Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2015–2051) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a multi-organ, immune-mediated condition. Timely treatment is critical, as disease flares often result in increased inflammation and organ damage. Glucocorticoids (GCs) are used as standard first-line treatment, followed by GC-sparing therapies including conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs, such as azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil etc.), or biologic DMARD (rituximab). This study describes patient characteristics, treatment patterns, and incidence of flares in patients with IgG4-RD using administrative claims databases in the United States.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted using 100% Medicare Fee-for-Service (FFS) and Inovalon MORE2 Registry® claims databases. Adults with IgG4-RD were identified using a previously validated algorithm (Wallace et al. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022) from January 1, 2018 through December 31, 2021 (FFS) and June 30, 2023 (MORE2). Index date was set as the first claim for an algorithm-defined ICD-10 diagnosis code associated with IgG4-RD. Demographics at the index date and comorbidities and medication use in the 12-month pre-index period were assessed. Medication use and claims-based proxy for IgG4-RD flare were evaluated in the ≥12-month post-index follow-up period. Claims-based proxy for flare was defined as: (1) ≥1 claim for an IgG4-RD-associated diagnosis code followed by initiation of IgG4-RD medication, addition of GCs to existing DMARD therapy, or ≥5mg increase in GC prednisone-equivalent daily dose (PEDD); (2) ≥1 claim for ureteral stent; or (3) ≥1 claim for endoscopy and biliary stent (Figure 1).
Results: Overall, 965 patients with IgG4-RD were identified: mean (SD) age 65.7 (14.2) years, 59.2% male, 61.5% white (Table 1). Most patients had health insurance coverage through Medicare FFS program (64.8%). In the pre-index period, hypertension (62.2%), infections (55.9%), and hyperlipidemia (55.1%) were commonly observed. Moreover, 65.4%, 11.7%, and 8.5% received oral or IV GCs, synthetic DMARDs, and rituximab, respectively, during baseline. The mean (SD) duration of the post-index follow-up period was 45.3 (19.5) months. During follow-up, 97.6%, 33.6%, and 35.2% patients received oral or IV GCs, synthetic DMARDs, and rituximab, respectively (Table 2). Among patients with oral GCs (N = 835, 86.5%), the mean (SD) PEDD was 20.8 (12.1) mg. Claims-based proxy for flare was observed in 90.5% of patients during follow-up.
Conclusion: Results showed a significant clinical burden among patients with IgG4-RD during follow-up, characterized by elevated GC use which might potentially increase the risk for GC-related toxicity events, as well as a high risk of disease flares. Study findings highlight the need for therapies that better control disease activity and minimize GC exposure in these patients in the long-term.
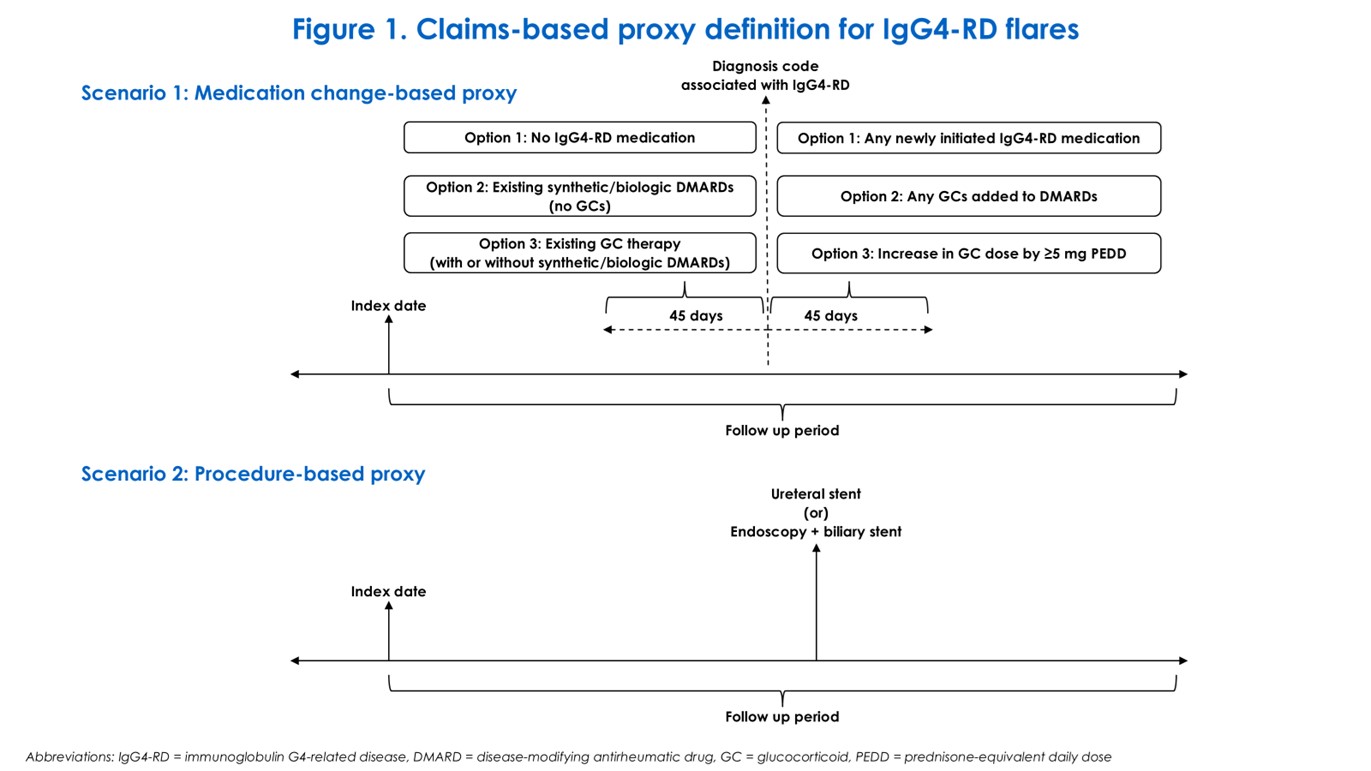 Figure 1. Claims-based proxy definition for IgG4-RD flares
Figure 1. Claims-based proxy definition for IgG4-RD flares
.jpg) Table 1. Demographics and baseline clinical characteristics in a national sample of patients with IgG4-RD in the United States
Table 1. Demographics and baseline clinical characteristics in a national sample of patients with IgG4-RD in the United States
.jpg) Table 2. Treatment patterns and clinical outcomes during ≥12 months of post-index follow-up period in a national sample of patients with IgG4-RD in the United States
Table 2. Treatment patterns and clinical outcomes during ≥12 months of post-index follow-up period in a national sample of patients with IgG4-RD in the United States
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Inguva S, Culver E, Rane P, Moore-Schiltz L, rosen m, Patterson K, McMorrow D, Pulungan Z, Hernandez-Barco Y, Stone J. Clinical Burden of Illness Among Patients with Immunoglobulin-G4-Related Disease in the United States [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-burden-of-illness-among-patients-with-immunoglobulin-g4-related-disease-in-the-united-states/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-burden-of-illness-among-patients-with-immunoglobulin-g4-related-disease-in-the-united-states/
