Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2470–2503) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a rare autoimmune disease with high mortality. Early stratification by autoantibody (SSc-Ab) profile may inform prognosis and management, but data in early SSc remain limited. This study evaluated clinical features, treatment, and outcomes by SSc-Ab subtype in early SSc.
Methods: We analyzed data from 116 patients (pts) enrolled in a prospective registry at a scleroderma center who had diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc) or at-risk for progression based on serologic and clinical features. The at-risk group included those with swollen hands or sclerodactyly with anti-Scl-70 (Scl70) or anti-RNA polymerase 3 (RNAP3) Abs, and/or tendon friction rubs(1). Patients were classified into three groups: RNAP3, Scl70, or Triple Negative (negative for RNAP3, Scl70, and anti-centromere). We analyzed longitudinal data including change in modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS), forced vital capacity (FVC), HAQ-DI, organ complications, and mortality. Time-to-event analyses stratified by SSc-Ab group were conducted using cumulative incidence curves and the log-rank test.
Results: A total of 116 pts had a median follow-up of 5.3 years (IQR: 2.1, 6.7); 109 (93.9%) had SSc-Ab data available (Table 1). The mean age was 51.1 years and 65.1% were female. Median disease duration from non-Raynaud phenomenon was 1.0 year . Of the 109, 38.5% were RNAP3+, 26.6% were Scl70+,and 34.8% were Triple Negative. dcSSc was present in 85.3%; 14.7% had at-risk features. RNAP3+ were older (mean 56 years), had the highest mRSS (mean 24.9 units), and the highest predicted FVC (mean 86.2%). At baseline, 61.5% of patients were receiving DMARDs, most commonly mycophenolate mofetil (40.4%), followed by methotrexate (12.8%) and cyclophosphamide (4.6%), while prednisone was used in 22.9%. During follow-up, immunosuppressive therapy was initiated or continued in 92.7% of patients, with variation across Ab subtypes (100% in Triple Negative, 85.7% in RNAP3+, and 93.1% in Scl70+; p=0.03). Mycophenolate mofetil remained the most frequently used agent (78.9%), followed by methotrexate (19.3%). Of 109 pts, 17 had an event before registry entry and were not included in the time to composite event analysis. Overall, 55.4% experienced ≥1 new clinical event (Table 2), with the majority having mRSS worsening (13%), FVC decline ≥10% (13%), and HAQ-DI worsening (16.3%) as the first event; mortality occurred in 4 (4.3%) pts.Cumulative incidence curves (Figure Panels A and B) show a trend toward a lower incidence of first events over time in the Triple Negative. mRSS worsening happened predominantly in the first 2 years, whereas FVC decline, HAQ-DI disability, and mortality continued over several years. Panels C-D show a trend toward higher incidence for mRSS worsening in pts with SCL70 and FVC decline in both RNAP3 and SCL70. Panel E-F show the impact of different SSc-Ab on HAQ-DI worsening and mortality. None of these trends were statistically significant.
Conclusion: Distinct SSc-Ab in early SSc are linked to distinct organ involvement and clinical trajectories. Pts continue to have progressive organ involvement and high mortality despite current management strategies.
