Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2437–2469) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Current goals of treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are to achieve low disease state/remission, prevent flares, minimize organ damage, and decrease long-term morbidity and mortality. Therapies providing durable clinical responses without requiring chronic administration are lacking. Rese-cel (formerly CABA-201) is a fully human, autologous 4-1BB CD19-CAR T cell therapy, designed to deeply and transiently deplete CD19 positive cells following a weight-based, single infusion. This approach may enable an “immune system reset” and durable meaningful clinical responses without chronic therapies. RESET-SLETM (NCT06121297) is an ongoing Phase 1/2 trial in 2 independent cohorts of non-renal SLE and lupus nephritis (LN).
Methods: Patients were 18 to 65 years with SLE, ANA+ or anti-dsDNA+, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000 (SLEDAI 2K) ≥8 despite standard of care (SOC) therapy (non-renal SLE cohort), or active, biopsy-confirmed class III or IV ± V LN despite SOC (LN cohort). A single infusion of 1×106 CAR T cells/kg was administered following preconditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide. All non-glucocorticoid (GC) immunomodulatory (IM) agents were discontinued by Day -5. Adverse events, use of SLE medications, SLEDAI-2K changes, achievement of the definition of remission in SLE (DORIS), lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS), and renal responses were assessed. CAR T cells and B cells were profiled in peripheral blood samples pre- and post-infusion by digital PCR and flow cytometry, respectively. Serum cytokines were measured using the mesoscale discovery platform.
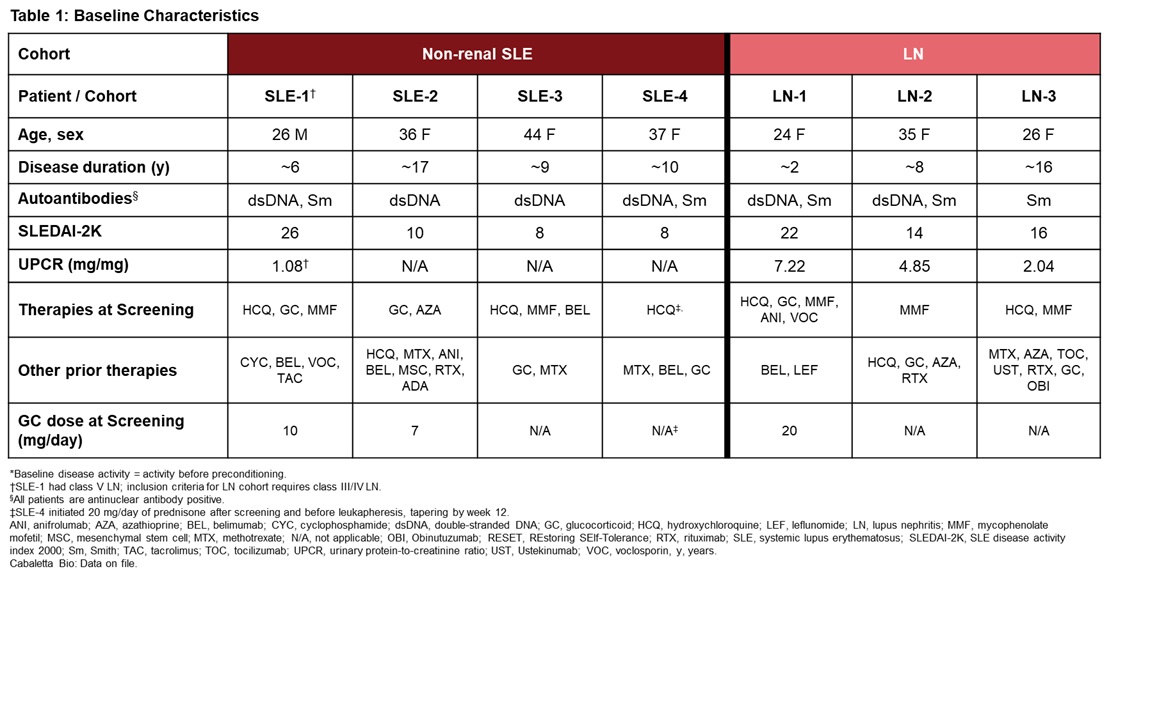
Results: As of 31 March 2025, 7 patients have been infused with rese-cel and have at least 4 weeks of follow-up (Table 1). One additional patient has been infused and is in early follow up.Rese-cel was well-tolerated with Grade 1 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) reported in 2 patients (SLE-2 and LN-1). As previously reported, LN-1 experienced Grade 4 immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS), associated with a potential occult infection based on cytokine and TCR clonality profiling, which rapidly resolved following standard management.Robust clinical improvement has been observed in all 7 patients (Table 2).CAR T cells expanded rapidly and peaked between days 7 and 16 post-infusion, with LN-1 also having a second peak at day 28, followed by contraction. Serum IFNγ rapidly increased concurrently with or prior to rese-cel expansion. Peripheral B cells were rapidly reduced within the first 2 weeks and started reconstituting between 8 and 20 weeks in all patients to date. Reemergent B cells presented initially with a transitional naïve phenotype (CD19+CD20+CD38++CD24++).
Conclusion: Data from SLE and LN patients infused with rese-cel shows early clinical responses, including meeting the DORIS remission criteria and complete renal response, and an acceptable safety profile, in the setting of CAR T cell expansion and peripheral B-cell reduction. These initial data suggest the potential for rese-cel to reset the immune system in SLE and LN, allowing patients to achieve meaningful clinical responses off all IM agents.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sheikh S, Derebail V, Grovner N, Gulati G, Abedi M, Sise M, Frigault M, Palma C, Reagan P, Edens C, Kosuri S, Elgarten C, Burnham J, Hogan J, White Y, diCasoli C, Estremera R, Volkov J, Nunez D, Hadi-Nezhad F, Furmanak T, Stadanlick J, Ishikawa L, Vorndran Z, Ellis A, Williams J, Flanagan S, Lam Q, Basu S, Tummala R, Chang D. RESET-SLE: Clinical Trial Evaluating Rese-cel (Resecabtagene Autoleucel), a Fully Human, Autologous 4-1BB CD19-CAR T Cell Therapy in Non-Renal SLE and Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reset-sle-clinical-trial-evaluating-rese-cel-resecabtagene-autoleucel-a-fully-human-autologous-4-1bb-cd19-car-t-cell-therapy-in-non-renal-sle-and-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reset-sle-clinical-trial-evaluating-rese-cel-resecabtagene-autoleucel-a-fully-human-autologous-4-1bb-cd19-car-t-cell-therapy-in-non-renal-sle-and-lupus-nephritis/

.jpg)