Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-1:15PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) are at increased risk for herpes zoster (HZ), especially those treated with B-cell depleting agents. Although the recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) has demonstrated high efficacy in healthy individuals, its immunogenicity in rituximab (RTX)-treated ARD patients remains poorly defined. This study aims to assess humoral immunogenicity to the RZV in ARD patients treated with RTX (ARD-RTX group), compared to both healthy control group (CG) and immunosuppressed ARD patients not exposed to RTX (ARD-NO RTX). Secondarily, to evaluate the influence of demographic variables, disease, and concomitant immunosuppressive drugs on RZV immune response in RTX-treated ARD patients.
Methods: This prospective controlled phase 4 study included adult ARD patients who had received at least one cycle of RTX 22–28 weeks prior to enrollment (ARD-RTX group). Two comparator groups were included: a CG of non-immunosuppressed individuals (1:3 ratio) and ARD-NO RTX group (1:3 ratio). All participants received two intramuscular doses of RZV six weeks apart. Anti-glycoprotein E (anti-gE) antibody levels were measured before the first dose and six weeks after the second dose. Anti-gE geometric mean titers (GMTs) were calculated and humoral response/seroconversion (SC) was defined as a 4-fold increase in titers. Adverse events were assessed.
Results: 76 patients ARD-RTX and 228 CG subjects were enrolled. The ARD-RTX included rheumatoid arthritis (36%), systemic lupus erythematosus (26%), Sjögren disease (13%), systemic sclerosis (11%), systemic autoimmune myopathy (17%), and ANCA-associated vasculitis (4%). Seventy-two ARD-RTX patients were compared to 216 ARD-NO RTX group with similar mean age, sex distribution and diagnoses (p > 0.05). Glucocorticoids use was higher in ARD-RTX (50% vs. 29.2%, p=0.001), whereas ARD-NO RTX used more leflunomide, iTNF, tocilizumab and belimumab (p < 0.05). Baseline GMTs were comparable between the three groups (p=0.487). Following full vaccination, ARD-RTX group had lower GMT compared to ARD-NO RTX group and CG [2.77 (95%CI 1.87–4.1) vs. 6.1 (95%CI 5.0–7.44) vs. 12.96 (95%CI 11.87–14.15) mUI/mL, p < 0.001] (Figure 1). Similarly, factor increase in GMT was reduced in ARD-RTX compared to ARD-NO RTX and CG [12.3 (95%CI 7.6-19.8) vs. 31.4 (95%CI 24.6-40.0) vs. 64.6 (95%CI 54.3-76.8), p< 0.001]. ARD-RTX patients also demonstrated a lower SC compared to ARD-NO RTX and CG group (66% vs. 85.6% vs. 99%, p< 0.001). There was no association of SC in ARD-RTX with age, ARD diagnosis, glucocorticoid, or immunosuppressive therapies (p >0.05). Regarding safety, no severe adverse events were reported. Local reactions (60.5% vs. 84.6%, p< 0.0001) and systemic reactions (39.5% vs. 63.2%, p< 0.0001) following first vaccine dose were significantly lower in ARD-RTX group compared to CG.
Conclusion: RTX significantly impairs humoral response to RZV in ARDs, independent of age, diagnosis, or concomitant immunosuppression. These findings highlight a possible vulnerability in vaccine protection and support the consideration of RZV before RTX use to optimize immune response (ClinicalTrials NCT05879419).
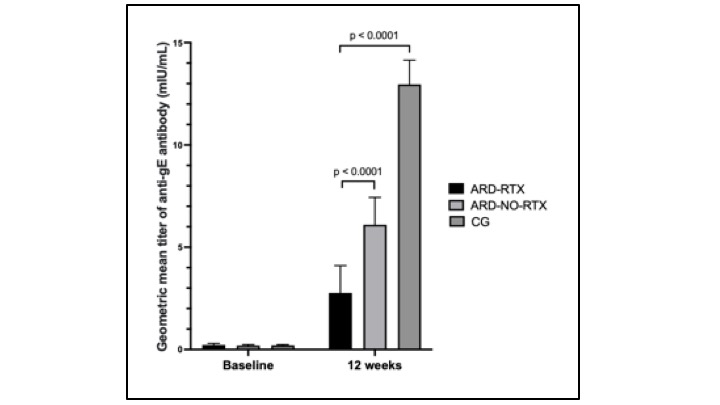 Comparison of humoral immunogenicity after RZV between autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARD) patients under rituximab (RTX) with ARD without RTX and healthy control group (CG)
Comparison of humoral immunogenicity after RZV between autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARD) patients under rituximab (RTX) with ARD without RTX and healthy control group (CG)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aikawa N, Dalmolin H, Pasoto S, Medeiros-Ribeiro A, Costa Seguro L, Figueiredo Neves Yuki E, Insfran Echauri C, Silva C, Bonfa E. Impaired Humoral Response to Recombinant Herpes Zoster Vaccine in Rituximab Treated Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases Patients: A Prospective Controlled Phase 4 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impaired-humoral-response-to-recombinant-herpes-zoster-vaccine-in-rituximab-treated-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-patients-a-prospective-controlled-phase-4-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impaired-humoral-response-to-recombinant-herpes-zoster-vaccine-in-rituximab-treated-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-patients-a-prospective-controlled-phase-4-study/
