Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid factor (RF) is an antibody that contributes to the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and is associated with greater disease severity. Seroconversion of RF after biological DMARD (bDMARD) treatment has been reported as infrequent. However, little is known about changes in serological status and their association with disease activity across different TNF inhibitors (TNFi).The objectives of this study were: a) To compare the change in RF levels and the rate of seroconversion over 6 months of treatment with certolizumab pegol (CZP), etanercept (ETN), and adalimumab (ADA); and b) To evaluate the association between the reduction in RF levels and the change in disease activity.
Methods: Longitudinal, retrospective, multicentre study including RA patients treated with CZP, ETN, or ADA between 2010 and 2024. RF levels and DAS28-ESR scores before TNFi initiation and after 6 months were collected. Two propensity score (PS) matching approaches (CZP vs. ETN and CZP vs. ADA) were used to balance the groups based on baseline imbalances. Paired t-tests evaluated changes in RF levels within treatments groups, and Pearson correlations assessed association between RF and DAS28 changes after confirming data normality. The proportions of seropositive patients who converted to seronegative and those achieving >50% reduction in RF after 6 months were compared using chi-square tests.
Results: A total of 1,185 RA patients treated with TNFi (246 CZP, 343 ETN, and 513 ADA) were included. After PS matching, 203 CZP vs. 203 ETN and 224 CZP vs. 224 ADA were analyzed, achieving balance in age, sex, disease duration, concomitant MTX use, and TNFi treatment line.ETN showed no significant difference in mean RF change after 6 months, whereas CZP showed a significant reduction (Figure 1A-B). Among seropositive, CZP-treated patients more often achieved >50% RF reduction than those on ETN (21.7% vs. 8.6%, p=0.010) (Figure 2A), and showed a numerically higher rate of seroconversion (9.4% vs. 5.2%). After 6 months, a direct association between RF and DAS28 reductions was observed in CZP-treated patients, whereas an inverse association was found in ETN-treated patients (Figure 3A–B), suggesting RF reduction was linked with an increase DAS28 in the ETN group.In the ADA vs. CZP comparison (Figure 1C–D), CZP showed a significant reduction in RF levels, while ADA did not. Among seropositive patients, more CZP-treated patients achieved >50% RF reduction than those on ADA (24.4% vs. 11.1%, p=0.028), and showed a numerically higher seroconversion rate (9.4% vs. 5.9%) (Figure 2B). After 6 months, RF and DAS28 changes were not associated in ADA-treated patients, while a significant association was seen in CZP group (Figure 3C–D).