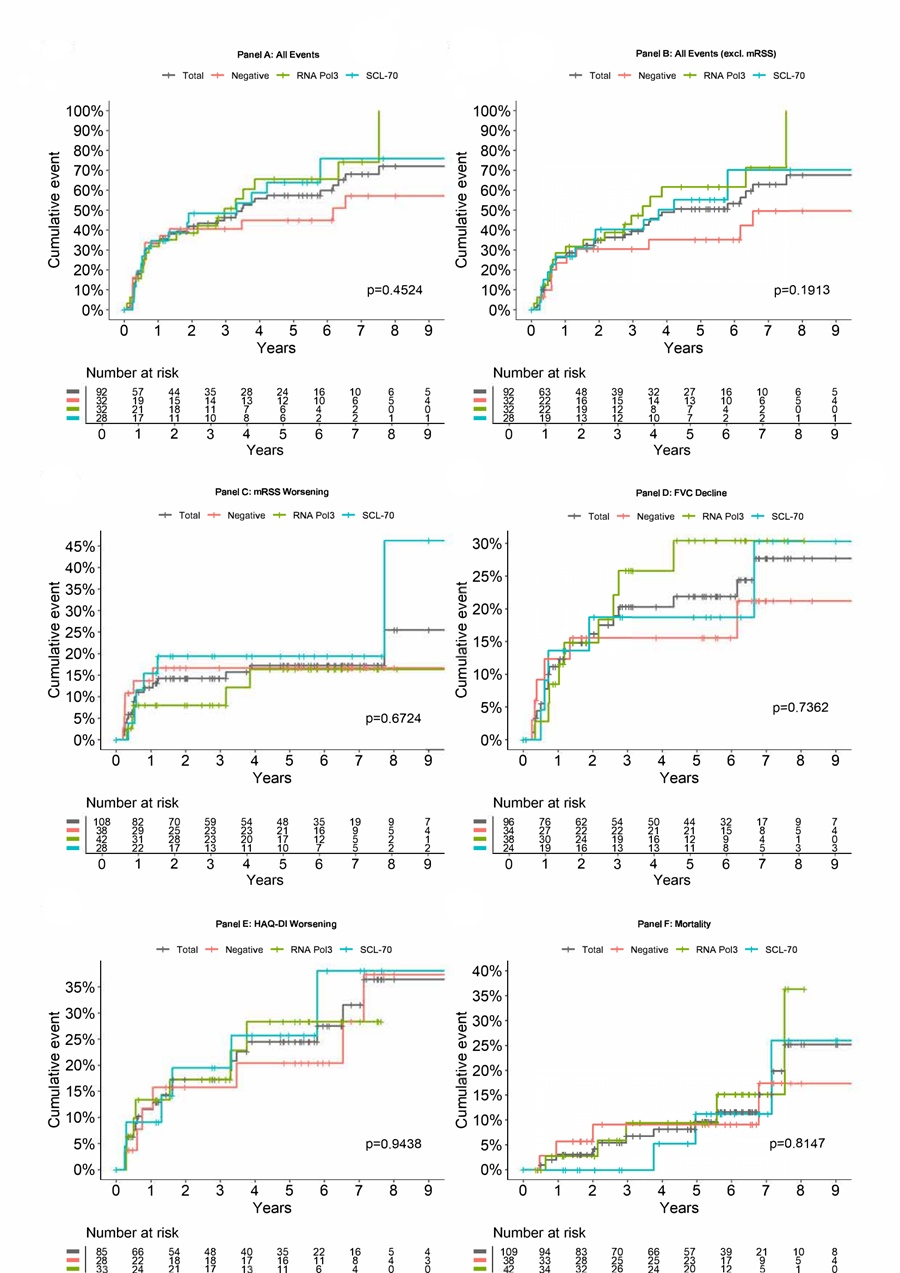 Cumulative incidence curves for the whole group and by SSc-Ab subtype. The data should be interpreted as time to the first clinical event. For Panel A, time to first event was assessed by meeting any of the following- mRSS worsening defined as as 5-unit absolute increase or 25% relative increase compared to baseline; FVC % absolute 10% decline compared to baseline; HAQ-DI as 0.5-unit absolute increase compared to baseline; Pulmonary hypertension as mean PAP ≥ 25 mmHg on right heart catheterization; Scleroderma renal crisis; Left heart failure defined as left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 45%; and mortality.
Cumulative incidence curves for the whole group and by SSc-Ab subtype. The data should be interpreted as time to the first clinical event. For Panel A, time to first event was assessed by meeting any of the following- mRSS worsening defined as as 5-unit absolute increase or 25% relative increase compared to baseline; FVC % absolute 10% decline compared to baseline; HAQ-DI as 0.5-unit absolute increase compared to baseline; Pulmonary hypertension as mean PAP ≥ 25 mmHg on right heart catheterization; Scleroderma renal crisis; Left heart failure defined as left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 45%; and mortality.
Panel A: Composite clinical events, including mRSS; Panel B: Composite events excluding mRSS; Panel C: Skin progression (mRSS worsening); Panel D: Lung function decline (FVC ≥10%); Panel E: Functional disability (HAQ-DI progression); Panel F: All-cause mortality.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jamali M, Kaur A, Huang S, St. Clair J, Varga J, Zahn C, Mulcaire-Jones E, Lescoat A, Khanna D. Autoantibody Profiles and Disease Trajectories in Early Systemic Sclerosis: Insights from a Prospective Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoantibody-profiles-and-disease-trajectories-in-early-systemic-sclerosis-insights-from-a-prospective-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/autoantibody-profiles-and-disease-trajectories-in-early-systemic-sclerosis-insights-from-a-prospective-cohort/

.jpg)
.jpg)