Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2437–2469) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: LN develops in ~40% of patients with SLE and is associated with increased risk of morbidity, including end-stage kidney disease, and mortality. Belimumab, a B-cell modulator that targets the central immunopathogenic pathway in SLE by selectively inhibiting B-lymphocyte stimulator, has been shown to prevent organ damage progression in SLE and preserve kidney function in LN. This study evaluated whether belimumab is associated with a protective effect and lower risk of progression to LN among patients with SLE versus standard of care (SOC) in real-world clinical practice, by comparing time to initiation of LN therapy.
Methods: A retrospective, longitudinal cohort study (GSK Study 217533) was conducted using claims linked with electronic health record data from the Optum Market Clarity database. Index was defined as the date of initiation of belimumab or SOC (immunosuppressant [IS, except for use in LN initial therapy], intravenous glucocorticoids [GCs], or oral GC escalation to ≥20 mg/day prednisone-equivalent) between Jan 1, 2017, and Mar 31, 2023. The unit of analysis was treatment episode and patients could be included in both study cohorts if they received both belimumab and SOC during the study period. Patients were ≥18 years old with an SLE diagnosis and had ≥12 months continuous enrollment pre-index. Those with LN diagnosis or LN induction therapy prior to the index date were excluded. Initiation of LN induction therapy served as a proxy for incident LN and was defined as earliest use of: subcutaneous belimumab 400 mg once-weekly for four doses; voclosporin; cyclophosphamide (either monotherapy or combined with MMF or azathioprine); high-dose MMF. For each treatment episode, the observation period spanned from index to the earliest of: end of continuous enrollment, end of data availability, death, or treatment switch. Time to initiation of LN induction therapy was assessed using a Cox proportional hazards (PH) model with a robust (Huber-White sandwich) variance estimator, weighted by average treatment effect among the treated weights (ATT-weights) based on propensity-score, and with covariates that remained imbalanced after weighting included in the model for a doubly robust approach.
