Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1780–1808) Osteoarthritis & Joint Biology – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: SEV-101 are exosomes that are isolated from cultures of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC)-derived hyaline cartilage tissue. Gene expression profiles of the tissue are consistent with early hyaline cartilage development. Given that the biological effects of exosomes tend to parallel those of the cells from which they were derived, we hypothesize that SEV-101 which is secreted from iPSC-derived hyaline cartilage tissue, could deliver effective regenerative cues for cartilage regeneration in addition to factors that promote anti-inflammatory activities.
Methods: Exosomes in iPSC-derived hyaline cartilage tissue culture medium were isolated through a series of centrifugation steps followed by ultracentrifugation. Particle concentration and size distribution was characterized utilizing Nanosight. Mixed Lymphocyte Reaction (MLR) cultures of human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) were performed in the presence of SEV-101 from multiple batches, and the results were analyzed using multiparametric flow cytometry to asses regulatory T cell populations, including Tregs and Tr1cells. Additionally, activation markers such as CD69 were evaluated to quantify activated Tregs and Tr1 cells. Proliferation of chondrocytes in the presence of SEV-101 were detected via Ki-67 based assays and colony formation assays. Preliminary proteomics was performed by mass spectrometry.
Results: SEV-101 contained high levels of anti-inflammatory molecules such as CD9 and CD81 compared to the exosomes isolated from undifferentiated iPSC culture medium. SEV-101 effectively reversed TNF𝛼-induced inflammation in PBMCs. Treatment with SEV-101 increased the frequency of CD4⁺FoxP3⁺ regulatory T cells (Tregs) by 1.3- to 2.03-fold and CD49b⁺LAG-3⁺ Tr1 cells by 1.33- to 3.34-fold. Furthermore, the proportion of CD69⁺ T cells, including CD69⁺ Tregs and CD69⁺ Tr1 cells-was significantly elevated in human MLR cultures treated with SEV-101. CD69+ T cells can induce indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in OA models and down-regulate inflammatory immune responses. Ki-67-based proliferation and colony formation assays demonstrated that SEV-101 induces chondrocyte proliferation by 82.18 to 96.29 fold. Preliminary proteomics showed the presence of pro-regenerative and anti-inflammatory proteins.
Conclusion: SEV-101 exhibits potent anti-inflammatory and chondro-regenerative properties in vitro, indicating its potential as a disease-modifying agent for the treatment of osteoarthritis.
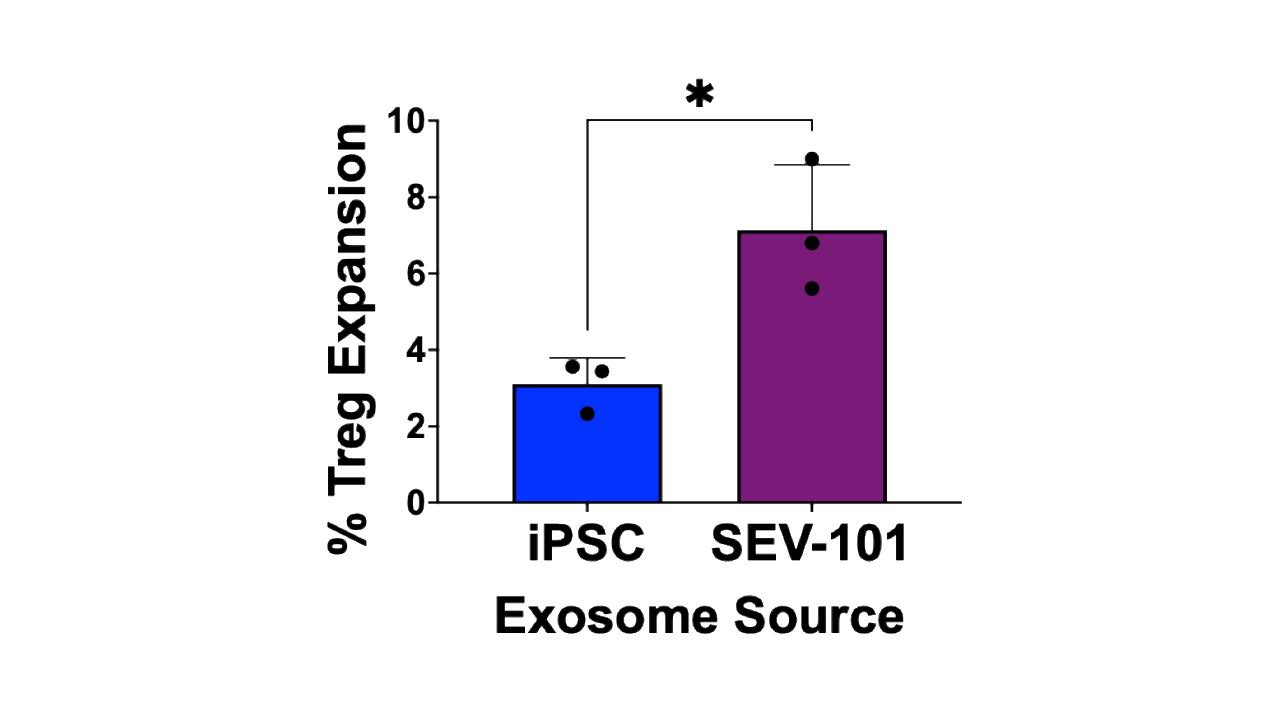 Figure 1. SEV-101 increase proliferation of Treg cells. Flow cytometric analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells treated with 100 µg of SEV-101 exosomes showed a significant (P < 0.0196) increase in the expansion of CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ Tregs compared to iPSC exosome treated controls. Each data point represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments and were analyzed with a student’s t-test (*P < 0.05).
