Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1855–1876) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Gastrointestinal (GI) involvement in systemic sclerosis (SSc) affects over 90% of patients and represents a large clinical burden and unmet need. Unlike the skin and lung, GI disease does not respond to immunosuppression and generally worsens with time despite treatment. Postmortem studies describe smooth muscle atrophy, fibrosis, and increased immune cells within the wall of the GI tract, but the cellular pathogenesis remains poorly understood. Here we investigate the single-cell composition of biopsies taken from SSc patients, particularly fibroblast subsets which may contribute to disease pathogenesis.
Methods: Gastric biopsies were obtained from four SSc patients, and four healthy controls (HC). Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) was performed on whole biopsies using 10X Genomics Chromium workflow. Data were analysed using scanpy, scvi-tools, pertpy and pydeseq2.
Results: After filtering we analyzed 30,872 cells. There was a significant expansion of T cells proportions in SSc compared to HC, and a significant reduction in fibroblast, plasma cell, and epithelial cell cluster frequencies (FDR < 0.2) (Figure 1).Within the stomal cell compartment, we identified several fibroblast clusters with similar gene expression to skin fibroblast subsets. Myofibroblasts and pericytes showed a trend to increased abundance in SSc compared to HC. Fibroblasts with similar gene expression to mesenchymal fibroblasts were most abundant across all samples, with no difference between SSc and HC. There was a significant reduction of SFRP1+ CXCL12+ and EGR1+ POSTN+ fibroblasts (FDR< 0.05) in SSc compared to HC. These have similar gene expression to secretory/papillary fibroblasts and proinflammatory skin fibroblasts. Pseudobulk differential gene expression analysis (Figure 2) across all fibroblasts revealed downregulation of KLF2, TNFSF10, and C3, whilst AREG, STC1, and FAM155A were upregulated in SSc compared to HC.Gene Set Enrichment analysis between SSc and HC of each fibroblast cluster (using Reactome and Hallmark pathways) revealed upregulation of the mTOR pathway in the mesenchymal-like fibroblasts in SSc. Within the EGR1+POSTN+ fibroblasts there was significant downregulation of interferon signalling and complement cascade pathways in SSc compared to HC (FDR < 0.05).There was significant expansion of CD8 T cells in SSc compared to HC (FDR< 0.05), with reduction in IgA plasma cells, SELL+ CD4 cells, and memory B cells (FDR< 0.2) (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Utilising scRNAseq on gastric tissue biopsies, we have identifed marked differences in immune cells, including increased abundance of cytotoxic CD8 T cells, and reduction in plasma cells in SSc compared to HC. Within the stromal compartment, there was a proportional increase in pericytes and myofibroblasts. Fibroblast gene expression analysis confirmed similarities to SSc skin (e.g. downregulation of KLF2), but also some notable differences including reduction in PTGDS, TNFSF10 and C3, and Interferon signaling. These represent a distinct population of gastric fibroblasts not present in SSc skin. Our findings may help to explain differences in natural history and treatment response between gut and other organs in SSc.
