BILAG renal scores (n = 72) or UPCR (n = 420) were identified; pathway analyses indicated dysregulated immune responses, including leukocyte activation, cytokine production, and cell adhesion regulation. At W32, deucravacitinib vs placebo significantly reduced expression of several biomarkers (eg, CD27, AXL, EPHB6, IL-18BP) associated with higher BILAG renal domain score at BL. Similarly, deucravacitinib significantly reduced expression of biomarkers associated with increasing UPCR at W32 vs placebo (Figure 1). Furthermore, biomarkers negatively associated with eGFR in the abatacept LN study were reduced with deucravacitinib vs placebo (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Deucravacitinib treatment demonstrated significant reduction of proteins associated with renal dysfunction in patients treated in the PAISLEY SLE study. Further investigation of the effects of deucravacitinib on renal biomarkers and attenuation of renal disease progression in the phase 3 POETYK SLE-1 and SLE-2 studies is warranted. Reference:1. Morand E, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2023;75:242–252.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Saxena A, Wu C, Rovin B, Touma Z, Chen X, Kouris I, Liu J. Effect of Deucravacitinib Treatment on Renal Dysfunction–Associated Plasma Biomarkers From a Phase 2 Study in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-deucravacitinib-treatment-on-renal-dysfunction-associated-plasma-biomarkers-from-a-phase-2-study-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-deucravacitinib-treatment-on-renal-dysfunction-associated-plasma-biomarkers-from-a-phase-2-study-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/

.jpg)