Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2524–2546) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Behçet´s Disease (BD) was traditionally classified according to the International Study Group (ISG) in which oral ulcers were mandatory. International Team for the Revision of the International Criteria for BD (ITR-ICBD)are based on a scoring system. Our aim was to assess a) the sensitivity and b) the concordance between ISG and the ICDB criteria in global and severe ocular, vascular and neurological) BD.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with BD by expert rheumatologists in a well-defined population in Northern Spain between January 1980-November 2023 were studied. Both ISG and ICBD criteria were compared. Sensitivity and concordance were evaluated using two statistical methods: the Prevalence-Adjusted and Bias-Adjusted Kappa (PABAK), which accounts for the effects of prevalence and bias, and the unadjusted Cohen’s Kappa coefficient.
Results: We studied 142 patients diagnosed with BD by expert rheumatologists (73 men, mean age: 36.4±13.9 years). Among them, 84 fulfilled the ISG criteria and 116 met the ICBD criteria, figure 1 shows the overlap between expert diagnosis and the two classification systems. a) The sensitivity of the ISG and ICBD criteria in the overall cohort was 59.1% and 81.6%, respectively. Among patients with severe manifestations (ocular, vascular, or neurological), sensitivity increased to 71.2% for ISG and 92.5% for ICBD as shown in figure 2. b) The overall concordance between the two criteria was moderate, with a Kappa of 0.490 (95% CI: 0.356–0.623), and 70.4% of patients classified identically. When adjusting for prevalence and bias, concordance improved slightly (PABAK = 0.549). The highest agreement between classification criteria was observed when ocular involvement was deliberately added to all patients in the cohort (PABAK = 0.788; Kappa = 0.405), whereas the lowest agreement occurred when vascular involvement was added (PABAK = 0.338; Kappa = 0.216) (figure 3).
Conclusion: Sensitivity of the ICBD criteria was higher than the traditional ISG criteria in classifying BD, particularly in severe cases. Greater differences in concordance between both diagnostic criteria for BD were found when modifying the ocular involvement variable.
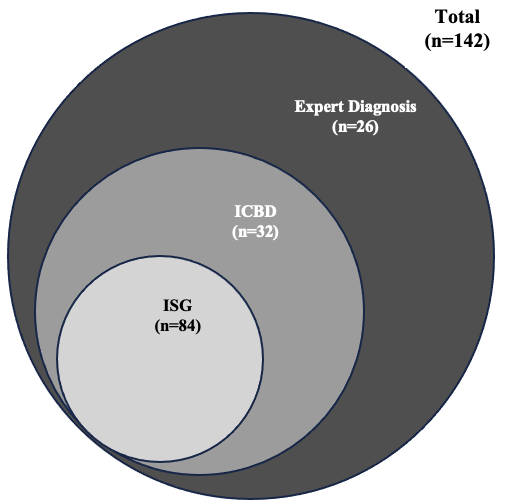 Figure 1: Overlap of Behçet’s Disease cases detected by Expert Diagnosis, ICBD, and ISG criteria. The Venn diagram shows the unique and shared cases among the three methods.
Figure 1: Overlap of Behçet’s Disease cases detected by Expert Diagnosis, ICBD, and ISG criteria. The Venn diagram shows the unique and shared cases among the three methods.
.jpg) Figure 2: Comparison of ISG and ICBD classification criteria performance in Behçet’s Disease.
Figure 2: Comparison of ISG and ICBD classification criteria performance in Behçet’s Disease.
.jpg) Figure 3. Variation in concordance between ISG and ICBD classification criteria when each severe manifestation is systematically added to or removed from all 142 patients.
Figure 3. Variation in concordance between ISG and ICBD classification criteria when each severe manifestation is systematically added to or removed from all 142 patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gálvez Sánchez R, Martín-Varillas J, Sánchez Bilbao L, Ferraz Amaro I, Lasa Teja C, Aurrecoechea E, Prieto-Peña D, Blanco R. Comparative Study of Two Classification Criteria Sets in Real Clinical Practice in Behçet’s Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-study-of-two-classification-criteria-sets-in-real-clinical-practice-in-behcets-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/comparative-study-of-two-classification-criteria-sets-in-real-clinical-practice-in-behcets-disease/