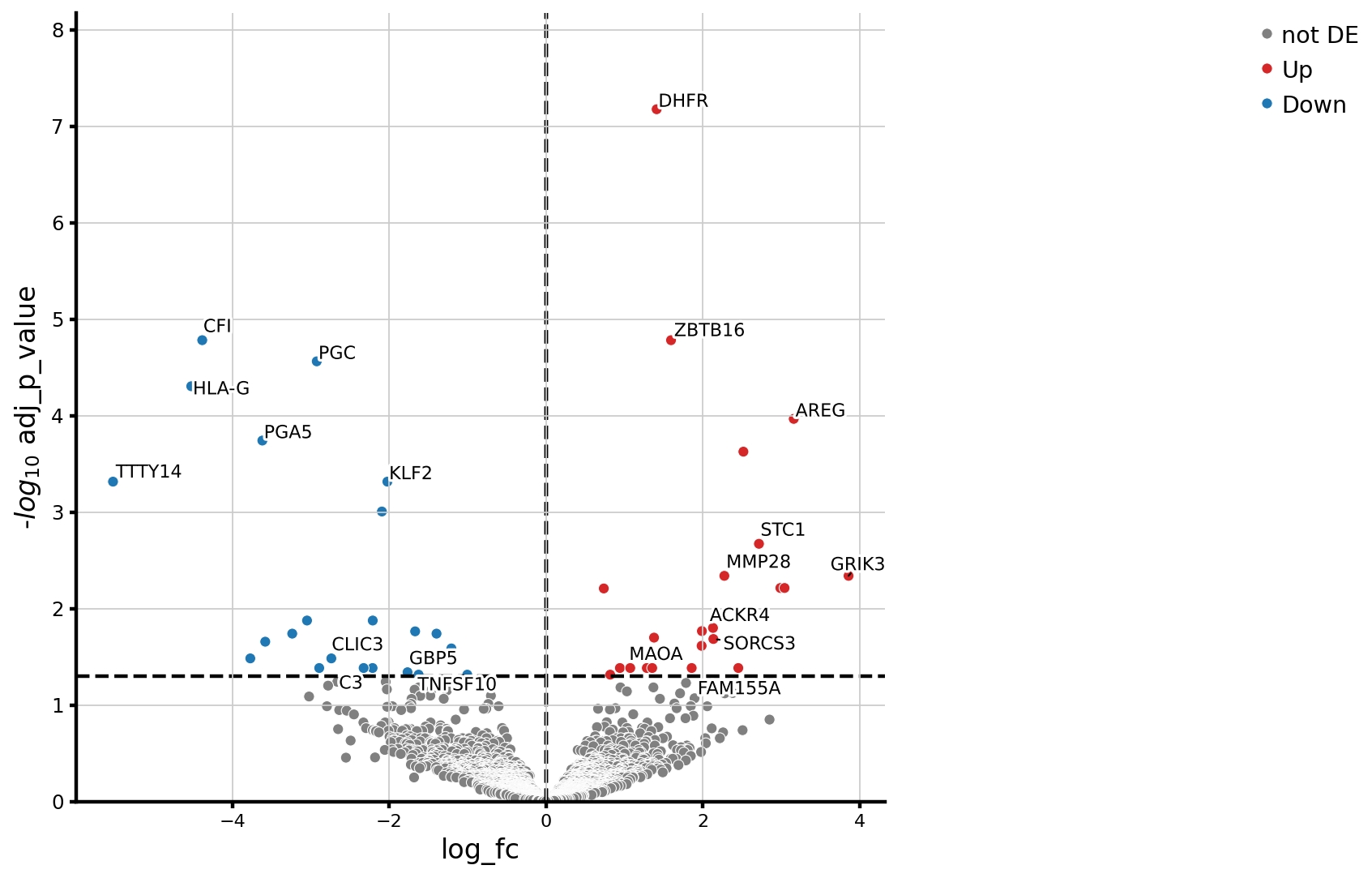 Figure 1: UMAP displaying differential abundance of all cells in the stomach, highlighting increased T cells, reduced plasma cells and perturbed fibroblast populations (Brown = increased, blue = reduced)
Figure 1: UMAP displaying differential abundance of all cells in the stomach, highlighting increased T cells, reduced plasma cells and perturbed fibroblast populations (Brown = increased, blue = reduced)
.jpg) Figure 2: Pseudobulk analysis of differential gene expression across the whole fibroblast compartment, comparing differentially expressed genes between SSc and HC
Figure 2: Pseudobulk analysis of differential gene expression across the whole fibroblast compartment, comparing differentially expressed genes between SSc and HC
.jpg) Figure 3: differential abundance within the immune cell compartment comparing SSc and HC. Activated CD8 T cells, plasma cells, SELL+CD4 T Cells and memory B cells all showed significant difference between SSc and HC (indicated by *).
Figure 3: differential abundance within the immune cell compartment comparing SSc and HC. Activated CD8 T cells, plasma cells, SELL+CD4 T Cells and memory B cells all showed significant difference between SSc and HC (indicated by *).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
clark k, Attar M, Friedrich M, Murray C, Clarke A, Denton C. Elucidating gastric pathology in systemic sclerosis using single-cell RNA sequencing [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elucidating-gastric-pathology-in-systemic-sclerosis-using-single-cell-rna-sequencing/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elucidating-gastric-pathology-in-systemic-sclerosis-using-single-cell-rna-sequencing/
