Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: This study sought to compare clinical characteristics between female and male patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA) in a Turkish population.
Methods: This study included 489 peripheral and axial SpA patients recruited from different regions of Türkiye in the ASAS-PerSpA study. Demographic and clinical characteristics such as axial involvement, peripheral arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, uveitis, psoriasis, and intestinal involvement, and clinometric information including BASDAI, ASDAS, tender joint count, swollen joint count, enthesitis count and FiRST fibromyalgia score were evaluated according to gender.
Results: Of the patients included in the study, 256 were male and 233 were female. The mean age was 40.24 (SD:11.27) years for males and 43.61 (SD:11.01) years for females (p=0.002). Body mass index was 26.23 (SD:3.97) kg/m2 for males and 27.01 (SD:5.58) kg/m2 for females (p=0.006). In axial SpA (n=391), 230 were male and 161 were female (p< 0.001), whereas in peripheral SpA (n=96), 43 were male and 53 were female (p=0.09), and in psoriatic arthritis (n=80), 19 were male and 61 were female (p< 0.001).Back pain with age at onset < 45 years, sacroiliitis on pelvis x-ray, and HLAB27 positivity were more common in males than females (p< 0.05). While axial involvement of SpA was more common in males, past or present arthritis compatible with SpA, peripheral articular disease, spondyloarthritis-related enthesitis, psoriasis, and dactylitis were more common in females (p< 0.05). There were no significant differences between the genders in the uveitis and inflammatory bowel disease. Regarding disease activity tender joint count, dactylitis, enthesitis, BASDAI and ASDAS scores of females were significantly higher than males (p< 0.05). FiRST fibromyalgia score were higher in females (p< 0.001) (Table).
Conclusion: There are some clinical differences according to gender in SpA. In our population, males had higher axial involvement and radiographic sacroiliitis, while females had more peripheral involvement, including arthritis, enthesitis, and dactylitis, as well as a higher prevalence of fibromyalgia and disease activity.
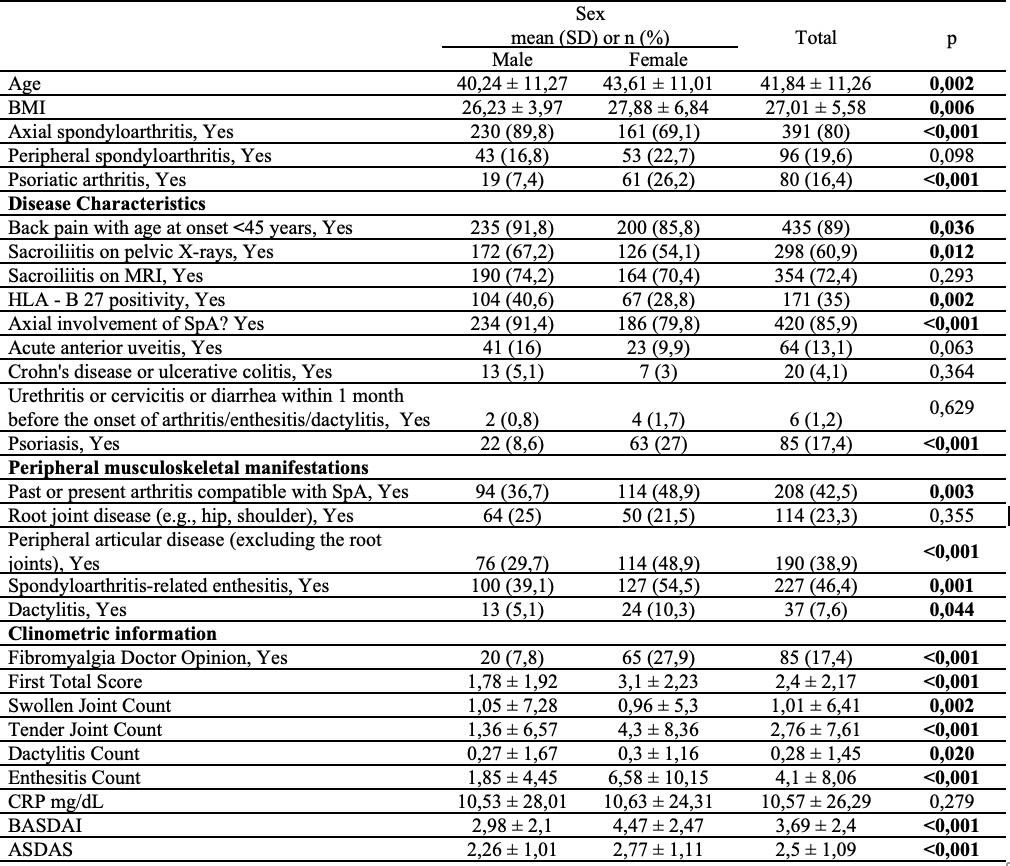 Table. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics According to Gender
Table. Comparison of Clinical Characteristics According to Gender
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Duruöz M, Gezer H, Aktaş İ, Akar S, Şahin N, Akgül Ö, Hizmetli S, Alkan Melikoğlu M, Kalyoncu U, Çapkın E, Ural f, Yılmaz F, ATAMAN S, Sezer İ. Gender-related Differences in Peripheral and Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gender-related-differences-in-peripheral-and-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gender-related-differences-in-peripheral-and-axial-spondyloarthritis/
