Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory joint disease which often leads to deformities and loss of function of hands. Despite the availability of new treatments for RA, patients can have persistent and refractory disease. Thus, optimal management requires a holistic personalized medicine approach and exercise programs are now broadly acknowledged to be a high priority in rheumatology. We have previously demonstrated that lymphatic drainage is dysfunctional in the hands of RA patients with active disease (Bell RD, et al. 2020 Arthritis Rheumatol 72:1447). In this pilot study, we aim to determine the correlation between hand strength as assessed by Manugraphy and lymphatic flow and study the effects of standardized hand exercises on these outcome measures.
Methods: Five subjects with RA of less than 6 years disease duration were recruited with four completing Manugraphy studies. Three subjects completed both hand strength assessments and lymphatic studies. Hand grip and strength measures were completed using a Jamar Dynamometer and Manugraphy device followed a day later by lymphatic flow measurements. Lymphatic function was assessed using a novel near-infrared indocyanine green (NIR-ICG) method as previously published. Briefly, 0.1mL ICG dye was injected into the webspaces of each hand and ICG flow was recorded for 10 minutes to calculate lymphatic contraction rate. One week later, hands were again measured to quantify clearance. Patients were educated on standardized hand exercises by an occupational therapist. Subjects were provided calendars to document compliance of exercises over the next 6 weeks. Hand strength and lymphatic function assessments were then repeated.
Results: Preliminary baseline results of the right hand of a subject are shown in Figure 1. Lymphatic function at baseline confirms the presence of contracting lymphatic vessels from each webspace and clearance was measured at 5373 fluorescence units. Parameters were quantified for each digit per hand to be correlated with lymphatic data. Peak pressure was measured for the 1st digit and found to be 120.6 +/- 8.2 kPa. Additional Manugraphy parameters measured include maximum force (49.3 N), force-time integral 125.4 (N*s), force for the mean value picture (MVP) (41.7N), contact area for MVP (11.17 cm2), and contact area for the maximum pressure picture (12.17 cm2).
Conclusion: We initiated a novel study to correlate lymphatic function with hand function measures in patients with RA. Preliminary baseline measures show altered lymphatic function consistent with prior data and confirm ability to measure hand function using Manugraphy. Post-exercise intervention studies will be completed to determine if active hand mobility and lymphatic function can be altered in subjects with RA.
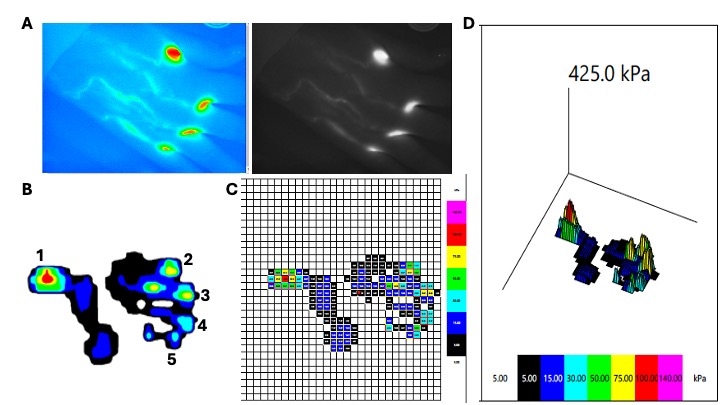 Fig 1: (A) Representative NIR-ICG images of active lymphatic flow after webspace injections and 1 week later. (B) Hand measurements via Manugraphy captures pictorial representation of digits (labeled 1-5) and further quantified via (C) “heat map”. (D) Pressure measurements analysis delineates specific pressures at each area of the hand with peak pressure (in red) of 120.6+/-8.2 kPa identified at 1st digit.
Fig 1: (A) Representative NIR-ICG images of active lymphatic flow after webspace injections and 1 week later. (B) Hand measurements via Manugraphy captures pictorial representation of digits (labeled 1-5) and further quantified via (C) “heat map”. (D) Pressure measurements analysis delineates specific pressures at each area of the hand with peak pressure (in red) of 120.6+/-8.2 kPa identified at 1st digit.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Anandarajah A, Wood R, Schwarz E, Haddas R, Rahimi H. Correlation of Hand and Lymphatic Function Post Exercise Intervention in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-of-hand-and-lymphatic-function-post-exercise-intervention-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/correlation-of-hand-and-lymphatic-function-post-exercise-intervention-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/
