Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: RA has been associated with an increase risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality1. The present analysis was performed to assess the efficacy (on ACR response and DAS28), safety (adverse events) and quality of life (QoL) (HAQ-DI) of an adalimumab biosimilars (FK-Ada) in patients with baseline cardiovascular (CV) diseases risk factors. Biosimilars offer similar efficacy and safety compared to their originators, thereby improving patient access to affordable treatments. K-ada was approved for the treatment of inflammatory diseases including Rheumatoid Arthritis. FK-ada development included 1,234 subjects treated up to 52 weeks (420 patients-year). Since first FK-ada approval in 2019 in EU and in 2022 in US, no unexpected safety signals have been reported. AURIEL-RA study evaluated the safety, immunogenicity and efficacy of FK-ada in patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) compared to reference adalimumab up to 52 weeks2.
Methods: Patients with moderately to severely active RA receiving treatment with methotrexate were randomised 1:1 to FK-ada or reference adalimumab in the double-blind, multicentre, phase III AURIEL-RA study (NCT03052322). Safety, efficacy and immunogenicity endpoints were assessed at scheduled visits up to week 52, safety being the study primary objective. Following baseline CV risk factors were assessed: Age ≥ 65 y, BMI ≥ 30kg/m2, Smoking status, and diagnostic of hypertension, cardiac disorders or Diabetes). Patients were categorized as “No”, “One” or “ >1” reported CV risk(s) at baseline and efficacy, safety and QoL were summarized for these subgroups.
Results: 288 patients with RA were randomised (FK-ada, n = 143; reference, n = 145). The 3 baseline CV diseases risk factors subgroups were similarly represented in the two treatment groups, each subgroup representing about 1/3 of each treatment arm. Patient baseline characteristics including CV diseases risk factors were comparable between treatment arms (Table 1). After one year, DAS28-ESR decreased in all subgroups in the two F-ada and reference treatment arms. However more subjects with no baseline CV risk were in DAS28-ESR remission status compared to subjects with CV risks. QoL improved in all patients. (Table 2). Subjects with several baseline CV risk factors experienced more adverse events compared to subjects without risks factors. (Table 3).
Conclusion: FK-ada and reference adalimumab were effective across subjects with and without CV risk factors. The safety profile of subjects with and without CV risks factors at baseline was as expected for these categories of patients.1. Singh S, et al., Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020 Apr;72(4):561-576.2. Edwards CJ, et al., Clin Rheumatol. 2019 Dec;38(12):3381-3390.
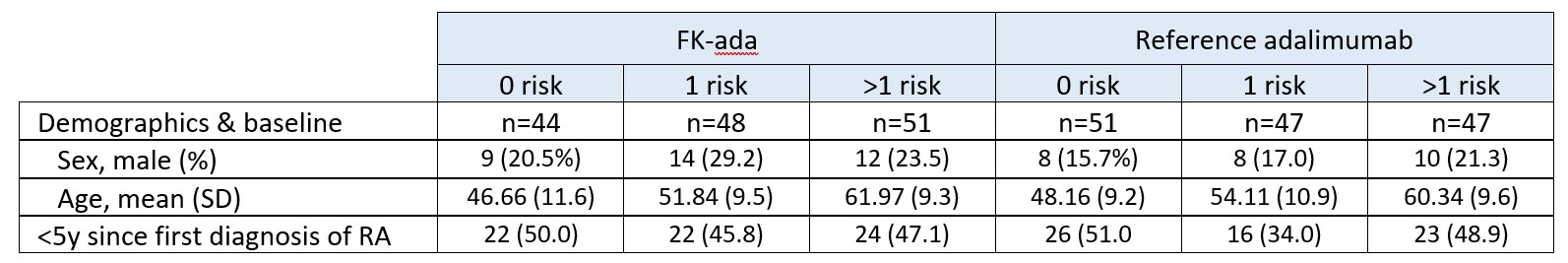 Table 1 – Demographics and baseline per subgroup of cardiovascular risks factors – ITT Analysis Set
Table 1 – Demographics and baseline per subgroup of cardiovascular risks factors – ITT Analysis Set
.jpg) Table 2 – Efficacy and Quality of life at Week 52 per subgroup of cardiovascular risks factors – ITT Analysis Set
Table 2 – Efficacy and Quality of life at Week 52 per subgroup of cardiovascular risks factors – ITT Analysis Set
.jpg) Table 3 – Adverse Events per subgroup of cardiovascular risks factors – Safety Analysis Set
Table 3 – Adverse Events per subgroup of cardiovascular risks factors – Safety Analysis Set
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Edwards C, Pope J, Monnet J, Romanova Michailidi M. Impact of Baseline Cardiovascular Risk Factors Comorbidities on an Adalimumab Biosimilar Efficacy, Quality of Life and Safety In Patients with Patients with Moderately to Severely Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from the AURIEL-RA study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-baseline-cardiovascular-risk-factors-comorbidities-on-an-adalimumab-biosimilar-efficacy-quality-of-life-and-safety-in-patients-with-patients-with-moderately-to-severely-active-rheumatoid-ar/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-baseline-cardiovascular-risk-factors-comorbidities-on-an-adalimumab-biosimilar-efficacy-quality-of-life-and-safety-in-patients-with-patients-with-moderately-to-severely-active-rheumatoid-ar/
