Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1780–1808) Osteoarthritis & Joint Biology – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: LEVI-04 is a novel fusion protein comprising the extracellular domain of p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) coupled to IgG1 Fc, being developed for the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) symptoms and disease progression. Results from a phase II study showed a significant reduction of WOMAC pain, function and stiffness vs placebo, supporting its clinical potential1
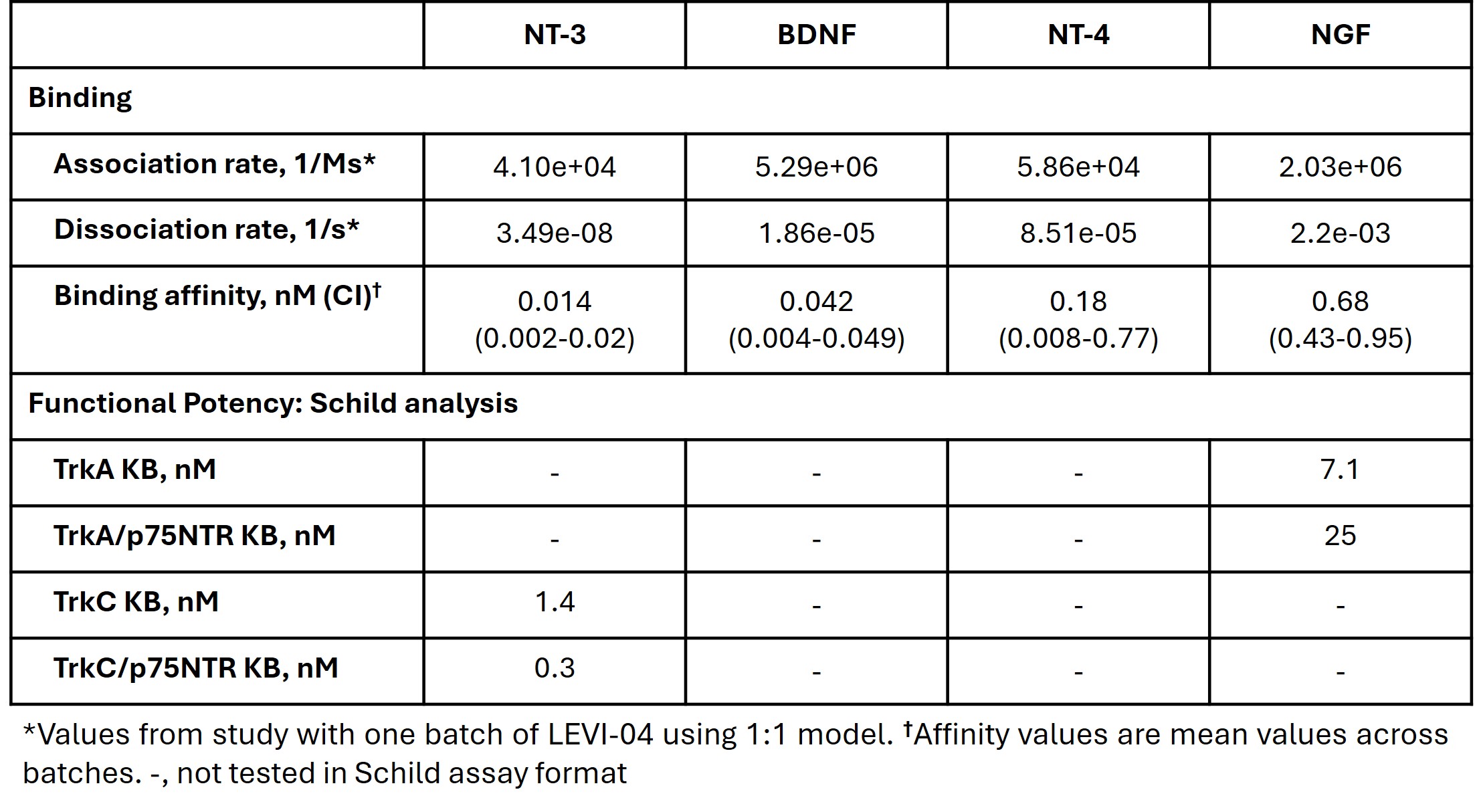
Methods: Binding affinities of LEVI-04 to neurotrophins (NTs) were determined using surface plasmon resonance assays. Functional potency was assessed in cell-based assays measuring inhibition of NT-induced activation of Trk and p75NTR/Trk receptors. Analgesia (weight-bearing) and disease modification (histopathology) were assessed in a monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) induced OA model in the rat.
Results: LEVI-04 bound to all NTs, with highest affinity for NT-3 (Table 1). However, while dissociation from NT-3, BDNF, and NT-4 was slow, such that rate measurement was challenging, dissociation from NGF was rapid. LEVI-04 inhibited the activation of Trk receptors by all NTs. However, while LEVI-04 completely inhibited NT-3-induced activity, inhibition of NGF, BDNF, and NT-4 was not complete (Figure 1), especially when Trk receptors were co-expressed with p75NTR. LEVI-04 had highest potency for inhibition of NT-3 at TrkC receptors and TrkC receptors co-expressed with p75NTR (Table 1).In the MIA model of OA, analgesia was seen with therapeutic LEVI-04 treatment (0.03–3 mg/kg SC) initiated following establishment of pain (determined by imbalance of weight distribution). LEVI-04 returned the MIA-induced imbalance in weight distribution to normal. MIA injection caused chondrocyte death, reduced cartilage thickness and reactive joint and bone pathology. LEVI-04 treatment resulted in chondroprotection, with reduced bone pathology and osteolysis-mediated bone erosion compared with IgG control. In MIA-injected joints in the LEVI-04-treated groups there was reduction in osteolysis, thus limiting myeloid cell activation, and osteoblast pool expansion thereby augmenting the mesenchyme cell pool, leading to repair and reduction in MIA-induced histopathology.
Conclusion: LEVI-04 supplements endogenous soluble p75NTR. Like soluble p75NTR, LEVI-04 interacts with all NTs but inhibits NT-3. Of note, NGF-, BDNF- and NT-4-induced Trk receptor activity cannot be fully inhibited by LEVI-04. In the MIA model of OA, LEVI-04 provided analgesia and reduced histopathology. Phase 3 trials to assess the effect of chronic LEVI-04 treatment on OA symptoms and disease progression are planned.Reference: 1. Conaghan P, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024;76 (suppl 9).
 In vitro pharmacology of LEVI-04
In vitro pharmacology of LEVI-04
.jpg) Inhibition of NT-induced activity by LEVI-04 in U20S cells expressing (A) TrkA and p75NTR, (B) TrkB and (C) TrkC receptors
Inhibition of NT-induced activity by LEVI-04 in U20S cells expressing (A) TrkA and p75NTR, (B) TrkB and (C) TrkC receptors
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Westbrook S, af Forselles K. Pharmacology of LEVI-04, a novel treatment for OA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacology-of-levi-04-a-novel-treatment-for-oa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacology-of-levi-04-a-novel-treatment-for-oa/