Conclusion: CZP treatment was associated with a significant reduction in absolute RF levels and in the proportion of patients achieving >50% RF reduction compared to both ETN and ADA after 6 months. In CZP-treated patients, RF reduction was positively associated with improved in disease activity, suggesting a potential biomarker role for RF in CZP therapy follow-up. These findings suggest that RF reduction and seroconversion may vary across TNFi, with CZP showing a more favorable serological and clinical profile.
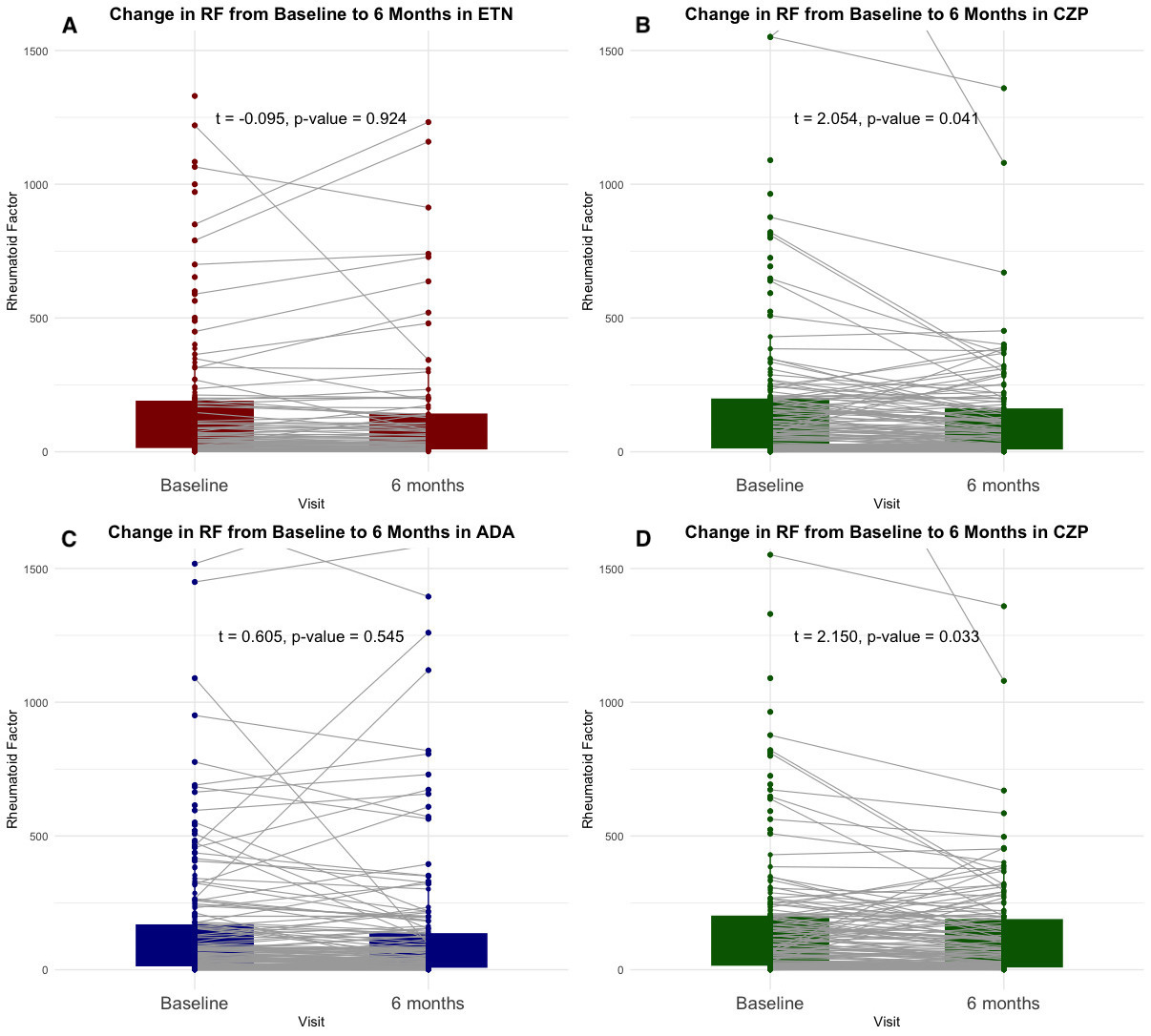 Figure 1. Paired t-Test Analysis of Rheumatoid Factor Changes at 6 Months in Propensity Score-Matched Comparisons Between ETN vs. CZP (A,B) and ADA vs. CZP (C,D).
Figure 1. Paired t-Test Analysis of Rheumatoid Factor Changes at 6 Months in Propensity Score-Matched Comparisons Between ETN vs. CZP (A,B) and ADA vs. CZP (C,D).
.jpg) Figure 2. Proportion of Patients Achieving >50% Reduction in Rheumatoid Factor at 6 Months in Propensity Score–Matched Comparisons: ETN vs. CZP (A) and ADA vs. CZP (B)
Figure 2. Proportion of Patients Achieving >50% Reduction in Rheumatoid Factor at 6 Months in Propensity Score–Matched Comparisons: ETN vs. CZP (A) and ADA vs. CZP (B)
.jpg) Figure 3. Correlation Analysis of Rheumatoid Factor Changes and DAS28-ESR changes at 6 Months in Propensity Score-Matched Comparisons Between ETN vs. CZP (A,B) and ADA vs. CZP (C,D).
Figure 3. Correlation Analysis of Rheumatoid Factor Changes and DAS28-ESR changes at 6 Months in Propensity Score-Matched Comparisons Between ETN vs. CZP (A,B) and ADA vs. CZP (C,D).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
López Medina C, Ortega-Castro R, Cepas F, Robustillo-Villarino M, Zuniga-Vera A, Martinez-Feito A, Costa-Moya E, Taverner-Torrent D, Sainz Comas L, Diaz-Torne C, Ruiz-Esquide V, Rojas C, Martin-de la Sierra Lopez L, Jimenez-Rodriguez L, Velasco-Sanchez D, Fará Garcia R, Juan-Mas A, Moreno Garcia M, Acosta Alfaro A, Muñoz S, Martín López M, Zas R, GODOY NAVARRETE F, Anon Onate I, Ortiz-Márquez F, Mena Vázquez N, Estrada-Alarcón P, Calvo J, Escudero Contreras A, Plasencia-Rodríguez C. Differential Impact of Certolizumab Pegol, Etanercept, and Adalimumab on Rheumatoid Factor Reduction and Seroconversion in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Propensity Score–Matched Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-impact-of-certolizumab-pegol-etanercept-and-adalimumab-on-rheumatoid-factor-reduction-and-seroconversion-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-propensity-score-matched-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/differential-impact-of-certolizumab-pegol-etanercept-and-adalimumab-on-rheumatoid-factor-reduction-and-seroconversion-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-propensity-score-matched-study/
