Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Neurologic involvement (NI) is common in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) and often irreversible. It is unknown whether patients with AAV and NI accumulate more damage than those without NI. The objective of this study was to evaluate the association between NI and cumulative damage in patients with AAV.
Methods: Data from adults with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) and eosinophilic GPA (EGPA) participating from 2006 to 2021 in a multicenter longitudinal observational study were analyzed. Cohorts were divided by the presence of NI at any point in their disease course. Neurologic damage items (NDI) were classified as disease-specific (cranial nerve lesion, chronic pachymeningitis, neuropathy, and neuropathic pain) and non-disease specific (strokes, seizures, transverse myelitis, and neurologic mass). Group differences were tested using Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables and Fisher’s exact test for categorical. General and robust linear regression models were generated to estimate the differences in Vasculitis Damage Index (VDI), ANCA Vasculitis Index of Damage (AVID), AAV-Disease-Specific Damage (AAV-DSD), and AAV-Non-DSD scores. We also estimated the differences in AAV-DSD and Non-DSD scores with NDI removed. These models were adjusted for sex, age at diagnosis, and time from diagnosis to last damage assessment.
Results: Data from 1322 patients [65.9% GPA, 12.7% MPA, 21.4% EGPA] were analyzed: 526 (39.8%) had NI and 796 (60.2%) did not. Of those with ANCA results, 995 (75.3%) were ANCA positive (49.0% PR3-ANCA, 25.4% MPO-ANCA, 0.8% both). Older patients had more NI. Two-thirds of adults with EGPA had NI (Table 1). Among all AAV, patients with NI were estimated to have higher VDI (0.6 points; 95% CI: [0.35, 0.86], p < 0.0001), AVID (1.1 points; 95% CI: [0.66, 1.54], p < 0.0001), and AAV-DSD (0.91 points; 95% CI: [0.71, 1.12], p < 0.0001) scores than those without NI. The AAV-DSD score remained higher in those with NI even when NDI were removed. The AAV Non-DSD score was not different between NI groups. Among patients with GPA, those with NI had higher damage scores than those without, even with NDI removed. For MPA, those with NI only had higher AAV-DSD scores than those without. For EGPA, those with and without NI had no difference in scores. For both types of ANCA damage scores were higher among patients positive ANCA vs. those negative, even with NDI removed. Among patients negative for ANCA, those with NI only had higher AAV-DSD scores than those without (Table 2). Among patients with NI, those with GPA had more damage than those with MPA or EGPA. There were no differences in damage scores between PR3-ANCA, MPO-ANCA, and ANCA-negative groups (Table 3). Damage scores among patients with NI did not differ based on presence or absence of central vs. peripheral nervous system disease manifestations.
Conclusion: Patients with AAV and NI experience greater neurologic and non-neurologic cumulative damage than those without NI. The differences are driven by disease-specific items of damage. Of patients with NI, those with GPA, PR3-ANCA, or MPO-ANCA accumulate the most damage. These results highlight the importance and burden of NI in AAV.
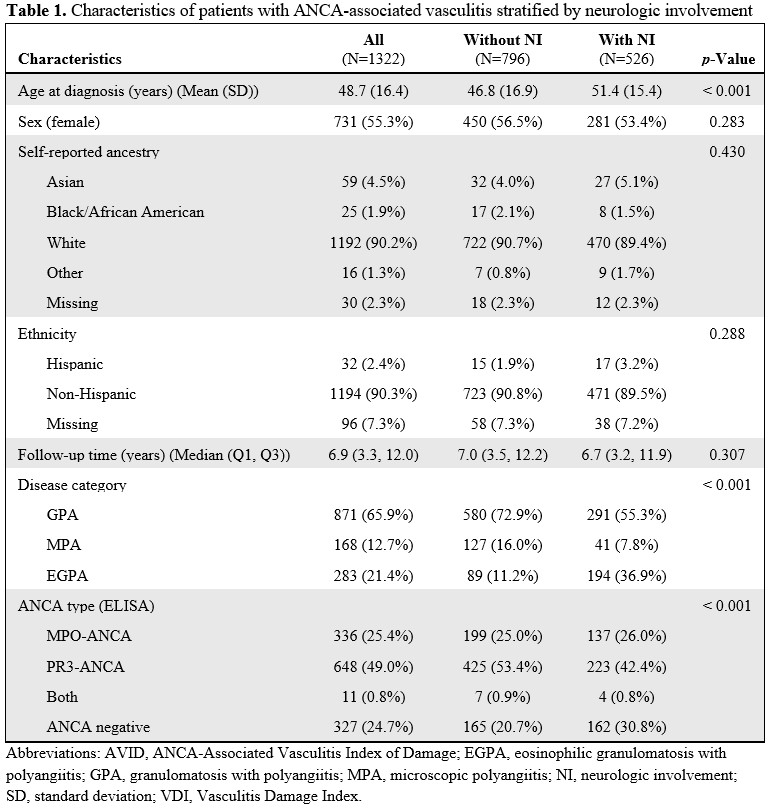 Characteristics of patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis stratified by neurologic involvement
Characteristics of patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis stratified by neurologic involvement
.jpg) Differences in damage scores based on presence of neurologic involvement among all patients with AAV, AAV subtypes and ANCA status
Differences in damage scores based on presence of neurologic involvement among all patients with AAV, AAV subtypes and ANCA status
.jpg) Differences in damage scores within subgroups among patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis and neurologic involvement based on disease subtypes and ANCA status.
Differences in damage scores within subgroups among patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis and neurologic involvement based on disease subtypes and ANCA status.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ni R, Bloom J, Pickett-Nairne K, Silveira L, Zhang C, Cuthbertson D, corbridge T, Khalidi N, Koening C, McAlear C, Monach P, Moreland L, Pagnoux C, Rhee R, Seo P, Silver J, Specks U, Warrington K, Wechsler M, Langford C, Merkel P, Hajj-Ali R. The Association Between Neurologic Involvement and Cumulative Damage in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-association-between-neurologic-involvement-and-cumulative-damage-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-association-between-neurologic-involvement-and-cumulative-damage-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/