Results: In total, 1408 belimumab and 74,288 SOC patients were included and contributed 3727 belimumab and 3621 SOC treatment episodes to the analysis. Prior to weighting, belimumab patients were younger (median age 47 vs 53 years) and more likely to have moderate (53.5% vs 31.0%) than mild (18.9% vs 42.9%) SLE severity and a greater number of SLE treatment types at baseline. ATT-weighted baseline characteristics (Table) were similar between treatment cohorts. The number of IS, oral GC, and antimalarial therapies remained imbalanced after weighting and were further adjusted in the Cox PH model. Patients receiving belimumab had a significantly lower hazard of initiating LN induction therapy versus SOC (hazard ratio [95% CI]: 0.77 [0.62, 0.95]).
Conclusion: Belimumab use was associated with a lower risk of initiating LN induction therapy versus SOC among patients with SLE, suggesting a potential renal protective effect through which belimumab may prevent progression to LN.Funding: GSK
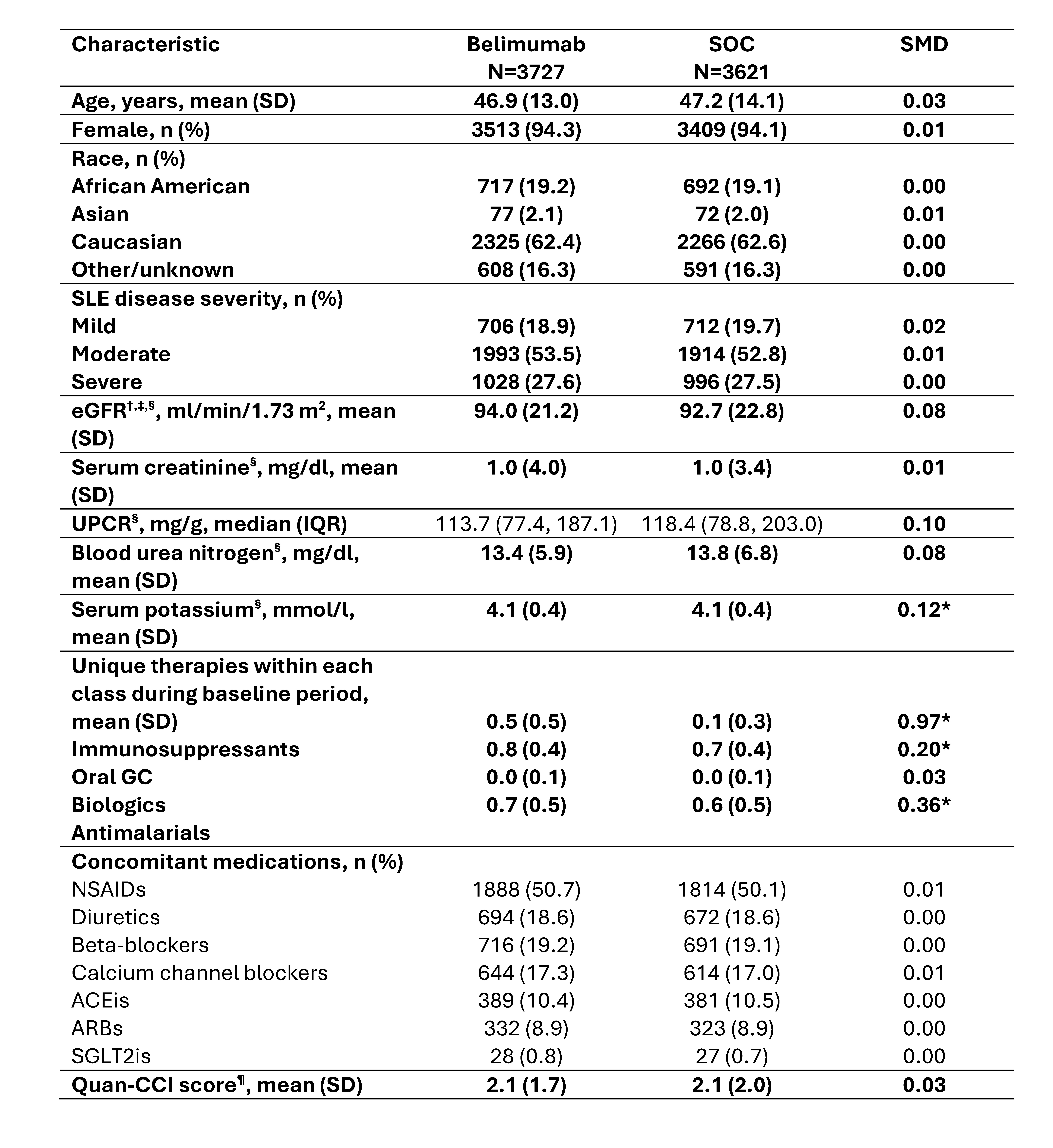 Table. Select ATT-weighted baseline characteristics.
Table. Select ATT-weighted baseline characteristics.
*Imbalanced after ATT weighting; †the most recent eGFR measurement prior to the index date was used; if multiple measurements were available on the same day, the median value of these measurements was used; ‡eGFR was calculated based on the 2021 CKD-EPI creatinine equation (Inker LA et al. N Engl J Med 2021;385:1737–49); §evaluated among patients with non-missing values during baseline period; ¶CCI was calculated per the Quan study (Quan H et al. Med Care 2005;43:1130–9). Mean (SD) treatment episode duration was 25.9 (20.5) months for belimumab and 36.0 (23.6) months for SOC; SMR 0.67*.
ACEis, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARBs, angiotensin receptor blockers; CCI, Charlson Comorbidity Index; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; GC, glucocorticoid; IQR, interquartile range; SD, standard deviation; SGLT2is, sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors; SMD, standardized mean difference; SMR, standardized mortality ratio; SOC, standard of care; UPCR, urine protein-to-creatinine ratio.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
DerSarkissian M, Chen Y, Chao A, Rui S, Moore B, Worley K, Moldaver D, Ellis J, Patel A. Belimumab Is Associated with Lower Risk of Progression to LN Compared with Standard of Care in Patients with SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/belimumab-is-associated-with-lower-risk-of-progression-to-ln-compared-with-standard-of-care-in-patients-with-sle/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/belimumab-is-associated-with-lower-risk-of-progression-to-ln-compared-with-standard-of-care-in-patients-with-sle/