Figure 1. SEV-101 increase proliferation of Treg cells. Flow cytometric analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells treated with 100 µg of SEV-101 exosomes showed a significant (P < 0.0196) increase in the expansion of CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ Tregs compared to iPSC exosome treated controls. Each data point represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments and were analyzed with a student’s t-test (*P < 0.05).
.jpg) Figure 2. SEV-101 exosomes increase proliferation of chondrocytes. Treatment with 50µg SEV-101 results in significant reversal of TNF- mediated inhibition in the proliferation of chondrocytes when compared to untreated controls. Each data point represents the mean ± SD of 4 independent experiments and were analyzed with a student’s t-test (*P < 0.05, nsP>0.05)
Figure 2. SEV-101 exosomes increase proliferation of chondrocytes. Treatment with 50µg SEV-101 results in significant reversal of TNF- mediated inhibition in the proliferation of chondrocytes when compared to untreated controls. Each data point represents the mean ± SD of 4 independent experiments and were analyzed with a student’s t-test (*P < 0.05, nsP>0.05)
.jpg) Figure 3. Immunoinhibitory receptors in SEV-301 exosomes. SEV-101 shows a significant level of expression of anti-inflammatory markers CD9 and CD81 when compared to the exosomes from iPSC culture media. Each data point represents the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments and were analyzed with a student’s t-test (***P < 0.001).
Figure 3. Immunoinhibitory receptors in SEV-301 exosomes. SEV-101 shows a significant level of expression of anti-inflammatory markers CD9 and CD81 when compared to the exosomes from iPSC culture media. Each data point represents the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments and were analyzed with a student’s t-test (***P < 0.001).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rangarajan P, Lindborg B, Vegoe A, Chai Y, Tran A, Steinhoff M, Hering B, O'Brien T, Ramachandran S. SEV-101 Exosomes Isolated from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell – Derived Hyaline Cartilage Tissue – Characterization of Immunomodulatory and Chondro-proliferative Effects In Vitro [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sev-101-exosomes-isolated-from-induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-derived-hyaline-cartilage-tissue-characterization-of-immunomodulatory-and-chondro-proliferative-effects-in-vitro/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sev-101-exosomes-isolated-from-induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-derived-hyaline-cartilage-tissue-characterization-of-immunomodulatory-and-chondro-proliferative-effects-in-vitro/
